Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio for the prognostic assessment of hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies
- PMID: 27304193
- PMCID: PMC5216723
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.9942
Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio for the prognostic assessment of hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies
Abstract
Background and aims: Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) is an inflammatory-based marker. A systematic review and meta-analysis was performed to explore the prognostic role of NLR in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
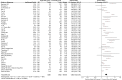
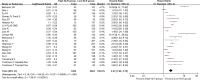
Results: Overall, 598 papers were identified, of which 90 papers including 20,475 HCC patients were finally included. Low baseline NLR was significantly associated with better overall survival (HR = 1.80, 95% CI: 1.59-2.04, p < 0.00001) and recurrence-free or disease-free survival (HR = 2.23, 95% CI: 1.80-2.76, p < 0.00001). Low post- treatment NLR was significantly associated with better overall survival (HR = 1.90, 95% CI: 1.22-2.94, p = 0.004). Decreased NLR was significantly associated with overall survival (HR = 2.23, 95%CI: 1.83-2.72, p < 0.00001) and recurrence-free or disease-free survival (HR = 2.23, 95% CI: 1.83-2.72, p < 0.00001). The findings from most of subgroup meta-analyses were consistent with those from the overall meta-analyses.
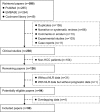
Materials and methods: All relevant literatures were identified via PubMed, EMBASE, and Cochrane library databases. Hazard ratio (HR) with 95% confidence interval (95%CI) was calculated. Subgroup meta-analyses were performed according to the treatment options, NLR cut-off value ranges, and regions.
Conclusions: NLR should be a major prognostic factor for HCC patients. NLR might be further incorporated into the prognostic model of HCC.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma; inflammatory; lymphocyte; neutrophil; prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTERESTS None.
Figures
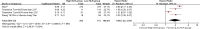
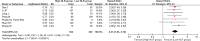
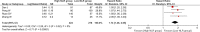
Similar articles
-
Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio and Platelet to Lymphocyte Ratio as Prognostic Predictors for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients with Various Treatments: a Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;44(3):967-981. doi: 10.1159/000485396. Epub 2017 Nov 27. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 29179180 Review.
-
The prognostic significance of preoperative neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma receiving hepatectomy: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Surg. 2018 Jul;55:73-80. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2018.05.022. Epub 2018 May 19. Int J Surg. 2018. PMID: 29787804 Review.
-
Prognostic significance of neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio in hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis.BMC Cancer. 2014 Feb 21;14:117. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-117. BMC Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24559042 Free PMC article.
-
The pretransplant neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio as a new prognostic predictor after liver transplantation for hepatocellular cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Biomark Med. 2018 Feb;12(2):189-199. doi: 10.2217/bmm-2017-0307. Epub 2018 Jan 12. Biomark Med. 2018. PMID: 29327595
-
[Correlation between postoperative neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio and recurrence and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma after radical liver resection].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2018 May 23;40(5):365-371. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3766.2018.05.009. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 29860764 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Preoperative inflammatory markers as prognostic predictors after hepatocellular carcinoma resection: data from a western referral center.BMC Surg. 2022 Sep 2;22(1):329. doi: 10.1186/s12893-022-01779-6. BMC Surg. 2022. PMID: 36056350 Free PMC article.
-
The prognostic significance of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio at different time points in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma receiving liver resection.Transl Cancer Res. 2020 Feb;9(2):441-457. doi: 10.21037/tcr.2019.11.29. Transl Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 35117389 Free PMC article.
-
The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a new prognostic factor in cancers: a narrative review.Front Oncol. 2023 Oct 4;13:1228076. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1228076. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37860198 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human leukocyte antigen gene polymorphisms are associated with systemic inflammation in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer Manag Res. 2018 Jul 31;10:2315-2324. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S167574. eCollection 2018. Cancer Manag Res. 2018. PMID: 30104900 Free PMC article.
-
Independent effect of postoperative neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio on the survival of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma with open distal pancreatosplenectomy and its nomogram-based prediction.J Cancer. 2019 Oct 15;10(24):5935-5943. doi: 10.7150/jca.35856. eCollection 2019. J Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31762803 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Forner A, Reig ME, de Lope CR, Bruix J. Current strategy for staging and treatment: the BCLC update and future prospects. Semin Liver Dis. 2010;30:61–74. - PubMed
-
- A new prognostic system for hepatocellular carcinoma: a retrospective study of 435 patients: the Cancer of the Liver Italian Program (CLIP) investigators. Hepatology. 1998;28:751–755. - PubMed
-
- Yau T, Tang VY, Yao TJ, Fan ST, Lo CM, Poon RT. Development of Hong Kong Liver Cancer staging system with treatment stratification for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2014;146:1691–1700. e1693. - PubMed
-
- Kudo M, Chung H, Osaki Y. Prognostic staging system for hepatocellular carcinoma (CLIP score): its value and limitations, and a proposal for a new staging system, the Japan Integrated Staging Score (JIS score) J Gastroenterol. 2003;38:207–215. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

