Structure of the Dictyostelium Myosin-II Heavy Chain Kinase A (MHCK-A) α-kinase domain apoenzyme reveals a novel autoinhibited conformation
- PMID: 27211275
- PMCID: PMC4876393
- DOI: 10.1038/srep26634
Structure of the Dictyostelium Myosin-II Heavy Chain Kinase A (MHCK-A) α-kinase domain apoenzyme reveals a novel autoinhibited conformation
Abstract
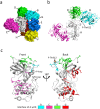
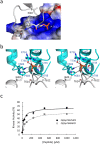
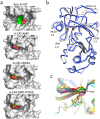
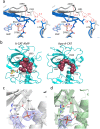
The α-kinases are a family of a typical protein kinases present in organisms ranging from protozoa to mammals. Here we report an autoinhibited conformation for the α-kinase domain of Dictyostelium myosin-II heavy chain kinase A (MHCK-A) in which nucleotide binding to the catalytic cleft, located at the interface between an N-terminal and C-terminal lobe, is sterically blocked by the side chain of a conserved arginine residue (Arg592). Previous α-kinase structures have shown that an invariant catalytic aspartic acid residue (Asp766) is phosphorylated. Unexpectedly, in the autoinhibited conformation the phosphoryl group is transferred to the adjacent Asp663, creating an interaction network that stabilizes the autoinhibited state. The results suggest that Asp766 phosphorylation may play both catalytic and regulatory roles. The autoinhibited structure also provides the first view of a phosphothreonine residue docked into the phospho-specific allosteric binding site (Pi-pocket) in the C-lobe of the α-kinase domain.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Determinants for substrate phosphorylation by Dictyostelium myosin II heavy chain kinases A and B and eukaryotic elongation factor-2 kinase.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008 Jun;1784(6):908-15. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2008.03.001. Epub 2008 Mar 12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008. PMID: 18381083
-
Structural analysis of myosin heavy chain kinase A from Dictyostelium. Evidence for a highly divergent protein kinase domain, an amino-terminal coiled-coil domain, and a domain homologous to the beta-subunit of heterotrimeric G proteins.J Biol Chem. 1995 Jan 13;270(2):523-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.2.523. J Biol Chem. 1995. PMID: 7822274
-
Crystal structure of the alpha-kinase domain of Dictyostelium myosin heavy chain kinase A.Sci Signal. 2010 Mar 2;3(111):ra17. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2000525. Sci Signal. 2010. PMID: 20197546 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling pathways regulating Dictyostelium myosin II.J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2002;23(7-8):703-18. doi: 10.1023/a:1024467426244. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2002. PMID: 12952069 Review.
-
Regulation of Dictyostelium myosin I and II.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2001 Mar 15;1525(3):245-61. doi: 10.1016/s0304-4165(01)00110-6. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2001. PMID: 11257438 Review.
Cited by
-
Structural basis for the calmodulin-mediated activation of eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase.Sci Adv. 2022 Jul 8;8(27):eabo2039. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abo2039. Epub 2022 Jul 6. Sci Adv. 2022. PMID: 35857468 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of the complex between calmodulin and a functional construct of eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase bound to an ATP-competitive inhibitor.J Biol Chem. 2023 Jun;299(6):104813. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2023.104813. Epub 2023 May 11. J Biol Chem. 2023. PMID: 37172726 Free PMC article.
-
Structural dynamics of the complex of calmodulin with a minimal functional construct of eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase and the role of Thr348 autophosphorylation.Protein Sci. 2021 Jun;30(6):1221-1234. doi: 10.1002/pro.4087. Epub 2021 May 5. Protein Sci. 2021. PMID: 33890716 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of Ligand-induced Conformational Changes in the Activation Loop of Aurora-A Kinase by PELDOR Spectroscopy.ChemistryOpen. 2016 Nov 11;5(6):531-534. doi: 10.1002/open.201600101. eCollection 2016 Dec. ChemistryOpen. 2016. PMID: 28032021 Free PMC article.
-
Revealing eEF-2 kinase: recent structural insights into function.Trends Biochem Sci. 2024 Feb;49(2):169-182. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2023.11.004. Epub 2023 Dec 16. Trends Biochem Sci. 2024. PMID: 38103971 Review.
References
-
- Côté G. P. & Bukiejko U. Purification and characterization of a myosin heavy chain kinase from Dictyostelium discoideum. J Biol Chem 262, 1065–1072 (1987). - PubMed
-
- De La Roche M. A., Smith J. L., Betapudi V., Egelhoff T. T. & Côté G. P. Signaling pathways regulating Dictyostelium myosin II. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 23, 703–718 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Luck-Vielmetter D., Schleicher M., Grabatin B., Wippler J. & Gerisch G. Replacement of threonine residues by serine and alanine in a phosphorylatable heavy chain fragment of Dictyostelium myosin II. FEBS Lett 269, 239–243 (1990). - PubMed
-
- Vaillancourt J. P., Lyons C. & Côté G. P. Identification of two phosphorylated threonines in the tail region of Dictyostelium myosin II. J Biol Chem 263, 10082–10087 (1988). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

