Mouse and Human CD1d-Self-Lipid Complexes Are Recognized Differently by Murine Invariant Natural Killer T Cell Receptors
- PMID: 27213277
- PMCID: PMC4877060
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0156114
Mouse and Human CD1d-Self-Lipid Complexes Are Recognized Differently by Murine Invariant Natural Killer T Cell Receptors
Abstract
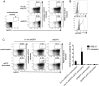
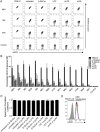
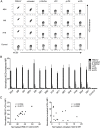
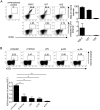
Invariant natural killer T (iNKT) cells recognize self-lipids presented by CD1d through characteristic TCRs, which mainly consist of the invariant Vα14-Jα18 TCRα chain and Vβ8.2, 7 or 2 TCRβ chains with hypervariable CDR3β sequences in mice. The iNKT cell-CD1d axis is conserved between humans and mice, and human CD1d reactivity of murine iNKT cells have been described. However, the detailed differences between the recognition of human and mouse CD1d bound to various self-lipids by mouse iNKT TCRs are largely unknown. In this study, we generated a de novo murine iNKT TCR repertoire with a wider range of autoreactivity compared with that of naturally occurring peripheral iNKT TCRs. Vβ8.2 mouse iNKT TCRs capable of recognizing the human CD1d-self-lipid tetramer were identified, although such clones were not detectable in the Vβ7 or Vβ2 iNKT TCR repertoire. In line with previously reports, clonotypic Vβ8.2 iNKT TCRs with unique CDR3β loops did not discriminate among lipids presented by mouse CD1d. Unexpectedly, however, these iNKT TCRs showed greater ligand selectivity toward human CD1d presenting the same lipids. Our findings demonstrated that the recognition of mouse and human CD1d-self-lipid complexes by murine iNKT TCRs is not conserved, thereby further elucidating the differences between cognate and cross-species reactivity of self-antigens by mouse iNKT TCRs.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
CDR3β sequence motifs regulate autoreactivity of human invariant NKT cell receptors.J Autoimmun. 2016 Apr;68:39-51. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2015.12.005. Epub 2015 Dec 31. J Autoimmun. 2016. PMID: 26748722 Free PMC article.
-
Lysophospholipid presentation by CD1d and recognition by a human Natural Killer T-cell receptor.EMBO J. 2012 Apr 18;31(8):2047-59. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.54. Epub 2012 Mar 6. EMBO J. 2012. PMID: 22395072 Free PMC article.
-
The hypervariable region 4 (HV4) and position 93 of the α chain modulate CD1d-glycolipid binding of iNKT TCRs.Eur J Immunol. 2015 Jul;45(7):2122-33. doi: 10.1002/eji.201545534. Epub 2015 May 12. Eur J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25900449
-
Turned on by danger: activation of CD1d-restricted invariant natural killer T cells.Immunology. 2012 Sep;137(1):20-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2012.03612.x. Immunology. 2012. PMID: 22734667 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Adaptor Proteins in the Biology of Natural Killer T (NKT) Cells.Front Immunol. 2019 Jun 25;10:1449. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01449. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31293596 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Protective effects of Ganoderma lucidum spores on estradiol benzoate-induced TEC apoptosis and compromised double-positive thymocyte development.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Aug 16;15:1419881. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1419881. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39221140 Free PMC article.
-
Novel lipid antigens for NKT cells in cancer.Front Immunol. 2023 Oct 16;14:1173375. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1173375. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37908366 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Monoclonal Invariant NKT (iNKT) Cell Mice Reveal a Role for Both Tissue of Origin and the TCR in Development of iNKT Functional Subsets.J Immunol. 2017 Jul 1;199(1):159-171. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1700214. Epub 2017 Jun 2. J Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28576977 Free PMC article.
-
Key Residues at Third CDR3β Position Impact Structure and Antigen Recognition of Human Invariant NK TCRs.J Immunol. 2017 Feb 1;198(3):1056-1065. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1601556. Epub 2016 Dec 21. J Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28003379 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

