Mitochondrial stress-induced p53 attenuates HIF-1α activity by physical association and enhanced ubiquitination
- PMID: 27345397
- PMCID: PMC5192009
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2016.211
Mitochondrial stress-induced p53 attenuates HIF-1α activity by physical association and enhanced ubiquitination
Abstract
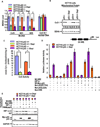
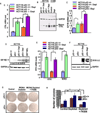
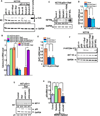
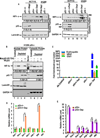
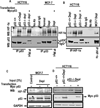
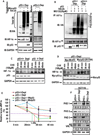
Retrograde signaling is a mechanism by which mitochondrial dysfunction is communicated to the nucleus for inducing a metabolic shift essential for cell survival. Previously, we showed that partial mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) depletion in different cell types induced mitochondrial retrograde signaling pathway (MtRS) involving Ca+2-sensitive Calcineurin (Cn) activation as an immediate upstream event of stress response. In multiple cell types, this stress signaling was shown to induce tumorigenic phenotypes in immortalized cells. In this study we show that MtRS also induces p53 expression, which was abrogated by Ca2+ chelators and short hairpin RNA-mediated knockdown of CnAβ mRNA. Mitochondrial dysfunction induced by mitochondrial ionophore, carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenyl hydrazone and other respiratory inhibitors, which perturb the transmembrane potential, were equally efficient in inducing the expression of p53 and downregulation of MDM2. Stress-induced p53 physically interacted with hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) and attenuated the latter's binding to promoter DNA motifs. In addition, p53 promoted ubiquitination and degradation of HIF-1α in partial mtDNA-depleted cells. The mtDNA depleted cells, with inhibited HIF-1α, showed upregulation of glycolytic pathway genes, glucose transporter 1-4 (Glut1-4), phosphoglycerate kinase 1 and Glucokinase but not of prolyl hydroxylase isoforms. For the first time we show that p53 is induced as part of MtRS and it renders HIF-1α inactive by physical interaction. In this respect, our results show that MtRS induces tumor growth independent of the HIF-1α pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of the interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
mtDNA as a Mediator for Expression of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1α and ROS in Hypoxic Neuroblastoma Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Jun 7;18(6):1220. doi: 10.3390/ijms18061220. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28590414 Free PMC article.
-
Sestrin2 inhibits hypoxia-inducible factor-1α accumulation via AMPK-mediated prolyl hydroxylase regulation.Free Radic Biol Med. 2016 Dec;101:511-523. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.11.014. Epub 2016 Nov 11. Free Radic Biol Med. 2016. PMID: 27840318
-
Flavonoids-induced accumulation of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1alpha/2alpha is mediated through chelation of iron.J Cell Biochem. 2008 Apr 15;103(6):1989-98. doi: 10.1002/jcb.21588. J Cell Biochem. 2008. PMID: 17973296
-
Lack of mitochondrial DNA impairs chemical hypoxia-induced autophagy in liver tumor cells through ROS-AMPK-ULK1 signaling dysregulation independently of HIF-1α.Free Radic Biol Med. 2016 Dec;101:71-84. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.09.025. Epub 2016 Sep 26. Free Radic Biol Med. 2016. PMID: 27687210
-
Mitochondrial retrograde signaling at the crossroads of tumor bioenergetics, genetics and epigenetics.Mitochondrion. 2013 Nov;13(6):577-91. doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2013.08.007. Epub 2013 Sep 1. Mitochondrion. 2013. PMID: 24004957 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mitochondrial dysfunction and mitochondrial dynamics-The cancer connection.Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg. 2017 Aug;1858(8):602-614. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2017.01.004. Epub 2017 Jan 16. Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg. 2017. PMID: 28104365 Free PMC article. Review.
-
mtDNA as a Mediator for Expression of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1α and ROS in Hypoxic Neuroblastoma Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Jun 7;18(6):1220. doi: 10.3390/ijms18061220. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28590414 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulation of RyR Calcium Channel Causes the Onset of Mitochondrial Retrograde Signaling.iScience. 2020 Aug 21;23(8):101370. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2020.101370. Epub 2020 Jul 15. iScience. 2020. PMID: 32738613 Free PMC article.
-
Defining the momiome: Promiscuous information transfer by mobile mitochondria and the mitochondrial genome.Semin Cancer Biol. 2017 Dec;47:1-17. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2017.05.004. Epub 2017 May 11. Semin Cancer Biol. 2017. PMID: 28502611 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The potential role and trend of HIF‑1α in intervertebral disc degeneration: Friend or foe? (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2021 Apr;23(4):239. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.11878. Epub 2021 Feb 4. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 33537810 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Amundson SA, Myers TG, Fornace AJ., Jr Roles for p53 in growth arrest and apoptosis: putting on the brakes after genotoxic stress. Oncogene. 1998;17:3287–3299. - PubMed
-
- Sun Y, Wicha M, Leopold WR. Regulation of metastasis-related gene expression by p53: a potential clinical implication. Mol Carcinog. 1999;24:25–28. - PubMed
-
- Roger L, Jullien L, Gire V, Roux P. Gain of oncogenic function of p53 mutants regulates E-cadherin expression uncoupled from cell invasion in colon cancer cells. J Cell Sci. 2010;123:1295–1305. - PubMed
-
- Liu G, Chen X. Regulation of the p53 transcriptional activity. J Cell Biochem. 2006;97:448–458. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

