Clonal relationships between lobular carcinoma in situ and other breast malignancies
- PMID: 27334989
- PMCID: PMC4918003
- DOI: 10.1186/s13058-016-0727-z
Clonal relationships between lobular carcinoma in situ and other breast malignancies
Abstract
Background: Recent evidence suggests that lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS) can be a clonal precursor of invasive breast cancers of both the ductal and lobular phenotypes. We sought to confirm these findings with an extensive study of fresh frozen breast specimens from women undergoing mastectomy.
Methods: Patients with a history of LCIS presenting for therapeutic mastectomy were identified prospectively. Frozen tissue blocks were collected, screened for lesions of interest, and subjected to microdissection and DNA extraction. Copy number profiling, whole-exome sequencing, or both were performed. Clonal relatedness was assessed using specialized statistical techniques developed for this purpose.
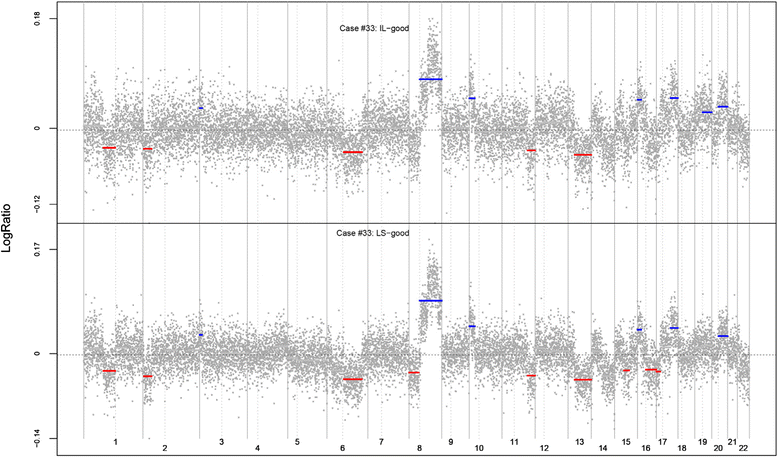
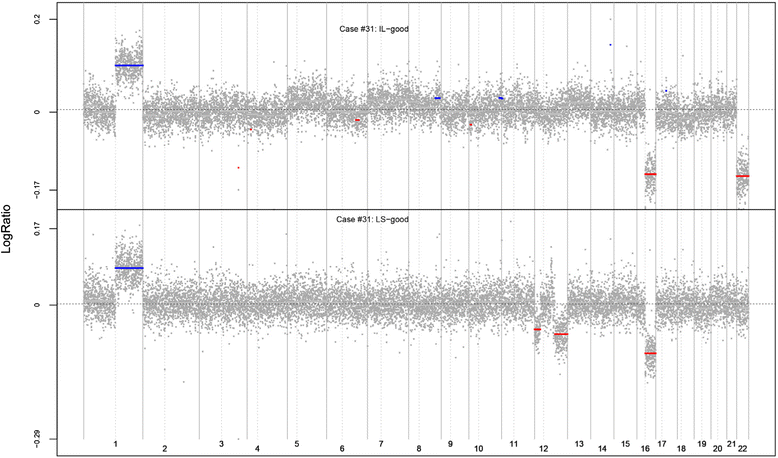
Results: After exclusions for genotyping failure, a total of 84 lesions from 30 patients were evaluated successfully. Strong evidence of clonal relatedness was observed between an LCIS lesion and the invasive cancer for the preponderance of cases with lobular carcinoma. Anatomically distinct in situ lesions of both ductal and lobular histology were also shown to be frequently clonally related.
Conclusions: These data derived from women with LCIS with or without invasive cancer confirm that LCIS is commonly the clonal precursor of invasive lobular carcinoma and that distinct foci of LCIS frequently share a clonal origin, as do foci of LCIS and ductal carcinoma in situ.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Clonal relatedness; Copy number array; Lobular carcinoma in situ; Molecular pathology in clinical prevention; Premalignant lesions; Whole-exome sequencing.
Figures
Similar articles
-
PIK3CA mutations are common in lobular carcinoma in situ, but are not a biomarker of progression.Breast Cancer Res. 2017 Jan 17;19(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s13058-016-0789-y. Breast Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28095868 Free PMC article.
-
Lobular Carcinomas In Situ Display Intralesion Genetic Heterogeneity and Clonal Evolution in the Progression to Invasive Lobular Carcinoma.Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Jan 15;25(2):674-686. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-1103. Epub 2018 Sep 5. Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30185420 Free PMC article.
-
Clonal relatedness between lobular carcinoma in situ and synchronous malignant lesions.Breast Cancer Res. 2012 Jul 9;14(4):R103. doi: 10.1186/bcr3222. Breast Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22776144 Free PMC article.
-
Pre-operative management of Pleomorphic and florid lobular carcinoma in situ of the breast: Report of a large multi-institutional series and review of the literature.Eur J Surg Oncol. 2019 Dec;45(12):2279-2286. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2019.07.011. Epub 2019 Jul 5. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31301938 Review.
-
Non-invasive lobular neoplasia of the breast: Morphologic features, clinical presentation, and management dilemmas.Breast J. 2020 Jun;26(6):1148-1155. doi: 10.1111/tbj.13857. Epub 2020 Jun 4. Breast J. 2020. PMID: 32500575 Review.
Cited by
-
Absence of lobular carcinoma in situ is a poor prognostic marker in invasive lobular carcinoma.Eur J Cancer. 2023 Sep;191:113250. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2023.113250. Epub 2023 Jul 22. Eur J Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37573674 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging Spectrum of Lobular Carcinoma In Situ and Correlation with Pathology Findings.Indian J Radiol Imaging. 2021 Aug 23;31(3):551-559. doi: 10.1055/s-0041-1734411. eCollection 2021 Jul. Indian J Radiol Imaging. 2021. PMID: 34790297 Free PMC article.
-
Invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast: the increasing importance of this special subtype.Breast Cancer Res. 2021 Jan 7;23(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s13058-020-01384-6. Breast Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33413533 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Testing clonal relatedness of two tumors from the same patient based on their mutational profiles: update of the Clonality R package.Bioinformatics. 2019 Nov 1;35(22):4776-4778. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btz486. Bioinformatics. 2019. PMID: 31198957 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment and survival outcomes of lobular carcinoma in situ of the breast: a SEER population based study.Oncotarget. 2017 Oct 3;8(61):103047-103054. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.21461. eCollection 2017 Nov 28. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29262543 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

