Comparison of Antibodies with Amylase Activity from Cerebrospinal Fluid and Serum of Patients with Multiple Sclerosis
- PMID: 27196086
- PMCID: PMC4873009
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0154688
Comparison of Antibodies with Amylase Activity from Cerebrospinal Fluid and Serum of Patients with Multiple Sclerosis
Abstract
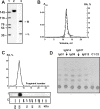
We have recently shown that IgGs from serum and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of MS patients are active in hydrolysis of DNA and myelin basic protein. According to literature data, anti-DNA and anti-MBP abzymes may promote important neuropathologic mechanisms in this chronic inflammatory disorder and in MS pathogenesis development. At the same time, the involvement of antibodies with amylase activity in the pathogenesis of any autoimmune disease has not yet been identified. Electrophoretically and immunologically homogeneous IgGs were obtained by a sequential affinity chromatography of the CSF proteins on protein G-Sepharose and FPLC gel filtration. We are able to present the first unpredictable evidence showing that IgGs from CSF possess amylase activity and efficiently hydrolyze maltoheptaose; their average specific Ab activity is ~30-fold higher than that of antibodies from sera of the same MS patients. Specific average RA (SAA) for IgGs from healthy volunteers was approximately ~1000 lower than that for MS patients. In addition, it was shown that a relative SAA of total proteins of CSF (including Abs) ~15-fold lower than that for purified IgGs, while the relative SAA of the total sera protein is higher than that of sera IgGs by a factor of 1033. This result speaks in favor of the fact that amylolytic activity of CSF proteins is mainly caused by the activity of amylase abzymes. One cannot exclude, that amylase abzymes of CSF can play a, as yet unknown, role in the pathogenesis of MS. Some possible reasons of these findings are discussed.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of DNA-hydrolyzing antibodies from the cerebrospinal fluid and serum of patients with multiple sclerosis.PLoS One. 2014 Apr 15;9(4):e93001. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0093001. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24736683 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of antibodies hydrolyzing myelin basic protein from the cerebrospinal fluid and serum of patients with multiple sclerosis.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 29;9(9):e107807. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0107807. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25265393 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple Sclerosis: Enzymatic Cross Site-Specific Hydrolysis of H1 Histone by IgGs against H1, H2A, H2B, H3, H4 Histones, and Myelin Basic Protein.Biomolecules. 2021 Aug 2;11(8):1140. doi: 10.3390/biom11081140. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34439806 Free PMC article.
-
The cerebrospinal fluid proteins in multiple sclerosis.Clin Lab Med. 1986 Sep;6(3):457-75. Clin Lab Med. 1986. PMID: 3091313 Review.
-
Cerebrospinal Fluid Testing for Multiple Sclerosis.Clin Lab Med. 2020 Sep;40(3):369-377. doi: 10.1016/j.cll.2020.06.002. Epub 2020 Jul 2. Clin Lab Med. 2020. PMID: 32718506 Review.
Cited by
-
The Blood of the HIV-Infected Patients Contains κ-IgG, λ-IgG, and Bispecific κλ-IgG, Which Possess DNase and Amylolytic Activity.Life (Basel). 2022 Feb 17;12(2):304. doi: 10.3390/life12020304. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35207591 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis of Mice: Enzymatic Cross Site-Specific Hydrolysis of H4 Histone by IgGs against Histones and Myelin Basic Protein.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 16;23(16):9182. doi: 10.3390/ijms23169182. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36012448 Free PMC article.
-
EAE of Mice: Enzymatic Cross Site-Specific Hydrolysis of H2A Histone by IgGs against H2A, H1, H2B, H3, and H4 Histones and Myelin Basic Protein.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 12;24(10):8636. doi: 10.3390/ijms24108636. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37239982 Free PMC article.
-
Cell Differentiation and Proliferation in the Bone Marrow and Other Organs of 2D2 Mice during Spontaneous Development of EAE Leading to the Production of Abzymes.Molecules. 2022 Mar 28;27(7):2195. doi: 10.3390/molecules27072195. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35408594 Free PMC article.
-
Essential Protective Role of Catalytically Active Antibodies (Abzymes) with Redox Antioxidant Functions in Animals and Humans.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 31;23(7):3898. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073898. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35409256 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- O’Connor KC, Bar-Or A, Hafler DA (2001) The neuroimmunology of multiple sclerosis: possible roles of T and B lymphocytes in immunopathogenesis. J. Clin. Immunol. 21: 81–92. - PubMed
-
- Hhachn BCh. Systemic lipus erythematosus. In: Braunvald EE, Isselbakher KD, Petersdorf RG, Wilson DD, Martin DB, Fauchi AS, editors. Internal diseases, Moscow:
-
- Pisetsky D (2001) Immune response to DNA in systemic lupus erythematosus. Isr. Med. Ass. J 3: 850–853. - PubMed
-
- Lerner RA, Tramontano A (1987) Antibodies as enzymes. Trends in Bioch. Sci 12: 427–438.
-
- Lerner RA, Janda KD (1995) Catalytic antibodies: evolution of protein function in real time. EXS 73: 121–138. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

