Protein Thiol Redox Signaling in Monocytes and Macrophages
- PMID: 27288099
- PMCID: PMC5107717
- DOI: 10.1089/ars.2016.6697
Protein Thiol Redox Signaling in Monocytes and Macrophages
Abstract
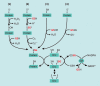
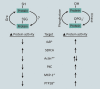
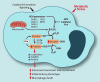
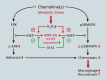
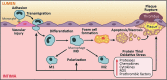
Significance: Monocyte and macrophage dysfunction plays a critical role in a wide range of inflammatory disease processes, including obesity, impaired wound healing diabetic complications, and atherosclerosis. Emerging evidence suggests that the earliest events in monocyte or macrophage dysregulation include elevated reactive oxygen species production, thiol modifications, and disruption of redox-sensitive signaling pathways. This review focuses on the current state of research in thiol redox signaling in monocytes and macrophages, including (i) the molecular mechanisms by which reversible protein-S-glutathionylation occurs, (ii) the identification of bona fide S-glutathionylated proteins that occur under physiological conditions, and (iii) how disruptions of thiol redox signaling affect monocyte and macrophage functions and contribute to atherosclerosis. Recent Advances: Recent advances in redox biochemistry and biology as well as redox proteomic techniques have led to the identification of many new thiol redox-regulated proteins and pathways. In addition, major advances have been made in expanding the list of S-glutathionylated proteins and assessing the role that protein-S-glutathionylation and S-glutathionylation-regulating enzymes play in monocyte and macrophage functions, including monocyte transmigration, macrophage polarization, foam cell formation, and macrophage cell death.
Critical issues: Protein-S-glutathionylation/deglutathionylation in monocytes and macrophages has emerged as a new and important signaling paradigm, which provides a molecular basis for the well-established relationship between metabolic disorders, oxidative stress, and cardiovascular diseases.
Future directions: The identification of specific S-glutathionylated proteins as well as the mechanisms that control this post-translational protein modification in monocytes and macrophages will facilitate the development of new preventive and therapeutic strategies to combat atherosclerosis and other metabolic diseases. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 25, 816-835.
Keywords: S-glutathionylation; atherosclerosis; macrophage; redox signaling; thiols.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Protein S-Glutathionylation Mediates Macrophage Responses to Metabolic Cues from the Extracellular Environment.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2016 Nov 20;25(15):836-851. doi: 10.1089/ars.2015.6531. Epub 2016 May 17. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2016. PMID: 26984580 Free PMC article.
-
S-glutathionylation in monocyte and macrophage (dys)function.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Jul 24;14(8):15212-32. doi: 10.3390/ijms140815212. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23887649 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reactive oxygen species and thiol redox signaling in the macrophage biology of atherosclerosis.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2012 Dec 15;17(12):1785-95. doi: 10.1089/ars.2012.4638. Epub 2012 Jun 11. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2012. PMID: 22540532 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluating the Oxidative Stress in Renal Diseases: What Is the Role for S-Glutathionylation?Antioxid Redox Signal. 2016 Jul 20;25(3):147-64. doi: 10.1089/ars.2016.6656. Epub 2016 Apr 19. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2016. PMID: 26972776 Review.
-
Mechanisms of reversible protein glutathionylation in redox signaling and oxidative stress.Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2007 Aug;7(4):381-91. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2007.06.003. Epub 2007 Jul 26. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17662654 Review.
Cited by
-
Nrf2 signaling and inflammation are key events in physical plasma-spurred wound healing.Theranostics. 2019 Jan 30;9(4):1066-1084. doi: 10.7150/thno.29754. eCollection 2019. Theranostics. 2019. PMID: 30867816 Free PMC article.
-
ROS from Physical Plasmas: Redox Chemistry for Biomedical Therapy.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019 Oct 8;2019:9062098. doi: 10.1155/2019/9062098. eCollection 2019. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019. PMID: 31687089 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidized GAPDH transfers S-glutathionylation to a nuclear protein Sirtuin-1 leading to apoptosis.Free Radic Biol Med. 2021 Oct;174:73-83. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.07.037. Epub 2021 Jul 28. Free Radic Biol Med. 2021. PMID: 34332079 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble Carrier Transporters and Mitochondria in the Immunometabolic Regulation of Macrophages.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2022 May;36(13-15):906-919. doi: 10.1089/ars.2021.0181. Epub 2022 Jan 4. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2022. PMID: 34555943 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diverse Roles of Mitochondria in Immune Responses: Novel Insights Into Immuno-Metabolism.Front Immunol. 2018 Jul 12;9:1605. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01605. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30050539 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adachi T, Weisbrod RM, Pimentel DR, Ying J, Sharov VS, Schoneich C, and Cohen RA. S-Glutathiolation by peroxynitrite activates SERCA during arterial relaxation by nitric oxide. Nat Med 10: 1200–1207, 2004 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

