Combination of the novel histone deacetylase inhibitor YCW1 and radiation induces autophagic cell death through the downregulation of BNIP3 in triple-negative breast cancer cells in vitro and in an orthotopic mouse model
- PMID: 27286975
- PMCID: PMC4902929
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-016-0531-5
Combination of the novel histone deacetylase inhibitor YCW1 and radiation induces autophagic cell death through the downregulation of BNIP3 in triple-negative breast cancer cells in vitro and in an orthotopic mouse model
Abstract
Background: Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is the most aggressive and invasive of the breast cancer subtypes. TNBC is a challenging disease that lacks targets for treatment. Histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACi) are a group of targeted anticancer agents that enhance radiosensitivity. Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19 kDa protein-interacting protein 3 (BNIP3) is a member of the Bcl-2 subfamily. BNIP3 is not found in normal breast tissue but is up-regulated in breast cancer. In the present study, we investigated the anti-cancer effects of a newly developed HDACi, YCW1, combined with ionizing radiation (IR) in TNBC in vitro and in an orthotopic mouse model. Furthermore, we examined the relationship between autophagy and BNIP3.
Methods: Trypan blue exclusion was used to investigate the viability of 4 T1 (a mouse TNBC cell line) and MDA-MB-231 cells (a human TNBC cell line) following combined YCW1 and IR treatment. Flow cytometry was used to determine apoptosis and autophagy. The expression levels of BNIP3, endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress- and autophagic-related proteins were measured using western blot analysis. An orthotopic mouse model was used to investigate the in vivo effects of YCW1 and IR alone and in combination. Tumor volumes were monitored using a bioluminescence-based IVIS Imaging System 200.
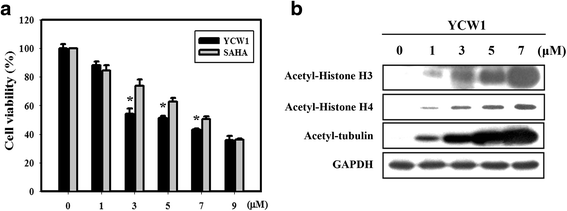
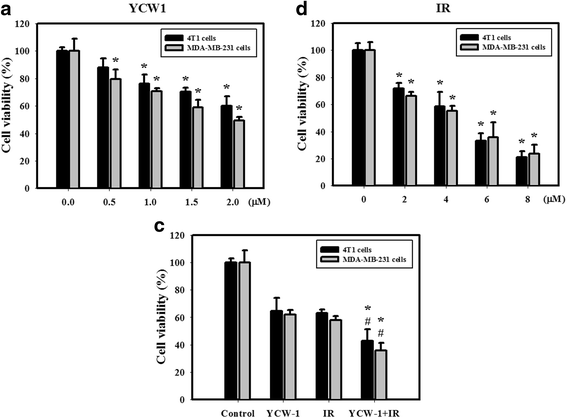
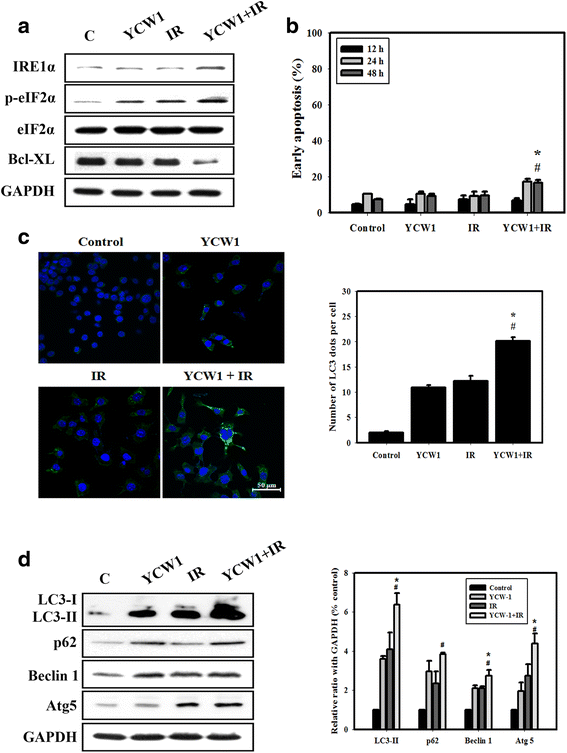
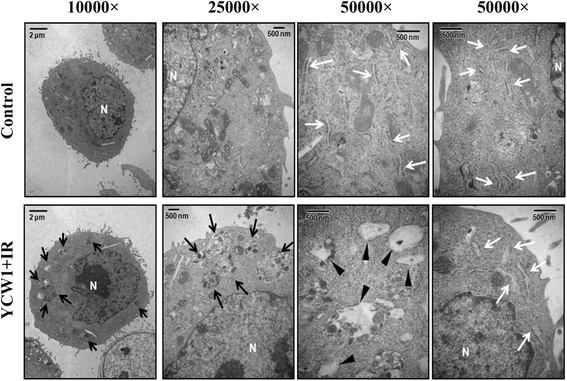
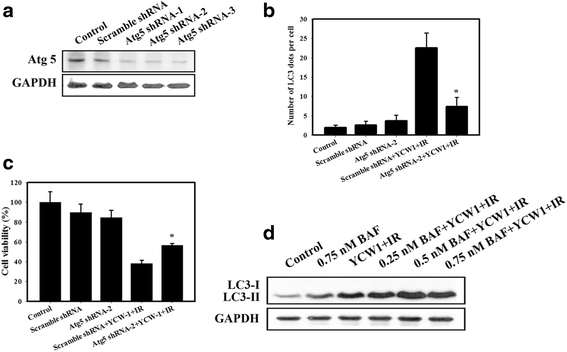
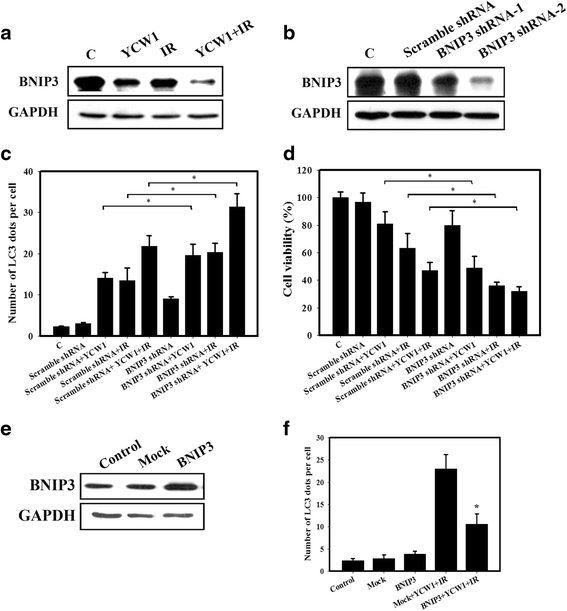
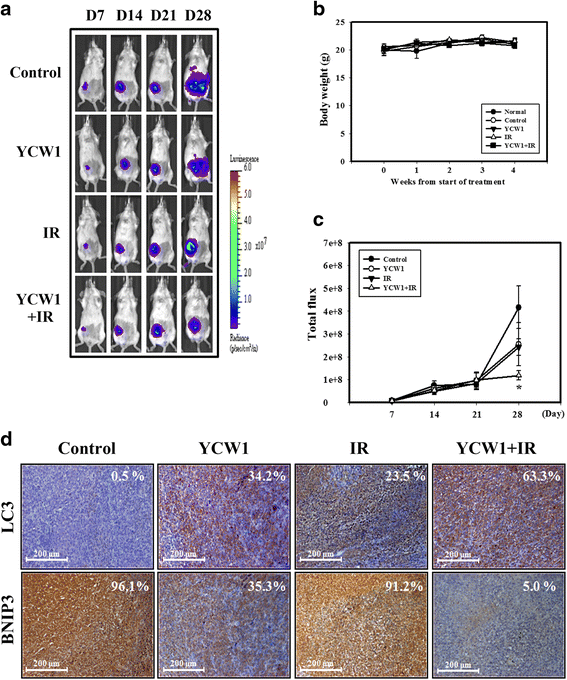
