Nonclassical MHC Ib-restricted CD8+ T Cells Recognize Mycobacterium tuberculosis-Derived Protein Antigens and Contribute to Protection Against Infection
- PMID: 27272249
- PMCID: PMC4896622
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005688
Nonclassical MHC Ib-restricted CD8+ T Cells Recognize Mycobacterium tuberculosis-Derived Protein Antigens and Contribute to Protection Against Infection
Abstract
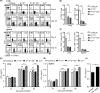
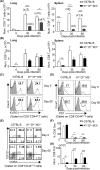
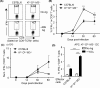
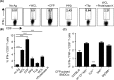
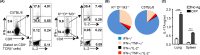
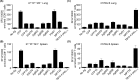
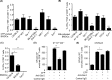
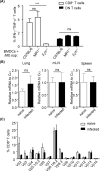
MHC Ib-restricted CD8+ T cells have been implicated in host defense against Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) infection. However, the relative contribution of various MHC Ib-restricted T cell populations to anti-mycobacterial immunity remains elusive. In this study, we used mice that lack MHC Ia (Kb-/-Db-/-), MHC Ia/H2-M3 (Kb-/-Db-/-M3-/-), or β2m (β2m-/-) to study the role of M3-restricted and other MHC Ib-restricted T cells in immunity against Mtb. Unlike their dominant role in Listeria infection, we found that M3-restricted CD8+ T cells only represented a small proportion of the CD8+ T cells responding to Mtb infection. Non-M3, MHC Ib-restricted CD8+ T cells expanded preferentially in the lungs of Mtb-infected Kb-/-Db-/-M3-/- mice, exhibited polyfunctional capacities and conferred protection against Mtb. These MHC Ib-restricted CD8+ T cells recognized several Mtb-derived protein antigens at a higher frequency than MHC Ia-restricted CD8+ T cells. The presentation of Mtb antigens to MHC Ib-restricted CD8+ T cells was mostly β2m-dependent but TAP-independent. Interestingly, a large proportion of Mtb-specific MHC Ib-restricted CD8+ T cells in Kb-/-Db-/-M3-/- mice were Qa-2-restricted while no considerable numbers of MR1 or CD1-restricted Mtb-specific CD8+ T cells were detected. Our findings indicate that nonclassical CD8+ T cells other than the known M3, CD1, and MR1-restricted CD8+ T cells contribute to host immune responses against Mtb infection. Targeting these MHC Ib-restricted CD8+ T cells would facilitate the design of better Mtb vaccines with broader coverage across MHC haplotypes due to the limited polymorphism of MHC class Ib molecules.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MHC Ib molecule Qa-1 presents Mycobacterium tuberculosis peptide antigens to CD8+ T cells and contributes to protection against infection.PLoS Pathog. 2017 May 5;13(5):e1006384. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006384. eCollection 2017 May. PLoS Pathog. 2017. PMID: 28475642 Free PMC article.
-
Role of MHC class Ib molecule, H2-M3 in host immunity against tuberculosis.Vaccine. 2013 Aug 20;31(37):3818-25. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.04.005. Epub 2013 Apr 28. Vaccine. 2013. PMID: 23628242 Review.
-
Nonconventional CD8+ T cell responses to Listeria infection in mice lacking MHC class Ia and H2-M3.J Immunol. 2011 Jan 1;186(1):489-98. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1002639. Epub 2010 Nov 22. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21098224 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of M3-restricted cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses by N-formylated peptides derived from Mycobacterium tuberculosis.J Exp Med. 2001 May 21;193(10):1213-20. doi: 10.1084/jem.193.10.1213. J Exp Med. 2001. PMID: 11369792 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Signatures of Human CD4 and CD8 T Cell Responses to Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Front Immunol. 2014 Apr 22;5:180. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00180. eCollection 2014. Front Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24795723 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
MHC Ib molecule Qa-1 presents Mycobacterium tuberculosis peptide antigens to CD8+ T cells and contributes to protection against infection.PLoS Pathog. 2017 May 5;13(5):e1006384. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006384. eCollection 2017 May. PLoS Pathog. 2017. PMID: 28475642 Free PMC article.
-
Mycobacterium tuberculosis Biofilms: Immune Responses, Role in TB Pathology, and Potential Treatment.Immunotargets Ther. 2024 Jul 3;13:335-342. doi: 10.2147/ITT.S455744. eCollection 2024. Immunotargets Ther. 2024. PMID: 38974843 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Promising Listeria-Vectored Vaccine Induces Th1-Type Immune Responses and Confers Protection Against Tuberculosis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 Sep 28;7:407. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00407. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 29034213 Free PMC article.
-
Murine cytomegalovirus downregulates ERAAP and induces an unconventional T cell response to self.Cell Rep. 2023 Apr 25;42(4):112317. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.112317. Epub 2023 Mar 29. Cell Rep. 2023. PMID: 36995940 Free PMC article.
-
An Anti-Tumor Vaccine Against Marek's Disease Virus Induces Differential Activation and Memory Response of γδ T Cells and CD8 T Cells in Chickens.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 15;12:645426. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.645426. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33659011 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO. Global Tuberculosis Report 2015. 2015 ed. Geneva: WHO Press; 2015.
-
- Colditz GA, Brewer TF, Berkey CS, Wilson ME, Burdick E, Fineberg HV, et al. Efficacy of BCG vaccine in the prevention of tuberculosis. Meta-analysis of the published literature. JAMA: the journal of the American Medical Association. 1994;271(9):698–702. . - PubMed
-
- Caruso AM, Serbina N, Klein E, Triebold K, Bloom BR, Flynn JL. Mice deficient in CD4 T cells have only transiently diminished levels of IFN-gamma, yet succumb to tuberculosis. J Immunol. 1999;162(9):5407–16. . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

