To live or let die - complexity within the E2F1 pathway
- PMID: 27308406
- PMCID: PMC4905241
- DOI: 10.4161/23723548.2014.970480
To live or let die - complexity within the E2F1 pathway
Abstract
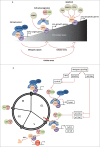
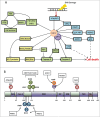
The E2F1 transcription factor is a recognized regulator of the cell cycle as well as a potent mediator of DNA damage-induced apoptosis and the checkpoint response. Understanding the diverse and seemingly dichotomous functions of E2F1 activity has been the focus of extensive ongoing research. Although the E2F pathway is frequently deregulated in cancer, the contributions of E2F1 itself to tumorigenesis, as a promoter of proliferation or cell death, are far from understood. In this review we aim to provide an update on our current understanding of E2F1, with particular insight into its novel interaction partners and post-translational modifications, as a means to explaining its diverse functional complexity.
Keywords: DNA damage response; E2F1; apoptosis; cancer; cell cycle; epigenetics.
Figures
Similar articles
-
E2F1 induces MRN foci formation and a cell cycle checkpoint response in human fibroblasts.Oncogene. 2006 Jun 1;25(23):3258-66. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209352. Epub 2006 Jan 23. Oncogene. 2006. PMID: 16434972
-
Up-regulation of Bcl-2 homology 3 (BH3)-only proteins by E2F1 mediates apoptosis.J Biol Chem. 2004 Mar 5;279(10):8627-34. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M312866200. Epub 2003 Dec 18. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 14684737
-
Promoter occupancy of MLL1 histone methyltransferase seems to specify the proliferative and apoptotic functions of E2F1 in a tumour microenvironment.J Cell Sci. 2013 Oct 15;126(Pt 20):4636-46. doi: 10.1242/jcs.126235. Epub 2013 Jul 18. J Cell Sci. 2013. PMID: 23868976
-
Transcriptional and nontranscriptional functions of E2F1 in response to DNA damage.Cancer Res. 2012 Jan 1;72(1):13-7. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-2196. Epub 2011 Dec 16. Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22180494 Free PMC article. Review.
-
E2F1 in gliomas: a paradigm of oncogene addiction.Cancer Lett. 2008 May 18;263(2):157-63. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2008.02.001. Epub 2008 Mar 10. Cancer Lett. 2008. PMID: 18334281 Review.
Cited by
-
Phf21b imprints the spatiotemporal epigenetic switch essential for neural stem cell differentiation.Genes Dev. 2020 Sep 1;34(17-18):1190-1209. doi: 10.1101/gad.333906.119. Epub 2020 Aug 20. Genes Dev. 2020. PMID: 32820037 Free PMC article.
-
Novel chemotherapeutic agent FX-9 activates NF-κB signaling and induces G1 phase arrest by activating CDKN1A in a human prostate cancer cell line.BMC Cancer. 2021 Oct 8;21(1):1088. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08836-y. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34625047 Free PMC article.
-
p53 modeling as a route to mesothelioma patients stratification and novel therapeutic identification.J Transl Med. 2018 Oct 13;16(1):282. doi: 10.1186/s12967-018-1650-0. J Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 30316293 Free PMC article.
-
E2F1 Regulates Adipocyte Differentiation and Adipogenesis by Activating ICAT.Cells. 2020 Apr 21;9(4):1024. doi: 10.3390/cells9041024. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32326181 Free PMC article.
-
The F-box protein FBXL16 up-regulates the stability of C-MYC oncoprotein by antagonizing the activity of the F-box protein FBW7.J Biol Chem. 2020 Jun 5;295(23):7970-7980. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.012658. Epub 2020 Apr 28. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32345600 Free PMC article.
References
-
- DeGregori J, Leone G, Miron A, Jakoi L, Nevins JR. Distinct roles for E2F proteins in cell growth control and apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci 1997; 94:7245-50; PMID:9207076; http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.94.14.7245 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Black EP, Hallstrom T, Dressman HK, West M, Nevins JR. Distinctions in the specificity of E2F function revealed by gene expression signatures. Proc Natl Acad Sci 2005; 102:15948-53; PMID:16249342; http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0504300102 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ingram L, Munro S, Coutts AS, La Thangue NB. E2F-1 regulation by an unusual DNA damage-responsive DP partner subunit. Cell Death Differ 2011; 18:122-32; PMID:20559320; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2010.70 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Narita M, Nunez S, Heard E, Lin AW, Hearn SA, Spector DL, Hannon GJ, Lowe SW. Rb-mediated heterochromatin formation and silencing of E2F target genes during cellular senescence. Cell 2003; 113:703-16; PMID:12809602; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(03)00401-X - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
