Mitochondrial pyruvate carrier function and cancer metabolism
- PMID: 27269731
- PMCID: PMC5017534
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gde.2016.05.003
Mitochondrial pyruvate carrier function and cancer metabolism
Abstract
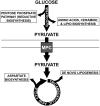
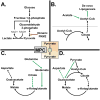
Metabolic reprogramming in cancer supports the increased biosynthesis required for unchecked proliferation. Increased glucose utilization is a defining feature of many cancers that is accompanied by altered pyruvate partitioning and mitochondrial metabolism. Cancer cells also require mitochondrial tricarboxylic acid cycle activity and electron transport chain function for biosynthetic competency and proliferation. Recent evidence demonstrates that mitochondrial pyruvate carrier (MPC) function is abnormal in some cancers and that increasing MPC activity may decrease cancer proliferation. Here we examine recent findings on MPC function and cancer metabolism. Special emphasis is placed on the compartmentalization of pyruvate metabolism and the alternative routes of metabolism that maintain the cellular biosynthetic pools required for unrestrained proliferation in cancer.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Multifaceted Pyruvate Metabolism: Role of the Mitochondrial Pyruvate Carrier.Biomolecules. 2020 Jul 17;10(7):1068. doi: 10.3390/biom10071068. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32708919 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondrial pyruvate import and its effects on homeostasis.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2015 Apr;33:35-41. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2014.10.008. Epub 2014 Nov 15. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25463844 Review.
-
Mitochondrial pyruvate carrier function determines cell stemness and metabolic reprogramming in cancer cells.Oncotarget. 2017 Jul 11;8(28):46363-46380. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.18199. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28624784 Free PMC article.
-
Embryonic Lethality of Mitochondrial Pyruvate Carrier 1 Deficient Mouse Can Be Rescued by a Ketogenic Diet.PLoS Genet. 2016 May 13;12(5):e1006056. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006056. eCollection 2016 May. PLoS Genet. 2016. PMID: 27176894 Free PMC article.
-
Control of intestinal stem cell function and proliferation by mitochondrial pyruvate metabolism.Nat Cell Biol. 2017 Sep;19(9):1027-1036. doi: 10.1038/ncb3593. Epub 2017 Aug 14. Nat Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28812582 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The mitochondrial carrier pathway transports non-canonical substrates with an odd number of transmembrane segments.BMC Biol. 2020 Jan 6;18(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s12915-019-0733-6. BMC Biol. 2020. PMID: 31907035 Free PMC article.
-
NMR and Patch-Clamp Characterization of Yeast Mitochondrial Pyruvate Carrier Complexes.Biomolecules. 2023 Apr 22;13(5):719. doi: 10.3390/biom13050719. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37238591 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial pyruvate carrier 1: a novel prognostic biomarker that predicts favourable patient survival in cancer.Cancer Cell Int. 2021 May 31;21(1):288. doi: 10.1186/s12935-021-01996-8. Cancer Cell Int. 2021. PMID: 34059057 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Experimental Investigations on the Structure of Yeast Mitochondrial Pyruvate Carriers.Membranes (Basel). 2022 Sep 22;12(10):916. doi: 10.3390/membranes12100916. Membranes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36295675 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Mitochondrial Transporters on Metabolic Rewiring of Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: A Comprehensive Review.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jan 8;15(2):411. doi: 10.3390/cancers15020411. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36672360 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Han YH, Kim SH, Kim SZ, Park WH. Antimycin A as a mitochondrial electron transport inhibitor prevents the growth of human lung cancer A549 cells. Oncol Rep. 2008;20:689–693. - PubMed
-
- Tan AS, Baty JW, Dong LF, Bezawork-Geleta A, Endaya B, Goodwin J, Bajzikova M, Kovarova J, Peterka M, Yan B, et al. Mitochondrial genome acquisition restores respiratory function and tumorigenic potential of cancer cells without mitochondrial DNA. Cell Metab. 2015;21:81–94. This investigation used mtDNA depleted cells for xenograft implantation and found tumors had delayed growth. Cells isolated from primary lung metastatic sites formed tumors without lag when re-injected subcutaneosly. It was found primary tumors contained host mtDNA implying horizontal mtDNA or mitochondrial transfer from host to tumor. This resulted in the recovery of respiration and the complete assembly of the respirasome within the tumor. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

