Lessons from making the Structural Classification of Proteins (SCOP) and their implications for protein structure modelling
- PMID: 27284063
- PMCID: PMC5011417
- DOI: 10.1042/BST20160053
Lessons from making the Structural Classification of Proteins (SCOP) and their implications for protein structure modelling
Abstract
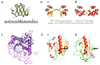
The Structural Classification of Proteins (SCOP) database has facilitated the development of many tools and algorithms and it has been successfully used in protein structure prediction and large-scale genome annotations. During the development of SCOP, numerous exceptions were found to topological rules, along with complex evolutionary scenarios and peculiarities in proteins including the ability to fold into alternative structures. This article reviews cases of structural variations observed for individual proteins and among groups of homologues, knowledge of which is essential for protein structure modelling.
Keywords: Structural Classification of Proteins (SCOP); homology modelling; metamorphic proteins; protein structure evolution.
© 2016 The Author(s). published by Portland Press Limited on behalf of the Biochemical Society.
Figures
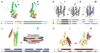

Similar articles
-
Automatic classification of protein structures using low-dimensional structure space mappings.BMC Bioinformatics. 2014;15 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):S1. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-15-S2-S1. Epub 2014 Jan 24. BMC Bioinformatics. 2014. PMID: 24564500 Free PMC article.
-
SCOP: a Structural Classification of Proteins database.Nucleic Acids Res. 1999 Jan 1;27(1):254-6. doi: 10.1093/nar/27.1.254. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999. PMID: 9847194 Free PMC article.
-
The value of protein structure classification information-Surveying the scientific literature.Proteins. 2015 Nov;83(11):2025-38. doi: 10.1002/prot.24915. Epub 2015 Sep 19. Proteins. 2015. PMID: 26313554 Free PMC article.
-
Large-scale prediction of protein structure and function from sequence.Curr Pharm Des. 2006;12(17):2067-86. doi: 10.2174/138161206777585238. Curr Pharm Des. 2006. PMID: 16796556 Review.
-
Progress in protein structure prediction.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1997 Jun;7(3):377-87. doi: 10.1016/s0959-440x(97)80055-3. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1997. PMID: 9204280 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification and molecular characterization of a metagenome-derived L-lysine decarboxylase gene from subtropical soil microorganisms.PLoS One. 2017 Sep 20;12(9):e0185060. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0185060. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28931053 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Site Discovery From Incomplete Training Data: A Case Study With Nucleic Acid-Binding Proteins.Front Genet. 2019 Aug 30;10:729. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00729. eCollection 2019. Front Genet. 2019. PMID: 31543893 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Murzin AG, Brenner SE, Hubbard T, Chothia C. SCOP: a structural classification of proteins database for the investigation of sequences and structures. J Mol Biol. 1995;247:536–540. - PubMed
-
- Lewis TE, Sillitoe I, Andreeva A, Blundell TL, Buchan DW, Chothia C, Cuff A, Dana JM, Filippis I, Gough J, et al. Genome3D: a UK collaborative project to annotate genomic sequences with predicted 3D structures based on SCOP and CATH domains. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;41:D499–507. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks1266. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

