Fibrotic microenvironment promotes the metastatic seeding of tumor cells via activating the fibronectin 1/secreted phosphoprotein 1-integrin signaling
- PMID: 27329720
- PMCID: PMC5216754
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.10157
Fibrotic microenvironment promotes the metastatic seeding of tumor cells via activating the fibronectin 1/secreted phosphoprotein 1-integrin signaling
Abstract
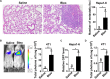
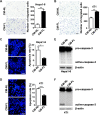
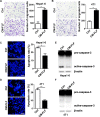
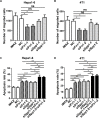
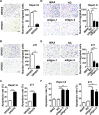
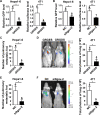
The seeding of tumor cells is a critical step in the process of metastasis, but whether and how the microenvironment of target organs affects metastatic seeding remain largely unknown. Based on cell and mouse models, we found that the metastatic seeding and outgrowth of tumor cells were significantly enhanced in fibrotic lungs. The conditioned medium from both fibrotic lungs and the fibrotic lung-derived fibroblasts (CM-FLF) had a strong activity to chemoattract tumor cells and to inhibit the apoptosis of tumor cells. Subsequent investigations revealed that the levels of fibronectin 1 (FN1) and secreted phosphoprotein 1 (SPP1) were significantly increased in fibrotic lungs. Silencing of FN1 in the fibrotic lung-derived fibroblasts dramatically decreased the chemoattracting activity of CM-FLF, while silencing of FN1 or SPP1 in fibroblasts attenuated the anti-apoptosis activity of CM-FLF. Moreover, the CM-FLF-induced apoptosis resistance or chemotaxis of tumor cells was attenuated when ITGAV, the common receptor of FN1 and SPP1, was silenced by RNA interference or blocked by GRGDS treatment in tumor cells. Consistently, ITGAV silencing or GRGDS treatment significantly inhibited the seeding and outgrowth of tumor cells in fibrotic lungs in vivo. Collectively, we suggest that fibrotic microenvironment may enhance the metastatic seeding of tumor cells in the lung by chemoattracting tumor cells and inhibiting their apoptosis via activating the FN1/SPP1-ITGAV signaling. These findings give a novel insight into the regulatory mechanisms of cancer metastasis and provide a potential target for anti-metastasis therapy.
Keywords: FN1; ITGAV; SPP1; fibrotic microenvironment; metastatic seeding.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Osteopontin shapes immunosuppression in the metastatic niche.Cancer Res. 2014 Sep 1;74(17):4706-19. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-3334. Epub 2014 Jul 17. Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 25035397
-
The protein disulfide isomerase A3 and osteopontin axis promotes influenza-induced lung remodelling.Br J Pharmacol. 2024 Nov;181(22):4610-4627. doi: 10.1111/bph.16511. Epub 2024 Aug 8. Br J Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39118388
-
Melanoma-derived extracellular vesicles instigate proinflammatory signaling in the metastatic microenvironment.Int J Cancer. 2019 Nov 1;145(9):2521-2534. doi: 10.1002/ijc.32521. Epub 2019 Jul 4. Int J Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31216364
-
Matrix control of pancreatic cancer: New insights into fibronectin signaling.Cancer Lett. 2016 Oct 10;381(1):252-8. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2015.12.027. Epub 2015 Dec 29. Cancer Lett. 2016. PMID: 26742464 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The origin of prostate metastases: emerging insights.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2015 Dec;34(4):765-73. doi: 10.1007/s10555-015-9597-6. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2015. PMID: 26363603 Review.
Cited by
-
Cerebrospinal fluid exosomal protein alterations via proteomic analysis of NSCLC with leptomeningeal carcinomatosis.J Neurooncol. 2023 Sep;164(2):367-376. doi: 10.1007/s11060-023-04428-x. Epub 2023 Sep 1. J Neurooncol. 2023. PMID: 37656377 Free PMC article.
-
The importance of 3D fibre architecture in cancer and implications for biomaterial model design.Nat Rev Cancer. 2024 Jul;24(7):461-479. doi: 10.1038/s41568-024-00704-8. Epub 2024 Jun 17. Nat Rev Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38886573 Review.
-
Up-regulated SPP1 increases the risk from IPF to lung cancer via activating the pro-tumor macrophages.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2023 Nov 14;21:5751-5764. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2023.11.018. eCollection 2023. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2023. PMID: 38074471 Free PMC article.
-
The fibrotic microenvironment promotes the metastatic seeding of tumor cells into the lungs via mediating the ZEB1-AS1/miR-200b-3p/ZEB1 signaling.Cell Cycle. 2020 Oct;19(20):2701-2719. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2020.1826236. Epub 2020 Oct 5. Cell Cycle. 2020. Retraction in: Cell Cycle. 2022 Dec;21(23):2557. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2022.2097805. PMID: 33017562 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Integrated analysis of single-cell and bulk RNA-sequencing reveals the poor prognostic value of ABCA1 in gastric adenocarcinoma.Discov Oncol. 2023 Oct 24;14(1):189. doi: 10.1007/s12672-023-00807-y. Discov Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37874419 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chaffer CL, Weinberg RA. A perspective on cancer cell metastasis. Science. 2011;331:1559–64. - PubMed
-
- Nguyen DX, Bos PD, Massague J. Metastasis: from dissemination to organ-specific colonization. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009;9:274–84. - PubMed
-
- Bonapace L, Coissieux MM, Wyckoff J, Mertz KD, Varga Z, Junt T, Bentires-Alj M. Cessation of CCL2 inhibition accelerates breast cancer metastasis by promoting angiogenesis. Nature. 2014;515:130–3. - PubMed
-
- Li Y, Chen L, Chan TH, Liu M, Kong KL, Qiu JL, Li Y, Yuan YF, Guan XY. SPOCK1 is regulated by CHD1L and blocks apoptosis and promotes HCC cell invasiveness and metastasis in mice. Gastroenterology. 2013;144:179–91. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

