Recent insights in nanotechnology-based drugs and formulations designed for effective anti-cancer therapy
- PMID: 27229857
- PMCID: PMC4881065
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-016-0193-x
Recent insights in nanotechnology-based drugs and formulations designed for effective anti-cancer therapy
Abstract
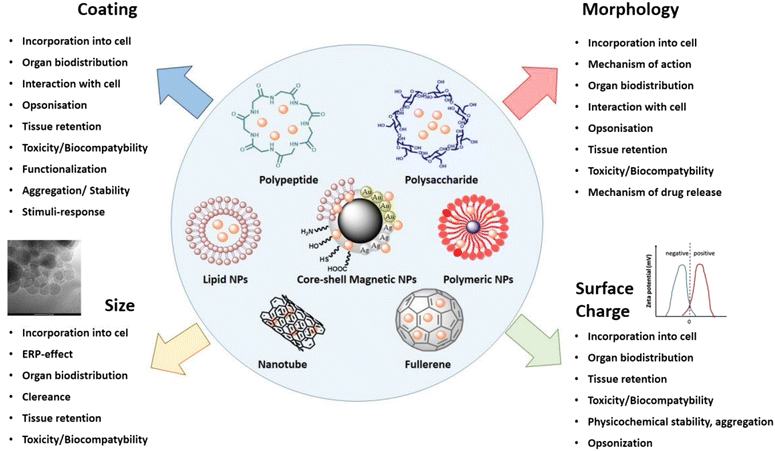
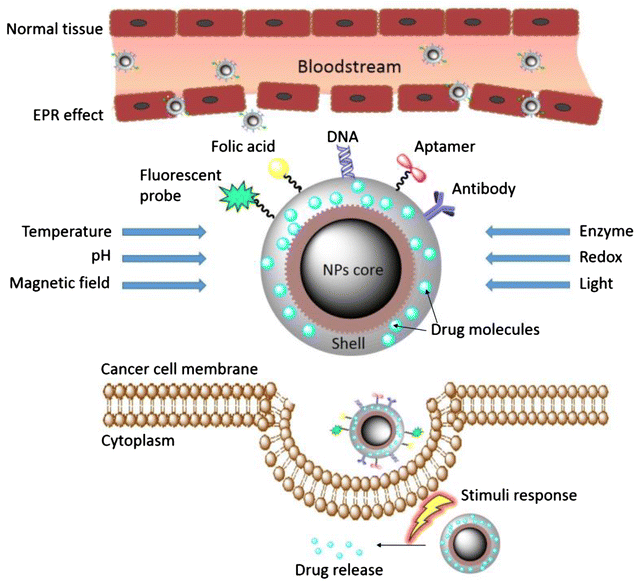
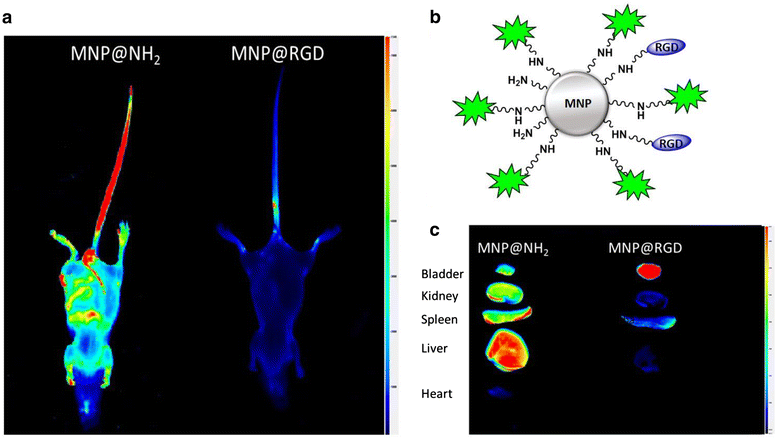
The rapid development of nanotechnology provides alternative approaches to overcome several limitations of conventional anti-cancer therapy. Drug targeting using functionalized nanoparticles to advance their transport to the dedicated site, became a new standard in novel anti-cancer methods. In effect, the employment of nanoparticles during design of antineoplastic drugs helps to improve pharmacokinetic properties, with subsequent development of high specific, non-toxic and biocompatible anti-cancer agents. However, the physicochemical and biological diversity of nanomaterials and a broad spectrum of unique features influencing their biological action requires continuous research to assess their activity. Among numerous nanosystems designed to eradicate cancer cells, only a limited number of them entered the clinical trials. It is anticipated that progress in development of nanotechnology-based anti-cancer materials will provide modern, individualized anti-cancer therapies assuring decrease in morbidity and mortality from cancer diseases. In this review we discussed the implication of nanomaterials in design of new drugs for effective antineoplastic therapy and describe a variety of mechanisms and challenges for selective tumor targeting. We emphasized the recent advantages in the field of nanotechnology-based strategies to fight cancer and discussed their part in effective anti-cancer therapy and successful drug delivery.
