A Role for the Chromatin-Remodeling Factor BAZ1A in Neurodevelopment
- PMID: 27328812
- PMCID: PMC6681169
- DOI: 10.1002/humu.23034
A Role for the Chromatin-Remodeling Factor BAZ1A in Neurodevelopment
Abstract
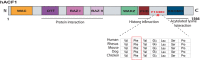
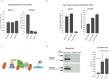
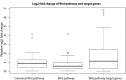
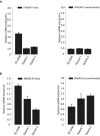
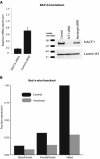
Chromatin-remodeling factors are required for a wide range of cellular and biological processes including development and cognition, mainly by regulating gene expression. As these functions would predict, deregulation of chromatin-remodeling factors causes various disease syndromes, including neurodevelopmental disorders. Recent reports have linked mutations in several genes coding for chromatin-remodeling factors to intellectual disability (ID). Here, we used exome sequencing and identified a nonsynonymous de novo mutation in BAZ1A (NM_182648.2:c.4043T > G, p.Phe1348Cys), encoding the ATP-utilizing chromatin assembly and remodeling factor 1 (ACF1), in a patient with unexplained ID. ACF1 has been previously reported to bind to the promoter of the vitamin D receptor (VDR)-regulated genes and suppress their expression. Our results show that the patient displays decreased binding of ACF1 to the promoter of the VDR-regulated gene CYP24A1. Using RNA sequencing, we find that the mutation affects the expression of genes involved in several pathways including vitamin D metabolism, Wnt signaling and synaptic formation. RNA sequencing of BAZ1A knockdown cells and Baz1a knockout mice revealed that BAZ1A carry out distinctive functions in different tissues. We also demonstrate that BAZ1A depletion influence the expression of genes important for nervous system development and function. Our data point to an important role for BAZ1A in neurodevelopment, and highlight a possible link for BAZ1A to ID.
Keywords: ACF1; BAZ1A; CYP24A1; Wnt signaling; epilepsy; intellectual disability; neurodevelopment; vitamin D metabolism.
© 2016 The Authors. **Human Mutation published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chromatin remodeling factor BAZ1A regulates cellular senescence in both cancer and normal cells.Life Sci. 2019 Jul 15;229:225-232. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.05.023. Epub 2019 May 11. Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 31085244
-
Mouse BAZ1A (ACF1) is dispensable for double-strand break repair but is essential for averting improper gene expression during spermatogenesis.PLoS Genet. 2013 Nov;9(11):e1003945. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003945. Epub 2013 Nov 7. PLoS Genet. 2013. PMID: 24244200 Free PMC article.
-
Exome sequencing in syndromic brain malformations identifies novel mutations in ACTB, and SLC9A6, and suggests BAZ1A as a new candidate gene.Birth Defects Res. 2018 Apr 17;110(7):587-597. doi: 10.1002/bdr2.1200. Epub 2018 Feb 1. Birth Defects Res. 2018. PMID: 29388391
-
A de novo mutation in RPL10 causes a rare X-linked ribosomopathy characterized by syndromic intellectual disability and epilepsy: A new case and review of the literature.Eur J Med Genet. 2018 Feb;61(2):89-93. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmg.2017.10.011. Epub 2017 Oct 21. Eur J Med Genet. 2018. PMID: 29066376 Review.
-
Molecular endocrinology of vitamin D on the epigenome level.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2017 Sep 15;453:14-21. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2017.03.016. Epub 2017 Mar 16. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2017. PMID: 28315703 Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenetic modifications in acute myeloid leukemia: The emerging role of circular RNAs (Review).Int J Oncol. 2021 Dec;59(6):107. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2021.5287. Epub 2021 Nov 18. Int J Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34792180 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TAF1, associated with intellectual disability in humans, is essential for embryogenesis and regulates neurodevelopmental processes in zebrafish.Sci Rep. 2019 Jul 24;9(1):10730. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-46632-8. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31341187 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoplastics impact the zebrafish (Danio rerio) transcriptome: Associated developmental and neurobehavioral consequences.Environ Pollut. 2020 Nov;266(Pt 2):115090. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115090. Epub 2020 Jul 16. Environ Pollut. 2020. PMID: 32693326 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic Discovery of Endogenous Human Ribonucleoprotein Complexes.Cell Rep. 2019 Oct 29;29(5):1351-1368.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.09.060. Cell Rep. 2019. PMID: 31665645 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetics in Neurodevelopment: Emerging Role of Circular RNA.Front Cell Neurosci. 2019 Jul 19;13:327. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00327. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31379511 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aasland R, Gibson TJ, Stewart AF. 1995. The PHD finger: implications for chromatin‐mediated transcriptional regulation. Trends Biochem Sci 20:56–59. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez‐Saavedra M, De Repentigny Y, Lagali PS, Raghu Ram EV, Yan K, Hashem E, Ivanochko D, Huh MS, Yang D, Mears AJ, Todd MA, Corcoran CP, et al. 2014. Snf2h‐mediated chromatin organization and histone H1 dynamics govern cerebellar morphogenesis and neural maturation. Nat Commun 5:4181. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Banting GS, Barak O, Ames TM, Burnham AC, Kardel MD, Cooch NS, Davidson CE, Godbout R, Mcdermid HE, Shiekhattar R. 2005. CECR2, a protein involved in neurulation, forms a novel chromatin remodeling complex with SNF2L. Hum Mol Genet 14:513–524. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

