Dual role of GRK5 in cancer development and progression
- PMID: 27326393
- PMCID: PMC4912336
Dual role of GRK5 in cancer development and progression
Abstract
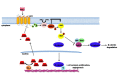
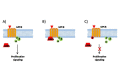
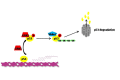
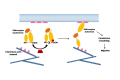
GRK5 is a multifunctional protein that is able to move within the cell in response to various stimuli to regulate key intracellular signaling from receptor activation, on plasmamembrane, to gene transcription, in the nucleus. Thus, GRK5 is involved in the development and progression of several pathological conditions including cancer. Several reports underline the involvement of GRK5 in the regulation of tumor growth even if they appear controversial. Indeed, depending on its subcellular localization and on the type of cancer, GRK5 is able to both inhibit cancer progression, through the desensitization of GPCR and non GPCR-receptors (TSH, PGE2R, PDGFR), and induce tumor growth, acting on non-receptor substrates (p53, AUKA and NPM1). All these findings suggest that targeting GRK5 could be an useful anti-cancer strategy, for specific tumor types. In this review, we will discuss the different effects of this kinase in the induction and progression of tumorigenesis, the molecular mechanisms by which GRK5 exerts its effects, and the potential therapeutic strategies to modulate them.
Keywords: GPCR; GRK5; cancer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeting GRK5 for Treating Chronic Degenerative Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 15;22(4):1920. doi: 10.3390/ijms22041920. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33671974 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GRK5 promotes tumor progression in renal cell carcinoma.Neoplasma. 2019 Feb 6;66(2):261-270. doi: 10.4149/neo_2018_180621N409. Neoplasma. 2019. PMID: 30784280
-
G-protein coupled receptor kinase 5 regulates prostate tumor growth.J Urol. 2012 Jan;187(1):322-9. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2011.09.049. Epub 2011 Nov 17. J Urol. 2012. PMID: 22099983
-
G protein-coupled receptor kinase 5 contains a DNA-binding nuclear localization sequence.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Dec;24(23):10169-79. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.23.10169-10179.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15542828 Free PMC article.
-
GRK2 and GRK5 as therapeutic targets and their role in maladaptive and pathological cardiac hypertrophy.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2019 Mar;23(3):201-214. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2019.1575363. Epub 2019 Feb 13. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2019. PMID: 30701991 Review.
Cited by
-
GRK5 functions as an oncogenic factor in non-small-cell lung cancer.Cell Death Dis. 2018 Feb 20;9(3):295. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0299-1. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 29463786 Free PMC article.
-
GRK5 - A Functional Bridge Between Cardiovascular and Neurodegenerative Disorders.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Dec 17;9:1484. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.01484. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30618771 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of microRNAs in regulation of doxorubicin and paclitaxel responses in lung tumor cells.Cell Div. 2023 Jul 21;18(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s13008-023-00093-8. Cell Div. 2023. PMID: 37480054 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploiting GRK2 Inhibition as a Therapeutic Option in Experimental Cancer Treatment: Role of p53-Induced Mitochondrial Apoptosis.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Nov 26;12(12):3530. doi: 10.3390/cancers12123530. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33256128 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting GRK5 for Treating Chronic Degenerative Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 15;22(4):1920. doi: 10.3390/ijms22041920. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33671974 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pitcher JA, Freedman NJ, Lefkowitz RJ. “G protein-coupled receptor kinases,”. Annu Rev Biochem. 1998;67:653–92. - PubMed
-
- Reiter E, Lefkowitz RJ. “GRKs and beta-arrestins: roles in receptor silencing, trafficking and signaling,”. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2006 May-Jun;17:159–65. - PubMed
-
- Tiberi M, Nash SR, Bertrand L, Lefkowitz RJ, Caron MG. “Differential regulation of dopamine D1A receptor responsiveness by various G protein-coupled receptor kinases,”. J Biol Chem. 1996 Feb 16;271:3771–8. - PubMed
-
- Gainetdinov RR, Bohn LM, Walker JK, Laporte SA, Macrae AD, Caron MG, Lefkowitz RJ, Premont RT. “Muscarinic supersensitivity and impaired receptor desensitization in G protein-coupled receptor kinase 5-deficient mice,”. Neuron. 1999 Dec;24:1029–36. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
