Species-specific temperature sensitivity of TRPA1
- PMID: 27227025
- PMCID: PMC4843866
- DOI: 10.1080/23328940.2014.1000702
Species-specific temperature sensitivity of TRPA1
Abstract
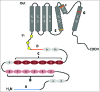
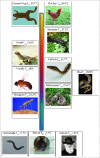
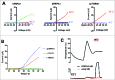
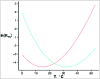
Transient receptor potential ankyrin 1 (TRPA1) is a polymodal ion channel sensitive to temperature and chemical stimuli. The importance of temperature and aversive chemical detection for survival has driven the evolutionary diversity of TRPA1 sensitivity. This diversity can be observed in the various roles of TRPA1 in different species, where it is proposed to act as a temperature-insensitive chemosensor, a heat transducer, a noxious cold transducer, or a detector of low-intensity heat for prey localization. Exploring the variation of TRPA1 functions among species provides evolutionary insight into molecular mechanisms that fine-tune thermal and chemical sensitivity, and offers an opportunity to address basic principles of temperature gating in ion channels. A decade of research has yielded a number of hypotheses describing physiological roles of TRPA1, modulators of its activity, and biophysical principles of gating. This review surveys the diversity of TRPA1 adaptations across evolutionary taxa and explores possible mechanisms of TRPA1 activation.
Keywords: AITC- allyl isothiocyanate; ANKTM1; ANKTM1- ankyrin-like with transmembrane domains protein 1; AR- ankyrin repeat; EC50- half maximal effective concentration; Ion channels; Keq- equillibrium constant; PH- pore helix; PI- phosphatidylinositol; Q10- temperature activation coefficient; S1-S6- transmembrane helices 1–6; TRP- Transient Receptor Potential; TRPA1; TRPA1- transient receptor potential ankyrin 1; TRPM8- transient receptor potential melastatin 8; TRPV1- transient receptor potential vanilloid 1; ThermoTRP; Thermosensation; ceTRPA1- Caenorhabditis elegans TRPA1; dTRPA1- Drosophila melanogaster TRPA1; hsTRPA1- hymenoptera-specific TRPA1; ΔCp -change in heat capacity.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The evolutionary divergence of TRPA1 channel: heat-sensitive, cold-sensitive and temperature-insensitive.Temperature (Austin). 2015 Feb 11;2(2):158-9. doi: 10.1080/23328940.2014.998903. eCollection 2015 Apr-Jun. Temperature (Austin). 2015. PMID: 27227016 Free PMC article.
-
ThermoTRP channels as modular proteins with allosteric gating.Cell Calcium. 2007 Oct-Nov;42(4-5):427-38. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2007.04.004. Epub 2007 May 17. Cell Calcium. 2007. PMID: 17499848 Review.
-
Heat and noxious chemical sensor, chicken TRPA1, as a target of bird repellents and identification of its structural determinants by multispecies functional comparison.Mol Biol Evol. 2014 Mar;31(3):708-22. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msu001. Epub 2014 Jan 7. Mol Biol Evol. 2014. PMID: 24398321
-
TRPA1 Channels in Drosophila and Honey Bee Ectoparasitic Mites Share Heat Sensitivity and Temperature-Related Physiological Functions.Front Physiol. 2016 Oct 5;7:447. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2016.00447. eCollection 2016. Front Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27761115 Free PMC article.
-
The role of TRPA1 channels in thermosensation.Cell Insight. 2022 Oct 11;1(6):100059. doi: 10.1016/j.cellin.2022.100059. eCollection 2022 Dec. Cell Insight. 2022. PMID: 37193355 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The evolutionary divergence of TRPA1 channel: heat-sensitive, cold-sensitive and temperature-insensitive.Temperature (Austin). 2015 Feb 11;2(2):158-9. doi: 10.1080/23328940.2014.998903. eCollection 2015 Apr-Jun. Temperature (Austin). 2015. PMID: 27227016 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioral and pharmacological characterization of planarian nociception.Front Mol Neurosci. 2024 May 1;17:1368009. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2024.1368009. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38751713 Free PMC article.
-
Dependence of heat-evoked TRPA1 activation on extracellular Ca2.Channels (Austin). 2017 Jul 4;11(4):271-272. doi: 10.1080/19336950.2017.1304750. Epub 2017 Mar 13. Channels (Austin). 2017. PMID: 28287333 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The Use of Zebrafish as a Non-traditional Model Organism in Translational Pain Research: The Knowns and the Unknowns.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2022 Mar 4;20(3):476-493. doi: 10.2174/1570159X19666210311104408. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2022. PMID: 33719974 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and functional characterization of a novel TRPA1 gene from sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus and interaction with miR-2013 in response to salt stress.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2023 Nov;28(6):1027-1039. doi: 10.1007/s12192-023-01398-x. Epub 2023 Dec 18. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2023. PMID: 38108989 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sengupta P, Garrity P. Sensing temperature. Curr Biol 2013; 23:R304-7; PMID:23618661; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2013.03.009 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gracheva EO, Ingolia NT, Kelly YM, Cordero-Morales JF, Hollopeter G, Chesler AT, Sanchez EE, Perez JC, Weissman JS, Julius D. Molecular basis of infrared detection by snakes. Nature 2010; 464:1006-11; PMID:20228791; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature08943 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jaquemar D, Schenker T, Trueb B. An ankyrin-like protein with transmembrane domains is specifically lost after oncogenic transformation of human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem 1999; 274:7325-33; PMID:10066796; http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.274.11.7325 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Story GM, Peier AM, Reeve AJ, Eid SR, Mosbacher J, Hricik TR, Earley TJ, Hergarden AC, Andersson DA, Hwang SW, et al. . ANKTM1, a TRP-like channel expressed in nociceptive neurons, is activated by cold temperatures. Cell 2003; 112:819-29; PMID:12654248; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(03)00158-2 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jordt SE, Bautista DM, Chuang HH, McKemy DD, Zygmunt PM, Hogestatt ED, Meng ID, Julius D. Mustard oils and cannabinoids excite sensory nerve fibres through the TRP channel ANKTM1. Nature 2004; 427:260-5; PMID:14712238; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature02282 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
