Somatic mutations in disorders with disrupted brain connectivity
- PMID: 27282107
- PMCID: PMC4929695
- DOI: 10.1038/emm.2016.53
Somatic mutations in disorders with disrupted brain connectivity
Abstract
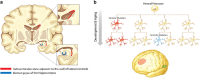
Mutations occur during cell division in all somatic lineages. Because neurogenesis persists throughout human life, somatic mutations in the brain arise during development and accumulate with the aging process. The human brain consists of 100 billion neurons that form an extraordinarily intricate network of connections to achieve higher level cognitive functions. Due to this network architecture, perturbed neuronal functions are rarely restricted to a focal area; instead, they are often spread via the neuronal network to affect other connected areas. Although somatic diversity is an evident feature of the brain, the extent to which somatic mutations affect the neuronal structure and function and their contribution to neurological disorders associated with disrupted brain connectivity remain largely unexplored. Notably, recent reports indicate that brain somatic mutations can indeed play a critical role that leads to the structural and functional abnormalities of the brain observed in several neurodevelopmental disorders. Here, I review the extent and significance of brain somatic mutations and provide my perspective regarding these mutations as potential molecular lesions underlying relatively common conditions with disrupted brain connectivity. Moreover, I discuss emerging technical platforms that will facilitate the detection of low-frequency somatic mutations and validate the biological functions of the identified mutations in the context of brain connectivity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Brain Somatic Mutations in Epileptic Disorders.Mol Cells. 2018 Oct 31;41(10):881-888. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2018.0247. Epub 2018 Oct 10. Mol Cells. 2018. PMID: 30352490 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Networks of anatomical covariance.Neuroimage. 2013 Oct 15;80:489-504. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.05.054. Epub 2013 May 25. Neuroimage. 2013. PMID: 23711536 Review.
-
Intrinsic gray-matter connectivity of the brain in adults with autism spectrum disorder.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Aug 6;110(32):13222-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1221880110. Epub 2013 Jul 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23878213 Free PMC article.
-
Single-Gene Determinants of Epilepsy Comorbidity.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2015 Nov 2;5(11):a022756. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a022756. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2015. PMID: 26525453 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A cross-disorder connectome landscape of brain dysconnectivity.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2019 Jul;20(7):435-446. doi: 10.1038/s41583-019-0177-6. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31127193 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Developing Gene-Based Personalised Interventions in Autism Spectrum Disorders.Genes (Basel). 2022 Jun 2;13(6):1004. doi: 10.3390/genes13061004. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35741766 Free PMC article.
-
Somatic mutations in neurons during aging and neurodegeneration.Acta Neuropathol. 2018 Jun;135(6):811-826. doi: 10.1007/s00401-018-1850-y. Epub 2018 Apr 28. Acta Neuropathol. 2018. PMID: 29705908 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dissecting single-cell genomes through the clonal organoid technique.Exp Mol Med. 2021 Oct;53(10):1503-1511. doi: 10.1038/s12276-021-00680-1. Epub 2021 Oct 18. Exp Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34663940 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brain somatic mutations observed in Alzheimer's disease associated with aging and dysregulation of tau phosphorylation.Nat Commun. 2019 Jul 12;10(1):3090. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-11000-7. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31300647 Free PMC article.
-
Robust elimination of genome-damaged cells safeguards against brain somatic aneuploidy following Knl1 deletion.Nat Commun. 2019 Jun 13;10(1):2588. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-10411-w. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31197172 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lupski JR. Genome mosaicism—one human, multiple genomes. Science 2013; 341: 358–359. - PubMed
-
- Biesecker LG, Spinner NB. A genomic view of mosaicism and human disease. Nat Rev Genet 2013; 14: 307–320. - PubMed
-
- Insel TR. Brain somatic mutations: the dark matter of psychiatric genetics? Mol Psychiatry 2014; 19: 156–158. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