Keywords: Cancer; Drug delivery; Nanotechnology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nanotechnology applied to overcome tumor drug resistance.J Control Release. 2012 Aug 20;162(1):45-55. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2012.05.051. Epub 2012 Jun 12. J Control Release. 2012. PMID: 22698943 Review.
-
Nanoscale drug delivery for targeted chemotherapy.Cancer Lett. 2016 Aug 28;379(1):24-31. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2016.05.023. Epub 2016 May 25. Cancer Lett. 2016. PMID: 27235607 Review.
-
Nanotechnology-based intelligent drug design for cancer metastasis treatment.Biotechnol Adv. 2014 Jul-Aug;32(4):761-77. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2013.10.013. Epub 2013 Nov 6. Biotechnol Adv. 2014. PMID: 24211475 Review.
-
Tailoring of physicochemical properties of nanocarriers for effective anti-cancer applications.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2017 Oct;105(10):2906-2928. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.36141. Epub 2017 Jul 14. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2017. PMID: 28643475 Review.
-
Recent progress in nanomedicine-based combination cancer therapy using a site-specific co-delivery strategy.Biomater Sci. 2017 Jul 25;5(8):1367-1381. doi: 10.1039/c7bm00297a. Biomater Sci. 2017. PMID: 28664207 Review.
Cited by
-
Nanoantibiotics containing membrane-active human cathelicidin LL-37 or synthetic ceragenins attached to the surface of magnetic nanoparticles as novel and innovative therapeutic tools: current status and potential future applications.J Nanobiotechnology. 2020 Jan 2;18(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s12951-019-0566-z. J Nanobiotechnology. 2020. PMID: 31898542 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metallic Nanoparticles and Core-Shell Nanosystems in the Treatment, Diagnosis, and Prevention of Parasitic Diseases.Pathogens. 2023 Jun 17;12(6):838. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12060838. Pathogens. 2023. PMID: 37375528 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bare Iron Oxide Nanoparticles as Drug Delivery Carrier for the Short Cationic Peptide Lasioglossin.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Apr 24;14(5):405. doi: 10.3390/ph14050405. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33923229 Free PMC article.
-
From antimicrobial to anticancer: unraveling the potential of pleurocidin and pleurocidin-derived peptides in the treatment of cancers.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jan 26;15:1340029. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1340029. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38344173 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transferrin-Conjugated Polymeric Nanoparticle for Receptor-Mediated Delivery of Doxorubicin in Doxorubicin-Resistant Breast Cancer Cells.Pharmaceutics. 2019 Feb 1;11(2):63. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics11020063. Pharmaceutics. 2019. PMID: 30717256 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chidambaram M, Manavalan R, Kathiresan K. Nanotherapeutics to overcome conventional cancer chemotherapy limitations. J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2011;14:67–77. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

