Optogenetic Visualization of Presynaptic Tonic Inhibition of Cerebellar Parallel Fibers
- PMID: 27225762
- PMCID: PMC4879193
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4366-15.2016
Optogenetic Visualization of Presynaptic Tonic Inhibition of Cerebellar Parallel Fibers
Abstract
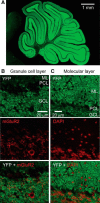
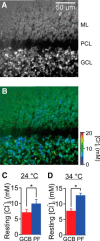
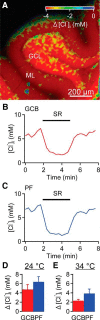
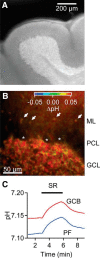
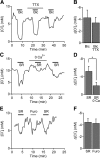
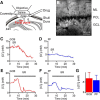
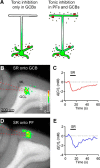
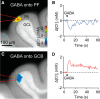
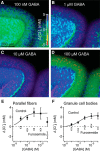
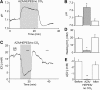
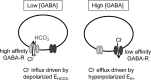
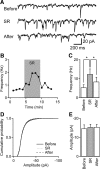
Tonic inhibition was imaged in cerebellar granule cells of transgenic mice expressing the optogenetic chloride indicator, Clomeleon. Blockade of GABAA receptors substantially reduced chloride concentration in granule cells due to block of tonic inhibition. This indicates that tonic inhibition is a significant contributor to the resting chloride concentration of these cells. Tonic inhibition was observed not only in granule cell bodies, but also in their axons, the parallel fibers (PFs). This presynaptic tonic inhibition could be observed in slices both at room and physiological temperatures, as well as in vivo, and has many of the same properties as tonic inhibition measured in granule cell bodies. GABA application revealed that PFs possess at least two types of GABAA receptor: one high-affinity receptor that is activated by ambient GABA and causes a chloride influx that mediates tonic inhibition, and a second with a low affinity for GABA that causes a chloride efflux that excites PFs. Presynaptic tonic inhibition regulates glutamate release from PFs because GABAA receptor blockade enhanced both the frequency of spontaneous EPSCs and the amplitude of evoked EPSCs at the PF-Purkinje cell synapse. We conclude that tonic inhibition of PFs could play an important role in regulating information flow though cerebellar synaptic circuits. Such cross talk between phasic and tonic signaling could be a general mechanism for fine tuning of synaptic circuits.
Significance statement: This paper demonstrates that an unconventional form of signaling, known as tonic inhibition, is found in presynaptic terminals and affects conventional synaptic communication. Our results establish the basic characteristics and mechanisms of presynaptic tonic inhibition and show that it occurs in vivo as well as in isolated brain tissue.
Keywords: GABA; cerebellum; chloride; imaging; parallel fibers; tonic inhibition.
Copyright © 2016 the authors 0270-6474/16/365709-15$15.00/0.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Multiple modes of GABAergic inhibition of rat cerebellar granule cells.J Physiol. 2003 Apr 1;548(Pt 1):97-110. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.036459. Epub 2003 Feb 14. J Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12588900 Free PMC article.
-
Axonal GABAA receptors depolarize presynaptic terminals and facilitate transmitter release in cerebellar Purkinje cells.J Physiol. 2017 Dec 15;595(24):7477-7493. doi: 10.1113/JP275369. Epub 2017 Nov 21. J Physiol. 2017. PMID: 29072780 Free PMC article.
-
Transmembrane AMPAR regulatory protein γ-2 is required for the modulation of GABA release by presynaptic AMPARs.J Neurosci. 2015 Mar 11;35(10):4203-14. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4075-14.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25762667 Free PMC article.
-
Tonically active GABA A receptors: modulating gain and maintaining the tone.Trends Neurosci. 2004 May;27(5):262-9. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2004.03.005. Trends Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15111008 Review.
-
Presynaptic ionotropic GABA receptors.Results Probl Cell Differ. 2008;44:69-85. doi: 10.1007/400_2007_040. Results Probl Cell Differ. 2008. PMID: 17609920 Review.
Cited by
-
Simultaneous two-photon imaging of intracellular chloride concentration and pH in mouse pyramidal neurons in vivo.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Oct 10;114(41):E8770-E8779. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1702861114. Epub 2017 Sep 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28973889 Free PMC article.
-
Odor-Induced Multi-Level Inhibitory Maps in Drosophila.eNeuro. 2020 Jan 10;7(1):ENEURO.0213-19.2019. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0213-19.2019. Print 2020 Jan/Feb. eNeuro. 2020. PMID: 31888962 Free PMC article.
-
Biophysical models reveal the relative importance of transporter proteins and impermeant anions in chloride homeostasis.Elife. 2018 Sep 27;7:e39575. doi: 10.7554/eLife.39575. Elife. 2018. PMID: 30260315 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of GABAB receptor enhancement of extrasynaptic GABAA receptor currents in cerebellar granule cells.Sci Rep. 2019 Nov 13;9(1):16683. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-53087-4. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31723152 Free PMC article.
-
Epilepsy insights revealed by intravital functional optical imaging.Front Neurol. 2024 Aug 29;15:1465232. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1465232. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39268067 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alvarez-Leefmans FJ, Delpire E. Thermodynamics and kinetics of chloride transport in neurons: an outline. In: Alvarez-Leefmans FJ, Delpire E, editors. Physiology and pathology of chloride transporters and channles in the nervous system. London: Academic; 2009. pp. 81–108.
-
- Berglund K, Dunbar RL, Lee P, Feng G, Augustine GJ. Imaging synaptic inhibition with Clomeleon, a genetically encoded chloride indicator. In: Konnerth A, Lanni F, Yuste R, editors. Imaging in neuroscience and development: a laboratory manual, Ed 2. New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory; 2005. pp. 495–498.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
