The Role of the PERK/eIF2α/ATF4/CHOP Signaling Pathway in Tumor Progression During Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress
- PMID: 27211800
- PMCID: PMC5008685
- DOI: 10.2174/1566524016666160523143937
The Role of the PERK/eIF2α/ATF4/CHOP Signaling Pathway in Tumor Progression During Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress
Abstract
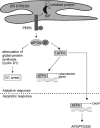
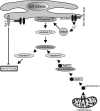
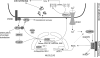
Hypoxia is a major hallmark of the tumor microenvironment that is strictly associated with rapid cancer progression and induction of metastasis. Hypoxia inhibits disulfide bond formation and impairs protein folding in the Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER). The stress in the ER induces the activation of Unfolded Protein Response (UPR) pathways via the induction of protein kinase RNA-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK). As a result, the level of phosphorylated Eukaryotic Initiation Factor 2 alpha (eIF2α) is markedly elevated, resulting in the promotion of a pro-adaptive signaling pathway by the inhibition of global protein synthesis and selective translation of Activating Transcription Factor 4 (ATF4). On the contrary, during conditions of prolonged ER stress, pro-adaptive responses fail and apoptotic cell death ensues. Interestingly, similar to the activity of the mitochondria, the ER may also directly activate the apoptotic pathway through ER stress-mediated leakage of calcium into the cytoplasm that leads to the activation of death effectors. Apoptotic cell death also ensues by ATF4-CHOP- mediated induction of several pro-apoptotic genes and suppression of the synthesis of anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 proteins. Advancing molecular insight into the transition of tumor cells from adaptation to apoptosis under hypoxia-induced ER stress may provide answers on how to overcome the limitations of current anti-tumor therapies. Targeting components of the UPR pathways may provide more effective elimination of tumor cells and as a result, contribute to the development of more promising anti-tumor therapeutic agents.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mechanism of the induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress by the anti-cancer agent, di-2-pyridylketone 4,4-dimethyl-3-thiosemicarbazone (Dp44mT): Activation of PERK/eIF2α, IRE1α, ATF6 and calmodulin kinase.Biochem Pharmacol. 2016 Jun 1;109:27-47. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2016.04.001. Epub 2016 Apr 6. Biochem Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27059255
-
Endoplasmic reticulum stress response mediated by the PERK-eIF2(alpha)-ATF4 pathway is involved in osteoblast differentiation induced by BMP2.J Biol Chem. 2011 Feb 11;286(6):4809-18. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.152900. Epub 2010 Dec 6. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21135100 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the cerebrovascular smooth muscle cell phenotype by mitochondrial oxidative injury and endoplasmic reticulum stress in simulated microgravity rats via the PERK-eIF2α-ATF4-CHOP pathway.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2020 Aug 1;1866(8):165799. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2020.165799. Epub 2020 Apr 15. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2020. PMID: 32304741
-
The PERK/eIF2alpha/ATF4 module of the UPR in hypoxia resistance and tumor growth.Cancer Biol Ther. 2006 Jul;5(7):723-8. doi: 10.4161/cbt.5.7.2967. Epub 2006 Jul 1. Cancer Biol Ther. 2006. PMID: 16861899 Review.
-
ER stress, hypoxia tolerance and tumor progression.Curr Mol Med. 2006 Feb;6(1):55-69. doi: 10.2174/156652406775574604. Curr Mol Med. 2006. PMID: 16472113 Review.
Cited by
-
Marizomib (Salinosporamide A) Promotes Apoptosis in A375 and G361 Melanoma Cancer Cells.Mar Drugs. 2024 Jul 15;22(7):315. doi: 10.3390/md22070315. Mar Drugs. 2024. PMID: 39057424 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction Between the PERK/ATF4 Branch of the Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Mitochondrial One-Carbon Metabolism Regulates Neuronal Survival After Intracerebral Hemorrhage.Int J Biol Sci. 2024 Aug 6;20(11):4277-4296. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.93787. eCollection 2024. Int J Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39247810 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay of α-Synuclein Oligomers and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Parkinson'S Disease: Insights into Cellular Dysfunctions.Inflammation. 2024 Oct 9. doi: 10.1007/s10753-024-02156-6. Online ahead of print. Inflammation. 2024. PMID: 39382817 Review.
-
Effects of PGE1 on the ERS pathway in neonatal rats with hyperoxic lung injury.Pediatr Res. 2024 Jul 16. doi: 10.1038/s41390-024-03381-3. Online ahead of print. Pediatr Res. 2024. PMID: 39014239
-
Pathological Crosstalk Between Oxidized LDL and ER Stress in Human Diseases: A Comprehensive Review.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 May 26;9:674103. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.674103. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34124059 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cooper GM. The cell: a molecular approach. 2nd ed. ASM Press Sinauer Associates; Washington, D.C. Sunderland, Massachusetts: 2000.
-
- Sudhakar A. History of Cancer, Ancient and Modern Treatment Methods. J Cancer Sci Ther. 2009;1:1–4. - PubMed
-
- Schirrmacher V, Schwartz-Albiez R. Cancer metastasis: molecular and cellular biology, host, immune response, and perspectives for treatment. Springer-Verlag; Berlin ; New York: 1989.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
