Engineering galectin-glycan interactions for immunotherapy and immunomodulation
- PMID: 27229902
- PMCID: PMC4950369
- DOI: 10.1177/1535370216650055
Engineering galectin-glycan interactions for immunotherapy and immunomodulation
Abstract
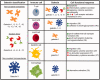
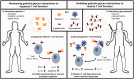
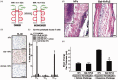
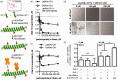
Galectins, a 15-member family of soluble carbohydrate-binding proteins, are receiving increasing interest as therapeutic targets for immunotherapy and immunomodulation due to their role as extracellular signals that regulate innate and adaptive immune cell phenotype and function. However, different galectins can have redundant, synergistic, or antagonistic signaling activity in normal immunological responses, such as resolution of inflammation and induction of antigen-specific tolerance. In addition, certain galectins can be hijacked to promote progression of immunopathologies, such as tumor immune privilege, metastasis, and viral infection, while others can inhibit these processes. Thus, eliciting a desired immunological outcome will likely necessitate therapeutics that can precisely enhance or inhibit particular galectin-glycan interactions. Multivalency is an important determinant of the affinity and specificity of natural galectin-glycan interactions, and is emerging as a key design element for therapeutics that can effectively manipulate galectin bioactivity. This minireview surveys current molecular and biomaterial engineering approaches to create therapeutics that can stabilize galectin multivalency or recapitulate natural glycan multivalency (i.e. "the glycocluster effect"). In particular, we highlight examples of using natural and engineered multivalent galectins for immunosuppression and immune tolerance, with a particular emphasis on treating autoimmune diseases or avoiding transplant rejection. In addition, we present examples of multivalent inhibitors of galectin-glycan interactions to maintain or restore T-cell function, with a particular emphasis on promoting antitumor immunity. Finally, we discuss emerging opportunities to further engineer galectin-glycan interactions for immunotherapy and immunomodulation.
Keywords: Biomaterial; bionanoscience; engineering; glycan; immunobiology; immunology.
© 2016 by the Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chemokines modulate glycan binding and the immunoregulatory activity of galectins.Commun Biol. 2021 Dec 20;4(1):1415. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-02922-4. Commun Biol. 2021. PMID: 34931005 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic potential of targeting galectins - A biomaterials-focused perspective.Biomaterials. 2022 Jul;286:121585. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2022.121585. Epub 2022 May 18. Biomaterials. 2022. PMID: 35623267 Review.
-
Decoding Strategies to Evade Immunoregulators Galectin-1, -3, and -9 and Their Ligands as Novel Therapeutics in Cancer Immunotherapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 8;23(24):15554. doi: 10.3390/ijms232415554. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36555198 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Galectin binding to cells and glycoproteins with genetically modified glycosylation reveals galectin-glycan specificities in a natural context.J Biol Chem. 2018 Dec 28;293(52):20249-20262. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.004636. Epub 2018 Nov 1. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 30385505 Free PMC article.
-
Coupling pathogen recognition to innate immunity through glycan-dependent mechanisms.Int Immunopharmacol. 2011 Oct;11(10):1457-63. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2011.05.002. Epub 2011 May 18. Int Immunopharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21600310 Review.
Cited by
-
Placental Galectins in Cancer: Why We Should Pay More Attention.Cells. 2023 Jan 29;12(3):437. doi: 10.3390/cells12030437. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36766779 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypoxia Controls the Glycome Signature and Galectin-8-Ligand Axis to Promote Protumorigenic Properties of Metastatic Melanoma.J Invest Dermatol. 2023 Mar;143(3):456-469.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2022.07.033. Epub 2022 Sep 27. J Invest Dermatol. 2023. PMID: 36174713 Free PMC article.
-
Physical tuning of galectin-3 signaling.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 May 11;118(19):e2024117118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2024117118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 33941700 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of a novel galectin in Sarcoptes scabiei and its role in regulating macrophage functions.Front Microbiol. 2023 Aug 24;14:1251475. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1251475. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37692380 Free PMC article.
-
Site-Specific Cross-Linking of Galectin-1 Homodimers via Poly(ethylene glycol) Bismaleimide.Cell Mol Bioeng. 2021 Jun 4;14(5):523-534. doi: 10.1007/s12195-021-00681-0. eCollection 2021 Oct. Cell Mol Bioeng. 2021. PMID: 34777608 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sharon N, Lis H. History of lectins: from hemagglutinins to biological recognition molecules. Glycobiology 2004; 14: 53R–62R. - PubMed
-
- Yamamoto K. Intracellular lectins involved in folding and transport in the endoplasmic reticulum. Biol Pharm Bull 2009; 32: 767–73. - PubMed
-
- Helenius A, Aebi M. Intracellular functions of N-linked glycans. Science 2001; 291: 2364–9. - PubMed
-
- Kaltner H, Stierstorfer B. Animal lectins as cell adhesion molecules. Acta Anat (Basel) 1998; 161: 162–79. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