Results: We found that YCW1 significantly enhanced toxicity in 4 T1 cells compared with suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA), which was the first HDACi approved by the Food and Drug Administration for clinical use in cancer patients. The combined treatment of YCW1 and IR enhanced cytotoxicity by inducing ER stress and increasing autophagy induction. Additionally, the combined treatment caused autophagic flux and autophagic cell death. Furthermore, the expression level of BNIP3 was significantly decreased in cells following combined treatment. The downregulation of BNIP3 led to a significant increase in autophagy and cytotoxicity. The combined anti-tumor effects of YCW1 and IR were also observed in an orthotopic mouse model; combination therapy resulted in a significant increase in autophagy and decreased tumor tissue expression of BNIP3 in the tumor tissue.
Conclusions: These data support the possibility of using a combination of HDACi and IR in the treatment of TNBC. Moreover, BNIP3 may be a potential target protein for TNBC treatment.
Keywords: Autophagy; Histone deacetylase inhibitor; Radiation; Triple-negative breast cancer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Histone Deacetylases as New Therapeutic Targets in Triple-negative Breast Cancer: Progress and Promises.Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2017 Sep-Oct;14(5):299-313. doi: 10.21873/cgp.20041. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2017. PMID: 28870998 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid, an inhibitor of histone deacetylase, enhances radiosensitivity and suppresses lung metastasis in breast cancer in vitro and in vivo.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 10;8(10):e76340. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076340. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24130769 Free PMC article.
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitor, suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA), enhances anti-tumor effects of the poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor olaparib in triple-negative breast cancer cells.Breast Cancer Res. 2015 Mar 7;17:33. doi: 10.1186/s13058-015-0534-y. Breast Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 25888415 Free PMC article.
-
Co-targeting poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) and histone deacetylase (HDAC) in triple-negative breast cancer: Higher synergism in BRCA mutated cells.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Mar;99:543-551. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.01.045. Epub 2018 Feb 20. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29902865
