Functions of PARylation in DNA Damage Repair Pathways
- PMID: 27240471
- PMCID: PMC4936651
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gpb.2016.05.001
Functions of PARylation in DNA Damage Repair Pathways
Abstract
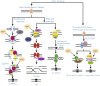
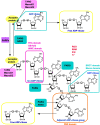
Protein poly ADP-ribosylation (PARylation) is a widespread post-translational modification at DNA lesions, which is catalyzed by poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases (PARPs). This modification regulates a number of biological processes including chromatin reorganization, DNA damage response (DDR), transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, and mitosis. PARP1, functioning as a DNA damage sensor, can be activated by DNA lesions, forming PAR chains that serve as a docking platform for DNA repair factors with high biochemical complexity. Here, we highlight molecular insights into PARylation recognition, the expanding role of PARylation in DDR pathways, and the functional interaction between PARylation and ubiquitination, which will offer us a better understanding of the biological roles of this unique post-translational modification.
Keywords: DNA damage response; PAR-binding modules; PARPs; Poly ADP-ribosylation; Ubiquitination.
Copyright © 2016 The Authors. Production and hosting by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Poly(ADP-ribose): PARadigms and PARadoxes.Mol Aspects Med. 2013 Dec;34(6):1046-65. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2012.12.010. Epub 2013 Jan 2. Mol Aspects Med. 2013. PMID: 23290998 Review.
-
Poly-ADP ribosylation in DNA damage response and cancer therapy.Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2019 Apr-Jun;780:82-91. doi: 10.1016/j.mrrev.2017.09.004. Epub 2017 Sep 20. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2019. PMID: 31395352 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of poly ADP-ribosylation in the first wave of DNA damage response.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Aug 21;45(14):8129-8141. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx565. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 28854736 Free PMC article.
-
Poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation in regulation of chromatin structure and the DNA damage response.Chromosoma. 2014 Mar;123(1-2):79-90. doi: 10.1007/s00412-013-0442-9. Epub 2013 Oct 27. Chromosoma. 2014. PMID: 24162931 Review.
-
Functional aspects of PARylation in induced and programmed DNA repair processes: preserving genome integrity and modulating physiological events.Mol Aspects Med. 2013 Dec;34(6):1138-52. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2013.02.001. Epub 2013 Feb 26. Mol Aspects Med. 2013. PMID: 23454615 Review.
Cited by
-
ADP-ribose hydrolases: biological functions and potential therapeutic targets.Expert Rev Mol Med. 2024 Oct 8;26:e21. doi: 10.1017/erm.2024.17. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39375922 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SPARCLE, a p53-induced lncRNA, controls apoptosis after genotoxic stress by promoting PARP-1 cleavage.Mol Cell. 2022 Feb 17;82(4):785-802.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2022.01.001. Epub 2022 Jan 31. Mol Cell. 2022. PMID: 35104452 Free PMC article.
-
ADP-Ribosylation and Antiviral Resistance in Plants.Viruses. 2023 Jan 14;15(1):241. doi: 10.3390/v15010241. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 36680280 Free PMC article.
-
Sensitization of colorectal cancer to irinotecan therapy by PARP inhibitor rucaparib.Invest New Drugs. 2019 Oct;37(5):948-960. doi: 10.1007/s10637-018-00717-9. Epub 2019 Jan 5. Invest New Drugs. 2019. PMID: 30612311
-
LCS-1 inhibition of superoxide dismutase 1 induces ROS-dependent death of glioma cells and degradates PARP and BRCA1.Front Oncol. 2022 Aug 1;12:937444. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.937444. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35978820 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lindahl T., Barnes D.E. Repair of endogenous DNA damage. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2000;65:127–133. - PubMed
-
- Hoeijmakers J.H. DNA damage, aging, and cancer. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:1475–1485. - PubMed
-
- Gibson B.A., Kraus W.L. New insights into the molecular and cellular functions of poly(ADP-ribose) and PARPs. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012;13:411–424. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

