Local microwave ablation with continued EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor as a treatment strategy in advanced non-small cell lung cancers that developed extra-central nervous system oligoprogressive disease during EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment: A pilot study
- PMID: 27336903
- PMCID: PMC4998341
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000003998
Local microwave ablation with continued EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor as a treatment strategy in advanced non-small cell lung cancers that developed extra-central nervous system oligoprogressive disease during EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment: A pilot study
Abstract
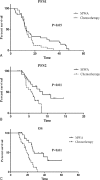
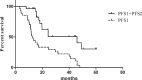
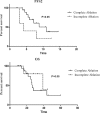
The non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients that experienced good clinical response to epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor (EGFR-TKIs) will ultimately develop acquired resistance. This retrospective study was performed to explore the potential survival benefit of microwave ablation (MWA) therapy in epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-mutant NSCLC that developed extra-central nervous system (CNS) oligoprogressive disease during TKI treatment.We retrospectively analyzed 54 NSCLC patients with EGFR mutations who showed a clinical benefit from initial EGFR-TKI therapy and developed extra-CNS oligoprogressive disease at our institutions. Twenty eight patients received MWA as a local therapy for the metastatic sites and continued on the same TKIs (MWA group). The following 26 patients received systemic chemotherapy after progression (chemotherapy group). The progression-free survival (PFS1) was calculated from initiation of targeted therapy to first progression. Progression-free survival (PFS2) was defined from first progression to second progression after MWA or chemotherapy. Overall survival (OS) was calculated from the time of diagnosis to the date of last follow-up or death.The median PFS1 for both groups was similar (median 12.6 vs. 12.9 months, HR 0.63). However, the MWA group patients had a significantly longer PFS2 (median 8.8 vs. 5.8 months, hazards ratio [HR] 0.357) and better OS (median 27.7 vs. 20.0, HR 0.238) in comparison with chemotherapy group. Multivariate analysis and the internal validation identified MWA as the main favorable prognostic factor for PFS2 and OS. In the MWA group, the median PFS2 for complete ablation was significantly longer than that for incomplete ablation (11 vs. 4.2 months, HR 0.29, P < 0.05).MWA with continued EGFR inhibition might be associated with favorable progression-free survival (PFS) and OS in patients with extra-CNS oligometastatic disease. MWA as a local therapy for extra-CNS oligometastatic disease should be considered for NSCLC with acquired resistance to EGFR-TKIs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Microwave ablation as local consolidative therapy for patients with extracranial oligometastatic EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer without progression after first-line EGFR-TKIs treatment.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2020 Jan;146(1):197-203. doi: 10.1007/s00432-019-03043-6. Epub 2019 Oct 10. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2020. PMID: 31599340
-
Microwave ablation with continued EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy prolongs disease control in non-small-cell lung cancers with acquired resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors.Thorac Cancer. 2018 Aug;9(8):1012-1017. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.12779. Epub 2018 Jun 20. Thorac Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29924498 Free PMC article.
-
Local Thermal Ablation with Continuous EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors for EGFR-Mutant Non-small Cell Lung Cancers that Developed Extra-Central Nervous System (CNS) Oligoprogressive Disease.Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2019 May;42(5):693-699. doi: 10.1007/s00270-018-02153-x. Epub 2019 Jan 30. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2019. PMID: 30701290
-
Gefitinib or Erlotinib vs Chemotherapy for EGFR Mutation-Positive Lung Cancer: Individual Patient Data Meta-Analysis of Overall Survival.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2017 Jun 1;109(6). doi: 10.1093/jnci/djw279. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2017. PMID: 28376144 Review.
-
Pneumothorax triggered by EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitors in three microwave ablation candidates: A review of the literature.Thorac Cancer. 2020 Jul;11(7):2031-2035. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13466. Epub 2020 May 12. Thorac Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32395860 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Microwave ablation as local consolidative therapy for patients with extracranial oligometastatic EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer without progression after first-line EGFR-TKIs treatment.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2020 Jan;146(1):197-203. doi: 10.1007/s00432-019-03043-6. Epub 2019 Oct 10. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2020. PMID: 31599340
-
Continued EGFR-TKI with concurrent radiotherapy to improve time to progression (TTP) in patients with locally progressive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) after front-line EGFR-TKI treatment.Clin Transl Oncol. 2018 Mar;20(3):366-373. doi: 10.1007/s12094-017-1723-1. Epub 2017 Aug 3. Clin Transl Oncol. 2018. PMID: 28776311
-
[Current Treatment Status and Prospect of Surgery and Thermal Ablation for Pulmonary Oligometastases in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2023 Mar 20;26(3):238-244. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2023.106.06. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 37035886 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Microwave ablation combined with EGFR-TKIs versus only EGFR-TKIs in advanced NSCLC patients with EGFR-sensitive mutations.Oncotarget. 2017 May 23;8(34):56714-56725. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.18083. eCollection 2017 Aug 22. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28915624 Free PMC article.
-
Microwave ablation with continued EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy prolongs disease control in non-small-cell lung cancers with acquired resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors.Thorac Cancer. 2018 Aug;9(8):1012-1017. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.12779. Epub 2018 Jun 20. Thorac Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29924498 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shigematsu H, Lin L, Takahashi T, et al. Clinical and biological features associated with epidermal growth factor receptor gene mutations in lung cancers. J Natl Cancer Inst 2005; 97:339–346. - PubMed
-
- Mok TS, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, et al. Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med 2009; 361:947–957. - PubMed
-
- Rosell R, Carcereny E, Gervais R, et al. Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): a multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 2012; 13:239–246. - PubMed
-
- Sequist LV, Yang JC, Yamamoto N, et al. Phase III study of afatinib or cisplatin plus pemetrexed in patients with metastatic lung adenocarcinoma with EGFR mutations. J Clin Oncol 2013; 31:3327–3334. - PubMed
-
- Maemondo M, Inoue A, Kobayashi K, et al. Gefitinib or chemotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer with mutated EGFR. N Engl J Med 2010; 362:2380–2388. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