-
New Insight into Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Therapy: The Potential Roles of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Autophagy Mechanisms.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2021;21(6):679-691. doi: 10.2174/1871520620666200619180716. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 32560613 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting Autophagy for Cancer Treatment and Tumor Chemosensitization.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Oct 19;11(10):1599. doi: 10.3390/cancers11101599. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31635099 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Autophagy as a Potential Therapy for Malignant Glioma.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020 Jul 19;13(7):156. doi: 10.3390/ph13070156. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32707662 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histone Deacetylases as New Therapeutic Targets in Triple-negative Breast Cancer: Progress and Promises.Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2017 Sep-Oct;14(5):299-313. doi: 10.21873/cgp.20041. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2017. PMID: 28870998 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cordycepin Enhances Radiosensitivity in Oral Squamous Carcinoma Cells by Inducing Autophagy and Apoptosis Through Cell Cycle Arrest.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Oct 28;20(21):5366. doi: 10.3390/ijms20215366. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31661901 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Regulation of Breast Cancer Stem Cells Contributing to Carcinogenesis and Therapeutic Implications.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 29;22(15):8113. doi: 10.3390/ijms22158113. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34360879 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chiu HW, Lin JH, Chen YA, Ho SY, Wang YJ. Combination treatment with arsenic trioxide and irradiation enhances cell-killing effects in human fibrosarcoma cells in vitro and in vivo through induction of both autophagy and apoptosis. Autophagy. 2010;6:353–65. doi: 10.4161/auto.6.3.11229. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

