Elevated expression of FABP3 and FABP4 cooperatively correlates with poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
- PMID: 27323829
- PMCID: PMC5216795
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.10086
Elevated expression of FABP3 and FABP4 cooperatively correlates with poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
Abstract
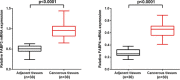
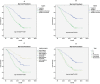
Fatty acid binding proteins (FABPs) are intracellular lipid-binding proteins that are involved in a variety of biological cellular processes, including tumorigenesis. In this study, we explored the expression pattern of FABP3 and FABP4 in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) as well as their roles in prognosis. We determined mRNA expression of FABP3 and FABP4 in matched pairs of cancerous and non-cancerous fresh frozen tissues from 30 NSCLC patients. Tissue microarray immunohistochemical analysis (TMA-IHC) was applied to determine the protein expression of FABP3 and FABP4 in 281 cancerous and 121 matched adjacent non-cancerous tissue samples. Our results showed that both mRNA and protein expression of FABP3 and FABP4 were significantly higher in cancerous tissues when compared to non-cancerous tissues. Furthermore, high expression of FABP3 or FABP4 in NSCLC was significantly associated with advanced tumor node metastasis (TNM) stage and had a negative impact on the overall survival of NSCLC patients. Concurrent high expression of FABP3 and FABP4 was significantly related to TNM stage. In conclusion, our research demonstrated that high FABP3 or FABP4 expression had strong prognostic value for overall survival in NSCLC. Detection of FABP3 and FABP4 cooperatively was helpful to predict the prognosis of NSCLC.
Keywords: fatty acid binding protein-3(FABP3); fatty acid binding protein-4(FABP4); immunohistochemistry; non-small cell lung cancer; prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
High TMPRSS11D protein expression predicts poor overall survival in non-small cell lung cancer.Oncotarget. 2017 Feb 21;8(8):12812-12819. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14559. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28086212 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of Alteration/Deficiency in Activation 3 correlates with poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer.Pathol Res Pract. 2019 Jun;215(6):152408. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2019.03.036. Epub 2019 Apr 2. Pathol Res Pract. 2019. PMID: 30954347
-
Clinicopathologic features and prognostic implications of Gankyrin protein expression in non-small cell lung cancer.Pathol Res Pract. 2015 Dec;211(12):939-47. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2015.09.010. Epub 2015 Sep 10. Pathol Res Pract. 2015. PMID: 26554593
-
Prognostic value of ERCC1 mRNA expression in non-small cell lung cancer, breast cancer, and gastric cancer in patients from Southern China.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014 Dec 1;7(12):8312-21. eCollection 2014. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014. PMID: 25674197 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small molecule inhibitors of human adipocyte fatty acid binding protein (FABP4).Med Chem. 2014 Jun;10(4):339-47. doi: 10.2174/15734064113096660045. Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 24024500 Review.
Cited by
-
Unraveling the intricate relationship between lipid metabolism and oncogenic signaling pathways.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Jun 12;12:1399065. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1399065. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 38933330 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FABP4 suppresses proliferation and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells and predicts a poor prognosis for hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer Med. 2018 Jun;7(6):2629-2640. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1511. Epub 2018 May 7. Cancer Med. 2018. PMID: 29733540 Free PMC article.
-
Communication in the Cancer Microenvironment as a Target for Therapeutic Interventions.Cancers (Basel). 2020 May 14;12(5):1232. doi: 10.3390/cancers12051232. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32422889 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anthocyanins prevent the development and progression of urethane-induced lung cancer by regulating energy metabolism in mice.Food Nutr Res. 2024 Apr 17;68. doi: 10.29219/fnr.v68.10434. eCollection 2024. Food Nutr Res. 2024. PMID: 38716355 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction and validation of common targets in atherosclerosis and non-small cell lung cancer influenced by atorvastatin.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023 Nov 17;23(1):415. doi: 10.1186/s12906-023-04255-7. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023. PMID: 37978381 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lin J, Beer DG. Molecular predictors of prognosis in lung cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2012;19:669–76. - PubMed
-
- Reckamp KL. Antiangiogenic agents as second-line therapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Lett. 2012;321:101–9. - PubMed
-
- Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 2010;127:2893–917. - PubMed
-
- Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ, He J. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:115–32. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

