Transcription factor TLX1 controls retinoic acid signaling to ensure spleen development
- PMID: 27214556
- PMCID: PMC4922703
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI82956
Transcription factor TLX1 controls retinoic acid signaling to ensure spleen development
Abstract
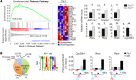
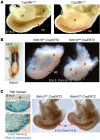
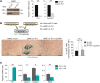
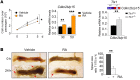
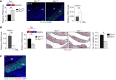
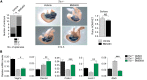
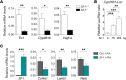
The molecular mechanisms that underlie spleen development and congenital asplenia, a condition linked to increased risk of overwhelming infections, remain largely unknown. The transcription factor TLX1 controls cell fate specification and organ expansion during spleen development, and Tlx1 deletion causes asplenia in mice. Deregulation of TLX1 expression has recently been proposed in the pathogenesis of congenital asplenia in patients carrying mutations of the gene-encoding transcription factor SF-1. Herein, we have shown that TLX1-dependent regulation of retinoic acid (RA) metabolism is critical for spleen organogenesis. In a murine model, loss of Tlx1 during formation of the splenic anlage increased RA signaling by regulating several genes involved in RA metabolism. Uncontrolled RA activity resulted in premature differentiation of mesenchymal cells and reduced vasculogenesis of the splenic primordium. Pharmacological inhibition of RA signaling in Tlx1-deficient animals partially rescued the spleen defect. Finally, spleen growth was impaired in mice lacking either cytochrome P450 26B1 (Cyp26b1), which results in excess RA, or retinol dehydrogenase 10 (Rdh10), which results in RA deficiency. Together, these findings establish TLX1 as a critical regulator of RA metabolism and provide mechanistic insights into the molecular determinants of human congenital asplenia.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Generation of a Tlx1(CreER-Venus) knock-in mouse strain for the study of spleen development.Genesis. 2014 Nov;52(11):916-23. doi: 10.1002/dvg.22829. Epub 2014 Oct 18. Genesis. 2014. PMID: 25283275
-
Congenital asplenia due to a tlx1 mutation reduces resistance to Aeromonas hydrophila infection in zebrafish.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019 Dec;95:538-545. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2019.10.065. Epub 2019 Oct 31. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31678534
-
Niche-induced extramedullary hematopoiesis in the spleen is regulated by the transcription factor Tlx1.Sci Rep. 2018 May 29;8(1):8308. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-26693-x. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29844356 Free PMC article.
-
The promise of Hox11+ stem cells of the spleen for treating autoimmune diseases.Horm Metab Res. 2008 Feb;40(2):137-46. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1022560. Horm Metab Res. 2008. PMID: 18283632 Review.
-
The Cdx1 homeodomain protein: an integrator of posterior signaling in the mouse.Bioessays. 2003 Oct;25(10):971-80. doi: 10.1002/bies.10340. Bioessays. 2003. PMID: 14505364 Review.
Cited by
-
Rdh10 loss-of-function and perturbed retinoid signaling underlies the etiology of choanal atresia.Hum Mol Genet. 2017 Apr 1;26(7):1268-1279. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddx031. Hum Mol Genet. 2017. PMID: 28169399 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of key genes involved in the recurrence of glioblastoma multiforme using weighted gene co-expression network analysis and differential expression analysis.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(1):3188-3200. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1943986. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34238116 Free PMC article.
-
Cyp26b1 is an essential regulator of distal airway epithelial differentiation during lung development.Development. 2020 Feb 20;147(4):dev181560. doi: 10.1242/dev.181560. Development. 2020. PMID: 32001436 Free PMC article.
-
Absence of Nkx2-3 induces ectopic lymphatic endothelial differentiation associated with impaired extramedullary stress hematopoiesis in the spleen.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Apr 5;11:1170389. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1170389. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37091975 Free PMC article.
-
Coevolution of the Tlx homeobox gene with medusa development (Cnidaria: Medusozoa).Commun Biol. 2023 Jul 11;6(1):709. doi: 10.1038/s42003-023-05077-6. Commun Biol. 2023. PMID: 37433830 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

