Efficacy of focal adhesion kinase inhibition in non-small cell lung cancer with oncogenically activated MAPK pathways
- PMID: 27336608
- PMCID: PMC4947704
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2016.190
Efficacy of focal adhesion kinase inhibition in non-small cell lung cancer with oncogenically activated MAPK pathways
Abstract
Background: Focal adhesion kinase (FAK) is overexpressed in many types of tumours, including lung cancer. Y15, a small molecule which inhibits Y397 FAK autophosphorylation, decreases growth of human neuroblastoma, breast and pancreatic cancers. In this study, we investigated the in vitro and in vivo effects of Y15, and the underlying mechanism on non-small cell lung cancer cells.
Methods: The cytotoxic effects of Y15 targeting FAK signalling were evaluated. Gene-knockdown experiments were performed to determine the anti-cancer mechanism. Xenografts with RAS or EGFR mutations were selected for in vivo Y15 treatment.
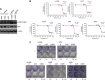
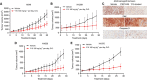
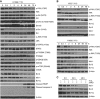
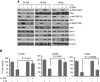
Results: Y15 blocked autophosphorylation of FAK in a time- and dose-dependent manner. It caused dose-dependent decrease of lung cancer cell viability and clonogenicity. Y15 inhibited tumour growth of RAS-mutant (A549 with KRAS mutation and H1299 with NRAS mutation), as well as epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutant (H1650 and H1975) lung cancer xenografts. JNK activation is a mechanism underlying Y15-induced Bcl-2 and Mcl-1 downregulation. Moreover, knockdown of Bcl-2 or Bcl-xL potentiated the effects of Y15. The combination of various inhibitors of the Bcl-2 family of proteins with FAK inhibitors demonstrated synergy in multiple lung cancer cell lines in vitro.
Conclusions: FAK inhibition demonstrated efficacy both in vitro and in vivo in lung cancers with either oncogenic RAS or EGFR mutations. In addition, FAK inhibition in combination with inhibitors of Bcl-2 family of anti-apoptotic proteins has synergistic activity in these MAPK-activated non-small cell lung cancer cell line models.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Focal adhesion kinase autophosphorylation inhibition decreases colon cancer cell growth and enhances the efficacy of chemotherapy.Cancer Biol Ther. 2013 Aug;14(8):761-72. doi: 10.4161/cbt.25185. Epub 2013 Jun 3. Cancer Biol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23792569 Free PMC article.
-
Focal Adhesion Kinase Inhibitors in Combination with Erlotinib Demonstrate Enhanced Anti-Tumor Activity in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.PLoS One. 2016 Mar 10;11(3):e0150567. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0150567. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26962872 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacologic blockade of FAK autophosphorylation decreases human glioblastoma tumor growth and synergizes with temozolomide.Mol Cancer Ther. 2013 Feb;12(2):162-72. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-12-0701. Epub 2012 Dec 12. Mol Cancer Ther. 2013. PMID: 23243059 Free PMC article.
-
Development of focal adhesion kinase inhibitors in cancer therapy.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2011 Sep;11(7):638-42. doi: 10.2174/187152011796817628. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21787276 Review.
-
Progress in the Development of Small Molecular Inhibitors of Focal Adhesion Kinase (FAK).J Med Chem. 2020 Dec 10;63(23):14382-14403. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c01248. Epub 2020 Oct 15. J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 33058670 Review.
Cited by
-
Design and investigation of interactions of novel peptide conjugates of purine and pyrimidine derivatives with EGFR and its mutant T790M/L858R: an in silico and laboratory study.Mol Divers. 2024 Dec;28(6):3683-3711. doi: 10.1007/s11030-023-10772-x. Epub 2024 Jan 19. Mol Divers. 2024. PMID: 38240950
-
Novel Antibody Exerts Antitumor Effect through Downregulation of CD147 and Activation of Multiple Stress Signals.J Oncol. 2022 Nov 4;2022:3552793. doi: 10.1155/2022/3552793. eCollection 2022. J Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36385956 Free PMC article.
-
Increased Expression and Activation of FAK in Small-Cell Lung Cancer Compared to Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Oct 10;11(10):1526. doi: 10.3390/cancers11101526. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31658694 Free PMC article.
-
Uncovering the Anti-Lung-Cancer Mechanisms of the Herbal Drug FDY2004 by Network Pharmacology.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Feb 4;2021:6644018. doi: 10.1155/2021/6644018. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 33628308 Free PMC article.
-
Matrix stiffness affects tumor-associated macrophage functional polarization and its potential in tumor therapy.J Transl Med. 2024 Jan 21;22(1):85. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04810-3. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38246995 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adams J, Cory S (1998) The Bcl-2 protein family: arbiters of cell survival. Science 281: 1322–1326. - PubMed
-
- Agochiya M, Brunton VG, Owens DW, Parkinson EK, Paraskeva C, Keith WN, Frame MC (1999) Increased dosage and amplification of the focal adhesion kinase gene in human cancer cells. Oncogene 18: 5646–5653. - PubMed
-
- Basu A, Haldar S (2003) Identification of a novel Bcl-xL phosphorylation site regulating the sensitivity of taxol-or 2-methoxyestradiol-induced apoptosis. FEBS Lett 538: 41–47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

