Transcriptomic analysis reveals distinct resistant response by physcion and chrysophanol against cucumber powdery mildew
- PMID: 27231648
- PMCID: PMC4878370
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.1991
Transcriptomic analysis reveals distinct resistant response by physcion and chrysophanol against cucumber powdery mildew
Abstract
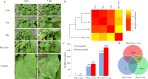
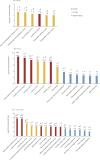
Physcion and chrysophanol induce defense responses against powdery mildew in cucumbers. The combination of these two compounds has synergistic interaction against the disease. We performed RNA-seq on cucumber leaf samples treated with physcion and chrysophanol alone and with their combination. We generated 17.6 Gb of high-quality sequencing data (∼2 Gb per sample) and catalogued the expressions profiles of 12,293 annotated cucumber genes in each sample. We identified numerous differentially expressed genes that exhibited distinct expression patterns among the three treatments. The gene expression patterns of the Chr and Phy treatments were more similar to each other than to the Phy × Chr treatment. The Phy × Chr treatment induced the highest number of differentially expressed genes. This dramatic transcriptional change after Phy × Chr treatment leaves reflects that physcion combined with chrysophanol treatment was most closely associated with induction of disease resistance. The analysis showed that the combination treatment caused expression changes of numerous defense-related genes. These genes have known or potential roles in structural, chemical and signaling defense responses and were enriched in functional gene categories potentially responsible for cucumber resistance. These results clearly demonstrated that disease resistance in cucumber leaves was significantly influenced by the combined physcion and chrysophanol treatment. Thus, physcion and chrysophanol are appealing candidates for further investigation of the gene expression and associated regulatory mechanisms related to the defense response.
Keywords: Cucumber; Gene expression; RNA-seq; Transcriptomic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Synergistic interaction of physcion and chrysophanol on plant powdery mildew.Pest Manag Sci. 2007 May;63(5):511-5. doi: 10.1002/ps.1362. Pest Manag Sci. 2007. PMID: 17397111
-
Direct Effects of Physcion, Chrysophanol, Emodin, and Pachybasin on Germination and Appressorium Formation of the Barley ( Hordeum vulgare L.) Powdery Mildew Fungus Blumeria graminis f. sp. hordei (DC.) Speer.J Agric Food Chem. 2018 Apr 4;66(13):3393-3401. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.7b05977. Epub 2018 Mar 22. J Agric Food Chem. 2018. PMID: 29554805
-
Transcriptome profiling analysis reveals distinct resistance response of cucumber leaves infected with powdery mildew.Plant Biol (Stuttg). 2021 Mar;23(2):327-340. doi: 10.1111/plb.13213. Epub 2020 Dec 26. Plant Biol (Stuttg). 2021. PMID: 33176053
-
[Cucumber downy mildew and the mechanisms of host resistance: a review].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2022 May 25;38(5):1724-1737. doi: 10.13345/j.cjb.210513. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2022. PMID: 35611725 Review. Chinese.
-
Research Advances in Genetic Mechanisms of Major Cucumber Diseases Resistance.Front Plant Sci. 2022 May 19;13:862486. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.862486. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35665153 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptome and miRNA analyses of the response to Corynespora cassiicola in cucumber.Sci Rep. 2018 May 17;8(1):7798. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-26080-6. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29773833 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the MYB transcription factor in moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis).PeerJ. 2019 Jan 11;6:e6242. doi: 10.7717/peerj.6242. eCollection 2019. PeerJ. 2019. PMID: 30648007 Free PMC article.
-
Gene co-expression network analysis reveals key pathways and hub genes in Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa L.) during vernalization.BMC Genomics. 2021 Apr 6;22(1):236. doi: 10.1186/s12864-021-07510-8. BMC Genomics. 2021. PMID: 33823810 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assembly and Annotation of a Draft Genome of the Medicinal Plant Polygonum cuspidatum.Front Plant Sci. 2019 Oct 18;10:1274. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.01274. eCollection 2019. Front Plant Sci. 2019. PMID: 31681373 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of powdery mildew resistant and susceptible cultivated cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) varieties to reveal the metabolic responses to Sphaerotheca fuliginea infection.BMC Plant Biol. 2021 Jan 7;21(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s12870-020-02797-3. BMC Plant Biol. 2021. PMID: 33413112 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aarts N, Metz M, Holub E, Staskawicz BJ, Daniels MJ, Parker JE. Different requirements for EDS1 and NDR1 by disease resistance genes define at least two R gene-mediated signaling pathways in Arabidopsis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1998;95:10306–10311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.17.10306. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barnard DL, Huffman JH, Morris JLB, Wood SG, Hughes BG, Sidwell RW. Evaluation of the antiviral activity of anthraquinones, anthrones and anthraquinone derivatives against human cytomegalovirus. Antiviral Research. 1992;17:63–77. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

