When Genome-Based Approach Meets the "Old but Good": Revealing Genes Involved in the Antibacterial Activity of Pseudomonas sp. P482 against Soft Rot Pathogens
- PMID: 27303376
- PMCID: PMC4880745
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00782
When Genome-Based Approach Meets the "Old but Good": Revealing Genes Involved in the Antibacterial Activity of Pseudomonas sp. P482 against Soft Rot Pathogens
Abstract
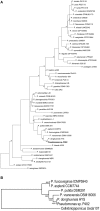
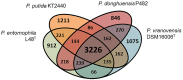
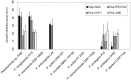
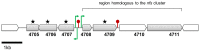
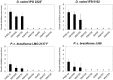
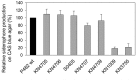
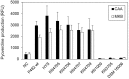
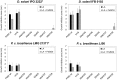
Dickeya solani and Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. brasiliense are recently established species of bacterial plant pathogens causing black leg and soft rot of many vegetables and ornamental plants. Pseudomonas sp. strain P482 inhibits the growth of these pathogens, a desired trait considering the limited measures to combat these diseases. In this study, we determined the genetic background of the antibacterial activity of P482, and established the phylogenetic position of this strain. Pseudomonas sp. P482 was classified as Pseudomonas donghuensis. Genome mining revealed that the P482 genome does not contain genes determining the synthesis of known antimicrobials. However, the ClusterFinder algorithm, designed to detect atypical or novel classes of secondary metabolite gene clusters, predicted 18 such clusters in the genome. Screening of a Tn5 mutant library yielded an antimicrobial negative transposon mutant. The transposon insertion was located in a gene encoding an HpcH/HpaI aldolase/citrate lyase family protein. This gene is located in a hypothetical cluster predicted by the ClusterFinder, together with the downstream homologs of four nfs genes, that confer production of a non-fluorescent siderophore by P. donghuensis HYS(T). Site-directed inactivation of the HpcH/HpaI aldolase gene, the adjacent short chain dehydrogenase gene, as well as a homolog of an essential nfs cluster gene, all abolished the antimicrobial activity of the P482, suggesting their involvement in a common biosynthesis pathway. However, none of the mutants showed a decreased siderophore yield, neither was the antimicrobial activity of the wild type P482 compromised by high iron bioavailability. A genomic region comprising the nfs cluster and three upstream genes is involved in the antibacterial activity of P. donghuensis P482 against D. solani and P. carotovorum subsp. brasiliense. The genes studied are unique to the two known P. donghuensis strains. This study illustrates that mining of microbial genomes is a powerful approach for predictingthe presence of novel secondary-metabolite encoding genes especially when coupled with transposon mutagenesis.
Keywords: Dickeya; Pectobacterium; antiSMASH; genome mining; nfs; secondary metabolites.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An iron fist in a velvet glove: The cooperation of a novel pyoverdine from Pseudomonas donghuensis P482 with 7-hydroxytropolone is pivotal for its antibacterial activity.Environ Microbiol. 2024 Jan;26(1):e16559. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.16559. Epub 2023 Dec 27. Environ Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38151794
-
High-Quality Complete Genome Resource of Tomato Rhizosphere Strain Pseudomonas donghuensis P482, a Representative of a Species with Biocontrol Activity Against Plant Pathogens.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2021 Dec;34(12):1450-1454. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-06-21-0136-A. Epub 2021 Nov 30. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2021. PMID: 34428926
-
The carbon source-dependent pattern of antimicrobial activity and gene expression in Pseudomonas donghuensis P482.Sci Rep. 2021 May 26;11(1):10994. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-90488-w. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34040089 Free PMC article.
-
Insight into the Global Negative Regulation of Iron Scavenger 7-HT Biosynthesis by the SigW/RsiW System in Pseudomonas donghuensis HYS.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 7;24(2):1184. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021184. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36674714 Free PMC article.
-
The antimicrobial volatile power of the rhizospheric isolate Pseudomonas donghuensis P482.PLoS One. 2017 Mar 30;12(3):e0174362. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0174362. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28358818 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Biosensors Used for Epifluorescence and Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopies to Study Dickeya and Pectobacterium Virulence and Biocontrol.Microorganisms. 2021 Feb 1;9(2):295. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9020295. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 33535657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Carbon Source and Substrate Surface Affect Biofilm Formation by the Plant-Associated Bacterium Pseudomonas donghuensis P482.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 30;25(15):8351. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158351. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125921 Free PMC article.
-
A Complex Mechanism Involving LysR and TetR/AcrR That Regulates Iron Scavenger Biosynthesis in Pseudomonas donghuensis HYS.J Bacteriol. 2018 Jun 11;200(13):e00087-18. doi: 10.1128/JB.00087-18. Print 2018 Jul 1. J Bacteriol. 2018. PMID: 29686142 Free PMC article.
-
Host-adaptive traits in the plant-colonizing Pseudomonas donghuensis P482 revealed by transcriptomic responses to exudates of tomato and maize.Sci Rep. 2023 Jun 9;13(1):9445. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-36494-6. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37296159 Free PMC article.
-
Pseudomonas species isolated via high-throughput screening significantly protect cotton plants against verticillium wilt.AMB Express. 2020 Oct 28;10(1):193. doi: 10.1186/s13568-020-01132-1. AMB Express. 2020. PMID: 33118043 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexeyev M. F. (1999). The pknock series of broad-host-range mobilizable suicide vectors for gene knockout and targeted DNA insertion into the chromosome of gram-negative bacteria. BioTechniques 26, 824–827. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

