ICAM-1 Binding Rhinoviruses A89 and B14 Uncoat in Different Endosomal Compartments
- PMID: 27334586
- PMCID: PMC4988135
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00712-16
ICAM-1 Binding Rhinoviruses A89 and B14 Uncoat in Different Endosomal Compartments
Erratum in
-
Erratum for Conzemius et al., ICAM-1 Binding Rhinoviruses A89 and B14 Uncoat in Different Endosomal Compartments.J Virol. 2017 Jan 3;91(2):e02118-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02118-16. Print 2017 Jan 15. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28049713 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
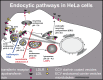
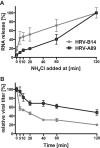
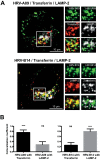
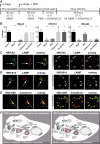
Human rhinovirus A89 (HRV-A89) and HRV-B14 bind to and are internalized by intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1); as demonstrated earlier, the RNA genome of HRV-B14 penetrates into the cytoplasm from endosomal compartments of the lysosomal pathway. Here, we show by immunofluorescence microscopy that HRV-A89 but not HRV-B14 colocalizes with transferrin in the endocytic recycling compartment (ERC). Applying drugs differentially interfering with endosomal recycling and with the pathway to lysosomes, we demonstrate that these two major-group HRVs productively uncoat in distinct endosomal compartments. Overexpression of constitutively active (Rab11-GTP) and dominant negative (Rab11-GDP) mutants revealed that uncoating of HRV-A89 depends on functional Rab11. Thus, two ICAM-1 binding HRVs are routed into distinct endosomal compartments for productive uncoating.
Importance: Based on similarity of their RNA genomic sequences, the more than 150 currently known common cold virus serotypes were classified as species A, B, and C. The majority of HRV-A viruses and all HRV-B viruses use ICAM-1 for cell attachment and entry. Our results highlight important differences of two ICAM-1 binding HRVs with respect to their intracellular trafficking and productive uncoating; they demonstrate that serotypes belonging to species A and B, but entering the cell via the same receptors, direct the endocytosis machinery to ferry them along distinct pathways toward different endocytic compartments for uncoating.
Copyright © 2016, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ICAM-1 Binding Rhinoviruses Enter HeLa Cells via Multiple Pathways and Travel to Distinct Intracellular Compartments for Uncoating.Viruses. 2017 Apr 1;9(4):68. doi: 10.3390/v9040068. Viruses. 2017. PMID: 28368306 Free PMC article.
-
Uncoating of human rhinoviruses.Rev Med Virol. 2010 Sep;20(5):281-97. doi: 10.1002/rmv.654. Rev Med Virol. 2010. PMID: 20629045 Review.
-
The ICAM-1 ligand HRV-A89 is internalized independently of clathrin-mediated endocytosis and its capsid reaches late endosomes.Virology. 2023 Jun;583:45-51. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2023.04.003. Epub 2023 May 3. Virology. 2023. PMID: 37148647
-
Formation of rhinovirus-soluble ICAM-1 complexes and conformational changes in the virion.J Virol. 1993 Jan;67(1):390-7. doi: 10.1128/JVI.67.1.390-397.1993. J Virol. 1993. PMID: 8093221 Free PMC article.
-
ICAM-1 receptors and cold viruses.Pharm Acta Helv. 2000 Mar;74(2-3):291-7. doi: 10.1016/s0031-6865(99)00056-4. Pharm Acta Helv. 2000. PMID: 10812972 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Impairing the function of MLCK, myosin Va or myosin Vb disrupts Rhinovirus B14 replication.Sci Rep. 2017 Dec 7;7(1):17153. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-17501-z. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29215055 Free PMC article.
-
Meningitic Escherichia coli-induced upregulation of PDGF-B and ICAM-1 aggravates blood-brain barrier disruption and neuroinflammatory response.J Neuroinflammation. 2019 May 15;16(1):101. doi: 10.1186/s12974-019-1497-1. J Neuroinflammation. 2019. PMID: 31092253 Free PMC article.
-
ICAM-1 Binding Rhinoviruses Enter HeLa Cells via Multiple Pathways and Travel to Distinct Intracellular Compartments for Uncoating.Viruses. 2017 Apr 1;9(4):68. doi: 10.3390/v9040068. Viruses. 2017. PMID: 28368306 Free PMC article.
-
Lactoferrin affects rhinovirus B-14 entry into H1-HeLa cells.Arch Virol. 2021 Apr;166(4):1203-1211. doi: 10.1007/s00705-021-04993-4. Epub 2021 Feb 19. Arch Virol. 2021. PMID: 33606112 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vlasak M, Roivainen M, Reithmayer M, Goesler I, Laine P, Snyers L, Hovi T, Blaas D. 2005. The minor receptor group of human rhinovirus (HRV) includes HRV23 and HRV25, but the presence of a lysine in the VP1 HI loop is not sufficient for receptor binding. J Virol 79:7389–7395. doi:10.1128/JVI.79.12.7389-7395.2005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bochkov YA, Watters K, Ashraf S, Griggs TF, Devries MK, Jackson DJ, Palmenberg AC, Gern JE. 2015. Cadherin-related family member 3, a childhood asthma susceptibility gene product, mediates rhinovirus C binding and replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112:5485–5490. doi:10.1073/pnas.1421178112. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Goldstein JL, Brown MS. 1974. Binding and degradation of low density lipoproteins by cultured human fibroblasts. Comparison of cells from a normal subject and from a patient with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. J Biol Chem 249:5153–5162. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

