Fn14 deficiency protects lupus-prone mice from histological lupus erythematosus-like skin inflammation induced by ultraviolet light
- PMID: 27305603
- PMCID: PMC5127760
- DOI: 10.1111/exd.13108
Fn14 deficiency protects lupus-prone mice from histological lupus erythematosus-like skin inflammation induced by ultraviolet light
Abstract
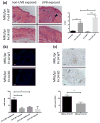
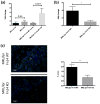
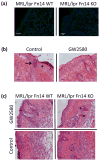
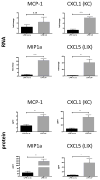
The cytokine TNF-like weak inducer of apoptosis (TWEAK) and its receptor Fn14 are involved in cell survival and cytokine production. The TWEAK/Fn14 pathway plays a role in the pathogenesis of spontaneous cutaneous lesions in the MRL/lpr lupus strain; however, the role of TWEAK/Fn14 in disease induced by ultraviolet B (UVB) irradiation has not been explored. MRL/lpr Fn14 knockout (KO) was compared to MRL/lpr Fn14 wild-type (WT) mice following exposure to UVB. We found that irradiated MRL/lpr KO mice had significantly attenuated cutaneous disease when compared to their WT counterparts. There were also fewer infiltrating immune cells (CD3+ , IBA-1+ and NGAL+ ) in the UVB-exposed skin of MRL/lpr Fn14KO mice, as compared to Fn14WT. Furthermore, we identified several macrophage-derived proinflammatory chemokines with elevated expression in MRL/lpr mice after UV exposure. Depletion of macrophages, using a CSF-1R inhibitor, was found to be protective against the development of skin lesions after UVB exposure. In combination with the phenotype of the MRL/lpr Fn14KO mice, these findings indicate a critical role for Fn14 and recruited macrophages in UVB-triggered cutaneous lupus. Our data strongly suggest that TWEAK/Fn14 signalling is important in the pathogenesis of UVB-induced cutaneous disease manifestations in the MRL/lpr model of lupus and further support this pathway as a possible target for therapeutic intervention.
Keywords: MRL-lpr/lpr; TNF-like weak inducer of apoptosis; cutaneous lupus; macrophages; photosensitivity.
© 2016 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
TWEAK/Fn14 Activation Participates in Skin Inflammation.Mediators Inflamm. 2017;2017:6746870. doi: 10.1155/2017/6746870. Epub 2017 Sep 6. Mediators Inflamm. 2017. PMID: 29038621 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TWEAK/Fn14 Signaling Involvement in the Pathogenesis of Cutaneous Disease in the MRL/lpr Model of Spontaneous Lupus.J Invest Dermatol. 2015 Aug;135(8):1986-1995. doi: 10.1038/jid.2015.124. Epub 2015 Mar 31. J Invest Dermatol. 2015. PMID: 25826425 Free PMC article.
-
Neuropsychiatric disease in murine lupus is dependent on the TWEAK/Fn14 pathway.J Autoimmun. 2013 Jun;43:44-54. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2013.03.002. Epub 2013 Apr 8. J Autoimmun. 2013. PMID: 23578591 Free PMC article.
-
TNF-like weak inducer of apoptosis promotes blood brain barrier disruption and increases neuronal cell death in MRL/lpr mice.J Autoimmun. 2015 Jun;60:40-50. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2015.03.005. Epub 2015 Apr 22. J Autoimmun. 2015. PMID: 25911200 Free PMC article.
-
Out of the TWEAKlight: Elucidating the Role of Fn14 and TWEAK in Acute Kidney Injury.Semin Nephrol. 2016 May;36(3):189-98. doi: 10.1016/j.semnephrol.2016.03.006. Semin Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 27339384 Review.
Cited by
-
TWEAK/Fn14 Activation Participates in Skin Inflammation.Mediators Inflamm. 2017;2017:6746870. doi: 10.1155/2017/6746870. Epub 2017 Sep 6. Mediators Inflamm. 2017. PMID: 29038621 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Highly selective inhibition of Bruton's tyrosine kinase attenuates skin and brain disease in murine lupus.Arthritis Res Ther. 2018 Jan 25;20(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s13075-017-1500-0. Arthritis Res Ther. 2018. PMID: 29370834 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in cutaneous lupus.J Autoimmun. 2022 Oct;132:102865. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2022.102865. Epub 2022 Jul 17. J Autoimmun. 2022. PMID: 35858957 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New concepts on abnormal UV reactions in systemic lupus erythematosus and a screening tool for assessment of photosensitivity.Skin Res Technol. 2023 Mar;29(3):e13247. doi: 10.1111/srt.13247. Skin Res Technol. 2023. PMID: 36973991 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Rho Kinase regulates neutrophil NET formation that is involved in UVB-induced skin inflammation.Theranostics. 2022 Feb 7;12(5):2133-2149. doi: 10.7150/thno.66457. eCollection 2022. Theranostics. 2022. PMID: 35265203 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

