A case report of SPG11 mutations in a Chinese ARHSP-TCC family
- PMID: 27256065
- PMCID: PMC4891852
- DOI: 10.1186/s12883-016-0604-5
A case report of SPG11 mutations in a Chinese ARHSP-TCC family
Abstract
Background: Autosomal recessive hereditary spastic paraplegia (ARHSP) with thin corpus callosum (TCC) is a complicated form of hereditary spastic paraplegia, characterized by progressive spastic paraplegia, weakness of the lower extremities and is usually accompanied by mental retardation. Mutations in the Spastic Paraplegia gene 11 (SPG11) account for a large proportion of ARHSP-TCC cases worldwide.
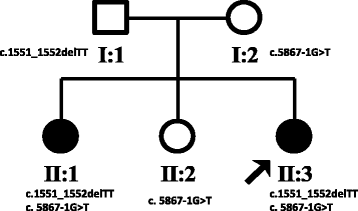
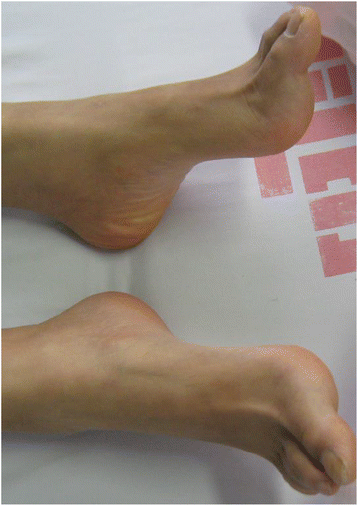
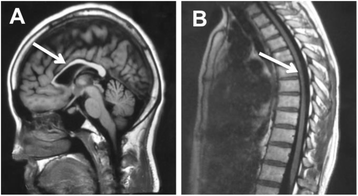
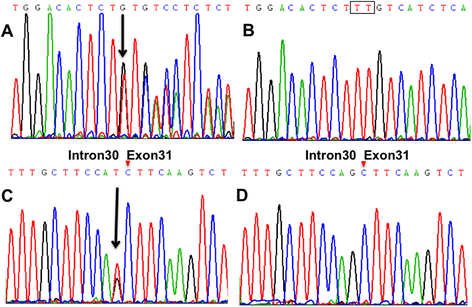
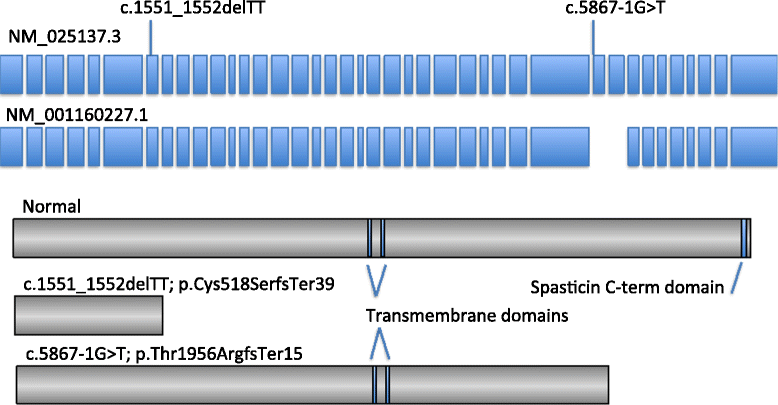
Case presentation: We describe a Chinese family with ARHSP-TCC. Two daughters of this family presented with a spastic gait and cognitive impairment. Brain imaging of the index patient revealed a thin corpus callosum. We performed detailed physical and auxiliary examinations and were able to exclude acquired causes of spastic paraplegia. To determine the causative mutation, we took a candidate gene approach and screened the coding sequence and some flanking intronic sequence of SPG11 by direct Sanger sequencing. We identified two novel compound heterozygous mutations in SPG11 in affected individuals (c.1551_1552delTT, p.Cys518SerfsTer39 and c.5867-1G > T (IVS30-1G > T), p.Thr1956ArgfsTer15). Bioinformatic analysis predicts that these mutations would lead to a loss of protein function due to the truncation of the SPG11 protein.
Conclusions: The results of this case report indicate a broader approach to include screening for SPG11 mutations in ARHSP-TCC patients. Our findings enrich the phenotypic spectrum of SPG11 mutations.
Keywords: Autosomal recessive hereditary spastic paraplegia with thin corpus callosum (ARHSP-TCC); Gene mutation; Heterozygous mutations; SPG11.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Novel mutations c.[5121_5122insAG]+[6859C>T] of the SPG11 gene associated with cerebellum hypometabolism in a Chinese case of hereditary spastic paraplegia with thin corpus callosum.Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2014 Feb;20(2):256-9. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2013.11.004. Epub 2013 Nov 14. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2014. PMID: 24315199
-
Novel mutations of the SPG11 gene in hereditary spastic paraplegia with thin corpus callosum.J Neurol Sci. 2008 Dec 15;275(1-2):92-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2008.07.038. Epub 2008 Oct 2. J Neurol Sci. 2008. PMID: 18835492
-
Exome sequencing identifies novel compound heterozygous mutations in SPG11 that cause autosomal recessive hereditary spastic paraplegia.J Neurol Sci. 2013 Dec 15;335(1-2):112-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2013.09.004. Epub 2013 Sep 10. J Neurol Sci. 2013. PMID: 24090761
-
[Recent advances of study on hereditary spastic paraplegia type 11].Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 2009 Dec;26(6):670-3. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1003-9406.2009.06.013. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 2009. PMID: 19953491 Review. Chinese.
-
Janus-faced spatacsin (SPG11): involvement in neurodevelopment and multisystem neurodegeneration.Brain. 2020 Aug 1;143(8):2369-2379. doi: 10.1093/brain/awaa099. Brain. 2020. PMID: 32355960 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Case report: Novel mutations in the SPG11 gene in a case of autosomal recessive hereditary spastic paraplegia with a thin corpus callosum.Front Integr Neurosci. 2023 Mar 24;17:1117617. doi: 10.3389/fnint.2023.1117617. eCollection 2023. Front Integr Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37035454 Free PMC article.
-
Mild cognitive impairment in novel SPG11 mutation-related sporadic hereditary spastic paraplegia with thin corpus callosum: case series.BMC Neurol. 2021 Jan 11;21(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s12883-020-02040-4. BMC Neurol. 2021. PMID: 33430805 Free PMC article.
-
Research on clinical and molecular genetics of hereditary spastic paraplegia 11 patients in China.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022 Dec 28;47(12):1729-1732. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2022.190651. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022. PMID: 36748384 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

