Preventive Effects of Rhodiola rosea L. on Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Rats
- PMID: 27271612
- PMCID: PMC4926413
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms17060879
Preventive Effects of Rhodiola rosea L. on Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Rats
Abstract
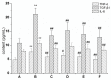
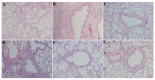
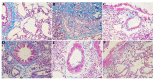
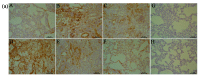
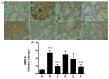
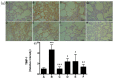
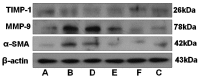
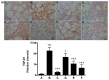
Rhodiola rosea L. (RRL) possesses a wide range of pharmacological properties, including lung-protective activity, and has been utilized in folk medicine for several 100 years. However, the lung-protective mechanism remains unclear. This study investigated the possible lung-protective activity mechanism of RRL in a pulmonary fibrosis (PF) rat model. Lung fibrotic injury was induced in Sprague-Dawley rats by single intratracheal instillation of saline containing bleomycin (BLM; 5 mg/kg). The rats were administered 125, 250, or 500 mg/kg of a 95% ethanol extract of RRL for 28 days. The animals were killed to detect changes in body weight, serum levels of glutathione (GSH) and total superoxide dismutase (T-SOD), as well as lung tissue hydroxyproline (HYP) content. Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1), and interleukin 6 (IL-6) levels were measured in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Hematoxylin and eosin, Masson's trichrome, and immunohistochemical staining were performed to observe the histopathological changes in lung tissues. Additionally, target-related proteins were measured by Western blotting. RRL alleviated the loss of body weight induced by instilling BLM in PF rats, particularly at the 500 mg/kg per day dose. RRL reduced HYP (p < 0.01) and increased GSH and T-SOD contents. BALF levels of TNF-α, TGF-β1, and IL-6 decreased significantly in the RRL-treated groups. Expression levels of matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) and α-smooth muscle actin decreased significantly in a dose-dependent manner in response to RRL. Moreover, the levels of TGF-β1 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 in lung tissues also decreased in the RRL-treated groups. RRL alleviated BLM-induced PF in rats. Our results reveal that the protective effects of RRL against fibrotic lung injury in rats are correlated with its anti-inflammatory, antioxidative, and anti-fibrotic properties. MMP-9 may play important roles in BLM-induced PF.
Keywords: MMP-9; Rhodiola rosea L.; TGF-β1; bleomycin; pulmonary fibrosis.
Figures
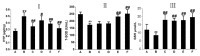

Similar articles
-
Preventive effects of Ecliptae Herba extract and its component, ecliptasaponin A, on bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice.J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Dec 4;175:172-80. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.08.034. Epub 2015 Sep 16. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26385580
-
[Effects of andrographolide on the concentration of cytokines in BALF and the expressions of type I and III collagen mRNA in lung tissue in bleomycin-induced rat pulmonary fibrosis].Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2011 Jul;27(7):725-9. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2011. PMID: 21722520 Chinese.
-
Zingerone ameliorates oxidative stress and inflammation in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis: modulation of the expression of TGF-β1 and iNOS.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2020 Sep;393(9):1659-1670. doi: 10.1007/s00210-020-01881-7. Epub 2020 May 6. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32377772
-
Effects of plant extracts and bioactive compounds on attenuation of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Nov;107:1454-1465. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.08.111. Epub 2018 Sep 3. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 30257362 Review.
-
Anti-inflammatory effects of Rhodiola rosea L.: A review.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Jan;121:109552. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109552. Epub 2019 Nov 9. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 31715370 Review.
Cited by
-
Traditional Tibetan medicine: therapeutic potential in lung diseases.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Mar 18;15:1365911. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1365911. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38567353 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural products as home-based prophylactic and symptom management agents in the setting of COVID-19.Phytother Res. 2020 Dec;34(12):3148-3167. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6794. Epub 2020 Aug 17. Phytother Res. 2020. PMID: 32881214 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Promising Natural Medicines for the Treatment of High-Altitude Illness.High Alt Med Biol. 2023 Sep;24(3):175-185. doi: 10.1089/ham.2022.0139. Epub 2023 Jul 27. High Alt Med Biol. 2023. PMID: 37504973 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rosavin Ameliorates Hepatic Inflammation and Fibrosis in the NASH Rat Model via Targeting Hepatic Cell Death.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 5;23(17):10148. doi: 10.3390/ijms231710148. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36077546 Free PMC article.
-
Rhodiola rosea L. Attenuates Cigarette Smoke and Lipopolysaccharide-Induced COPD in Rats via Inflammation Inhibition and Antioxidant and Antifibrosis Pathways.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Mar 2;2021:6103158. doi: 10.1155/2021/6103158. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 33747104 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Calabrese F., Kipar A., Lunardi F., Balestro E., Perissinotto E., Rossi E., Nannini N., Marulli G., Stewart J.P., Rea F. Herpes virus infection is associated with vascular remodeling and pulmonary hypertension in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:879. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055715. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Smith R.E., Strieter R.M., Phan S.H., Lukacs N., Kunkel S.L. TNF and IL-6 mediate MIP-1α expression in bleomycin-induced lung injury. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1998;64:528–536. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

