Immunometabolism of regulatory T cells
- PMID: 27196520
- PMCID: PMC5006394
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.3466
Immunometabolism of regulatory T cells
Abstract
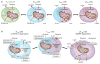
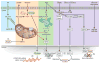
The bidirectional interaction between the immune system and whole-body metabolism has been well recognized for many years. Via effects on adipocytes and hepatocytes, immune cells can modulate whole-body metabolism (in metabolic syndromes such as type 2 diabetes and obesity) and, reciprocally, host nutrition and commensal-microbiota-derived metabolites modulate immunological homeostasis. Studies demonstrating the metabolic similarities of proliferating immune cells and cancer cells have helped give birth to the new field of immunometabolism, which focuses on how the cell-intrinsic metabolic properties of lymphocytes and macrophages can themselves dictate the fate and function of the cells and eventually shape an immune response. We focus on this aspect here, particularly as it relates to regulatory T cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Toll-like receptors, inflammation, metabolism and obesity.Arch Physiol Biochem. 2011 Jul;117(3):151-64. doi: 10.3109/13813455.2011.562514. Epub 2011 May 23. Arch Physiol Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21599616 Review.
-
Immunometabolism of obesity and diabetes: microbiota link compartmentalized immunity in the gut to metabolic tissue inflammation.Clin Sci (Lond). 2015 Dec;129(12):1083-96. doi: 10.1042/CS20150431. Clin Sci (Lond). 2015. PMID: 26464517 Review.
-
The "Big Bang" in obese fat: Events initiating obesity-induced adipose tissue inflammation.Eur J Immunol. 2015 Sep;45(9):2446-56. doi: 10.1002/eji.201545502. Epub 2015 Aug 19. Eur J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26220361 Review.
-
[The role of T-regulatory cells in the pathogenesis of immunological disturbances accompanying obesity and atherosclerosis].Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2010 Mar 30;64:156-60. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2010. PMID: 20354263 Review. Polish.
-
Metabolic control of regulatory T cell development and function.Trends Immunol. 2015 Jan;36(1):3-12. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2014.08.003. Epub 2014 Sep 20. Trends Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25248463 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolic Reprogramming in Immune Response and Tissue Inflammation.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2020 Sep;40(9):1990-2001. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.120.314037. Epub 2020 Jul 23. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2020. PMID: 32698683 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Comparison of Automated Perfusion- and Manual Diffusion-Based Human Regulatory T Cell Expansion and Functionality Using a Soluble Activator Complex.Cell Transplant. 2020 Jan-Dec;29:963689720923578. doi: 10.1177/0963689720923578. Cell Transplant. 2020. PMID: 32662685 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial Oxidative Damage Underlies Regulatory T Cell Defects in Autoimmunity.Cell Metab. 2020 Oct 6;32(4):591-604.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.07.001. Epub 2020 Jul 31. Cell Metab. 2020. PMID: 32738205 Free PMC article.
-
TLR8-Mediated Metabolic Control of Human Treg Function: A Mechanistic Target for Cancer Immunotherapy.Cell Metab. 2019 Jan 8;29(1):103-123.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2018.09.020. Epub 2018 Oct 18. Cell Metab. 2019. PMID: 30344014 Free PMC article.
-
Graft Engineering and Adoptive Immunotherapy: New Approaches to Promote Immune Tolerance After Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation.Front Immunol. 2019 Jul 10;10:1342. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01342. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31354695 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abbas AK, et al. Regulatory T cells: recommendations to simplify the nomenclature. Nat Immunol. 2013;14:307–308. - PubMed
-
- Curotto de Lafaille MA, Lafaille JJ. Natural and adaptive foxp3+ regulatory T cells: more of the same or a division of labor? Immunity. 2009;30:626–635. - PubMed
-
- Ohkura N, et al. T cell receptor stimulation-induced epigenetic changes and Foxp3 expression are independent and complementary events required for Treg cell development. Immunity. 2012;37:785–799. - PubMed
-
- Maloy KJ, Powrie F. Fueling regulation: IL-2 keeps CD4+ Treg cells fit. Nat Immunol. 2005;6:1071–1072. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

