E3 ubiquitin ligase RFWD2 controls lung branching through protein-level regulation of ETV transcription factors
- PMID: 27335464
- PMCID: PMC4941481
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1603310113
E3 ubiquitin ligase RFWD2 controls lung branching through protein-level regulation of ETV transcription factors
Abstract
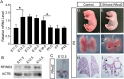
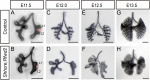
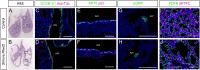
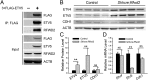
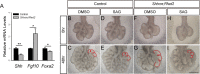
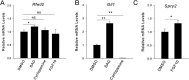
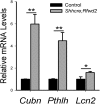
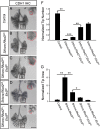
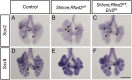
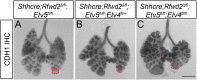
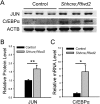
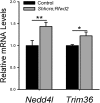
The mammalian lung is an elaborate branching organ, and it forms following a highly stereotypical morphogenesis program. It is well established that precise control at the transcript level is a key genetic underpinning of lung branching. In comparison, little is known about how regulation at the protein level may play a role. Ring finger and WD domain 2 (RFWD2, also termed COP1) is an E3 ubiquitin ligase that modifies specific target proteins, priming their degradation via the ubiquitin proteasome system. RFWD2 is known to function in the adult in pathogenic processes such as tumorigenesis. Here, we show that prenatal inactivation of Rfwd2 gene in the lung epithelium led to a striking halt in branching morphogenesis shortly after secondary branch formation. This defect is accompanied by distalization of the lung epithelium while growth and cellular differentiation still occurred. In the mutant lung, two E26 transformation-specific (ETS) transcription factors essential for normal lung branching, ETS translocation variant 4 (ETV4) and ETV5, were up-regulated at the protein level, but not at the transcript level. Introduction of Etv loss-of-function alleles into the Rfwd2 mutant background attenuated the branching phenotype, suggesting that RFWD2 functions, at least in part, through degrading ETV proteins. Because a number of E3 ligases are known to target factors important for lung development, our findings provide a preview of protein-level regulatory network essential for lung branching morphogenesis.
Keywords: COP1; E3 ubiquitin ligases; ETV transcription factors; RFWD2; lung branching.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
COP1 is a tumour suppressor that causes degradation of ETS transcription factors.Nature. 2011 May 15;474(7351):403-6. doi: 10.1038/nature10005. Nature. 2011. PMID: 21572435
-
FGF-Regulated ETV Transcription Factors Control FGF-SHH Feedback Loop in Lung Branching.Dev Cell. 2015 Nov 9;35(3):322-32. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2015.10.006. Dev Cell. 2015. PMID: 26555052 Free PMC article.
-
β-Cell Insulin Secretion Requires the Ubiquitin Ligase COP1.Cell. 2015 Dec 3;163(6):1457-67. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.10.076. Epub 2015 Nov 25. Cell. 2015. PMID: 26627735
-
Constitutive photomorphogenesis protein 1 (COP1) and COP9 signalosome, evolutionarily conserved photomorphogenic proteins as possible targets of melatonin.J Pineal Res. 2016 Aug;61(1):41-51. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12340. Epub 2016 Jun 13. J Pineal Res. 2016. PMID: 27121162 Review.
-
Sonic hedgehog regulates branching morphogenesis in the mammalian lung.Curr Biol. 1998 Sep 24;8(19):1083-6. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(98)70446-4. Curr Biol. 1998. PMID: 9768363 Review.
Cited by
-
Discovery of key genes as novel biomarkers specifically associated with HPV-negative cervical cancer.Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2021 Apr 6;21:492-506. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2021.03.026. eCollection 2021 Jun 11. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2021. PMID: 33997099 Free PMC article.
-
E3 ubiquitin ligase MDM2 acts through p53 to control respiratory progenitor cell number and lung size.Development. 2019 Dec 16;146(24):dev179820. doi: 10.1242/dev.179820. Development. 2019. PMID: 31767619 Free PMC article.
-
Capicua deficiency induces autoimmunity and promotes follicular helper T cell differentiation via derepression of ETV5.Nat Commun. 2017 Jul 12;8:16037. doi: 10.1038/ncomms16037. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 28855737 Free PMC article.
-
Turing Instability-Driven Biofabrication of Branching Tissue Structures: A Dynamic Simulation and Analysis Based on the Reaction⁻Diffusion Mechanism †.Micromachines (Basel). 2018 Mar 2;9(3):109. doi: 10.3390/mi9030109. Micromachines (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30424043 Free PMC article.
-
HDAC6-G3BP2 promotes lysosomal-TSC2 and suppresses mTORC1 under ETV4 targeting-induced low-lactate stress in non-small cell lung cancer.Oncogene. 2023 Apr;42(15):1181-1195. doi: 10.1038/s41388-023-02641-6. Epub 2023 Feb 23. Oncogene. 2023. PMID: 36823378
References
-
- Cardoso WV, Lü J. Regulation of early lung morphogenesis: Questions, facts and controversies. Development. 2006;133(9):1611–1624. - PubMed
-
- Short K, Hodson M, Smyth I. Spatial mapping and quantification of developmental branching morphogenesis. Development. 2013;140(2):471–478. - PubMed
-
- Shi W, et al. Overexpression of Smurf1 negatively regulates mouse embryonic lung branching morphogenesis by specifically reducing Smad1 and Smad5 proteins. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2004;286(2):L293–L300. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

