Role and structural mechanism of WASP-triggered conformational changes in branched actin filament nucleation by Arp2/3 complex
- PMID: 27325766
- PMCID: PMC4941453
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1517798113
Role and structural mechanism of WASP-triggered conformational changes in branched actin filament nucleation by Arp2/3 complex
Abstract
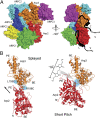
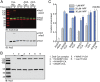
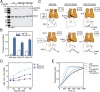
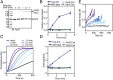
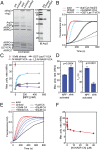
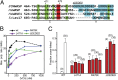
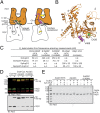
The Arp2/3 (Actin-related proteins 2/3) complex is activated by WASP (Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein) family proteins to nucleate branched actin filaments that are important for cellular motility. WASP recruits actin monomers to the complex and stimulates movement of Arp2 and Arp3 into a "short-pitch" conformation that mimics the arrangement of actin subunits within filaments. The relative contribution of these functions in Arp2/3 complex activation and the mechanism by which WASP stimulates the conformational change have been unknown. We purified budding yeast Arp2/3 complex held in or near the short-pitch conformation by an engineered covalent cross-link to determine if the WASP-induced conformational change is sufficient for activity. Remarkably, cross-linked Arp2/3 complex bypasses the need for WASP in activation and is more active than WASP-activated Arp2/3 complex. These data indicate that stimulation of the short-pitch conformation is the critical activating function of WASP and that monomer delivery is not a fundamental requirement for nucleation but is a specific requirement for WASP-mediated activation. During activation, WASP limits nucleation rates by releasing slowly from nascent branches. The cross-linked complex is inhibited by WASP's CA region, even though CA potently stimulates cross-linking, suggesting that slow WASP detachment masks the activating potential of the short-pitch conformational switch. We use structure-based mutations and WASP-Arp fusion chimeras to determine how WASP stimulates movement toward the short-pitch conformation. Our data indicate that WASP displaces the autoinhibitory Arp3 C-terminal tail from a hydrophobic groove at Arp3's barbed end to destabilize the inactive state, providing a mechanism by which WASP stimulates the short-pitch conformation and activates Arp2/3 complex.
Keywords: Arp2/3; WASP; actin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification of Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein (WASP) binding sites on the branched actin filament nucleator Arp2/3 complex.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Feb 13;115(7):E1409-E1418. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1716622115. Epub 2018 Jan 31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 29386393 Free PMC article.
-
Unconcerted conformational changes in Arp2/3 complex integrate multiple activating signals to assemble functional actin networks.Curr Biol. 2022 Mar 14;32(5):975-987.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2022.01.004. Epub 2022 Jan 31. Curr Biol. 2022. PMID: 35090589 Free PMC article.
-
Conformational changes in Arp2/3 complex induced by ATP, WASp-VCA, and actin filaments.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Sep 11;115(37):E8642-E8651. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1717594115. Epub 2018 Aug 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 30150414 Free PMC article.
-
WASP family proteins, more than Arp2/3 activators.Biochem Soc Trans. 2016 Oct 15;44(5):1339-1345. doi: 10.1042/BST20160176. Biochem Soc Trans. 2016. PMID: 27911716 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signalling to actin assembly via the WASP (Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein)-family proteins and the Arp2/3 complex.Biochem J. 2004 May 15;380(Pt 1):1-17. doi: 10.1042/BJ20040176. Biochem J. 2004. PMID: 15040784 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cryo-EM structure of NPF-bound human Arp2/3 complex and activation mechanism.Sci Adv. 2020 Jun 5;6(23):eaaz7651. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aaz7651. Print 2020 Jun. Sci Adv. 2020. PMID: 32917641 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulated inflammasome activity in intestinal inflammation - Insights from patients with very early onset IBD.Front Immunol. 2022 Nov 29;13:1027289. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1027289. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36524121 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regeneration of actin filament branches from the same Arp2/3 complex.Sci Adv. 2024 Jan 26;10(4):eadj7681. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adj7681. Epub 2024 Jan 26. Sci Adv. 2024. PMID: 38277459 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein (WASP) binding sites on the branched actin filament nucleator Arp2/3 complex.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Feb 13;115(7):E1409-E1418. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1716622115. Epub 2018 Jan 31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 29386393 Free PMC article.
-
Cryo-electron tomography structure of Arp2/3 complex in cells reveals new insights into the branch junction.Nat Commun. 2020 Dec 22;11(1):6437. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-20286-x. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 33353942 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amann KJ, Pollard TD. The Arp2/3 complex nucleates actin filament branches from the sides of pre-existing filaments. Nat Cell Biol. 2001;3(3):306–310. - PubMed
-
- Achard V, et al. A “primer”-based mechanism underlies branched actin filament network formation and motility. Curr Biol. 2010;20(5):423–428. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

