Pharmacoinformatic and molecular docking studies reveal potential novel antidepressants against neurodegenerative disorders by targeting HSPB8
- PMID: 27226709
- PMCID: PMC4866741
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S101929
Pharmacoinformatic and molecular docking studies reveal potential novel antidepressants against neurodegenerative disorders by targeting HSPB8
Abstract
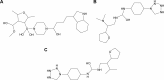
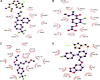
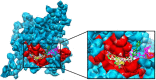
Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT) disease is an inherited peripheral neuromuscular disorder characterized by length-dependent and progressive degeneration of peripheral nerves, leading to muscular weakness. Research has shown that mutated HSPB8 may be responsible for depression, neurodegenerative disorders, and improper functioning of peripheral nerves, resulting in neuromuscular disorders like CMT. In the current work, a hybrid approach of virtual screening and molecular docking studies was followed by homology modeling and pharmacophore identification. Detailed screening analyses were carried out by 2-D similarity search against prescribed antidepressant drugs with physicochemical properties. LigandScout was employed to ascertain novel molecules and pharmacophore properties. In this study, we report three novel compounds that showed maximum binding affinity with HSPB8. Docking analysis elucidated that Met37, Ser57, Ser58, Trp60, Thr63, Thr114, Lys115, Asp116, Gly117, Val152, Val154, Leu186, Asp189, Ser190, Gln191, and Glu192 are critical residues for ligand-receptor interactions. Our analyses suggested paroxetine as a potent compound for targeting HSPB8. Selected compounds have more effective energy scores than the selected drug analogs. Additionally, site-directed mutagenesis could be significant for further analysis of the binding pocket. The novel findings based on an in silico approach may be momentous for potent drug design against depression and CMT.
Keywords: HSPB8; antidepressants; bioinformatics; computer-aided drug design; heat shock protein (HSP); modeling; molecular docking; neurodegenerative disorders; pharmacoinformatics; virtual screening.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Pharmacoinformatics elucidation of potential drug targets against migraine to target ion channel protein KCNK18.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2014 May 21;8:571-81. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S63096. eCollection 2014. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2014. PMID: 24899801 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptive evolution and elucidating the potential inhibitor against schizophrenia to target DAOA (G72) isoforms.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015 Jul 3;9:3471-80. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S63946. eCollection 2015. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015. PMID: 26170631 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacoinformatics and molecular docking reveal potential drug candidates against Schizophrenia to target TAAR6.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Aug;234(8):13263-13276. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27999. Epub 2018 Dec 19. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30569503
-
HPC Analysis of Multiple Binding Sites Communication and Allosteric Modulations in Drug Design: The HSP Case Study.Curr Drug Targets. 2016;17(14):1610-1625. doi: 10.2174/1389450117666151209123646. Curr Drug Targets. 2016. PMID: 26648062 Review.
-
In Silico Studies in Drug Research Against Neurodegenerative Diseases.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2018;16(6):664-725. doi: 10.2174/1570159X15666170823095628. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2018. PMID: 28831921 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
In-silico drug design for the novel Karachi-NF001 strain of brain-eating amoeba: Naegleria fowleri.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Feb 9;10:1098217. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1098217. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 36845543 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of fungus-growing termite-associated halogenated-PKS maduralactomycin a as a potential inhibitor of MurF protein of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Apr 21;10:1183073. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1183073. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 37152898 Free PMC article.
-
In Silico identification of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from MRJP1.PLoS One. 2020 Feb 3;15(2):e0228265. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0228265. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32012183 Free PMC article.
-
In-Silico Characterization and in-Vivo Validation of Albiziasaponin-A, Iso-Orientin, and Salvadorin Using a Rat Model of Alzheimer's Disease.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Aug 2;9:730. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00730. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30123124 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacoinformatics, Adaptive Evolution, and Elucidation of Six Novel Compounds for Schizophrenia Treatment by Targeting DAOA (G72) Isoforms.Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:5925714. doi: 10.1155/2017/5925714. Epub 2017 Jan 19. Biomed Res Int. 2017. PMID: 28197415 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lambert H, Charette SJ, Bernier AF, Guimond A, Landry J. HSP27 multimerization mediated by phosphorylation-sensitive intermolecular interactions at the amino terminus. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:9378–9385. - PubMed
-
- Liu C, Welsh MJ. Identification of a site of Hsp27 binding with Hsp27 and αB-crystallin as indicated by the yeast two-hybrid system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999;255:256–261. - PubMed
-
- Rogalla T, Ehrnsperger M, Preville X, et al. Regulation of Hsp27 oligomerization, chaperone function, and protective activity against oxidative stress/tumor necrosis factor α by phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:18947–18956. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

