Kidney stones
- PMID: 27188687
- PMCID: PMC5685519
- DOI: 10.1038/nrdp.2016.8
Kidney stones
Abstract
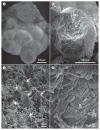
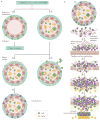
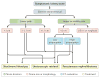
Kidney stones are mineral deposits in the renal calyces and pelvis that are found free or attached to the renal papillae. They contain crystalline and organic components and are formed when the urine becomes supersaturated with respect to a mineral. Calcium oxalate is the main constituent of most stones, many of which form on a foundation of calcium phosphate called Randall's plaques, which are present on the renal papillary surface. Stone formation is highly prevalent, with rates of up to 14.8% and increasing, and a recurrence rate of up to 50% within the first 5 years of the initial stone episode. Obesity, diabetes, hypertension and metabolic syndrome are considered risk factors for stone formation, which, in turn, can lead to hypertension, chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease. Management of symptomatic kidney stones has evolved from open surgical lithotomy to minimally invasive endourological treatments leading to a reduction in patient morbidity, improved stone-free rates and better quality of life. Prevention of recurrence requires behavioural and nutritional interventions, as well as pharmacological treatments that are specific for the type of stone. There is a great need for recurrence prevention that requires a better understanding of the mechanisms involved in stone formation to facilitate the development of more-effective drugs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
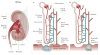



Comment in
-
Kidney stones.Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017 Jan 12;3:17001. doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2017.1. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017. PMID: 28079115 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Pathophysiology and Main Molecular Mechanisms of Urinary Stone Formation and Recurrence.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 6;25(5):3075. doi: 10.3390/ijms25053075. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38474319 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endoscopic mapping of renal papillae for Randall's plaques in patients with urinary stone disease.J Urol. 1997 Dec;158(6):2062-4. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(01)68153-9. J Urol. 1997. PMID: 9366312
-
[Pathophysiology, diagnosis and conservative therapy in calcium kidney calculi].Ther Umsch. 2003 Feb;60(2):79-87. doi: 10.1024/0040-5930.60.2.79. Ther Umsch. 2003. PMID: 12649986 German.
-
Helper T-cell signaling and inflammatory pathway lead to formation of calcium phosphate but not calcium oxalate stones on Randall's plaques.Int J Urol. 2019 Jun;26(6):670-677. doi: 10.1111/iju.13950. Epub 2019 Mar 28. Int J Urol. 2019. PMID: 30919502
-
Characteristics of renal papillae in kidney stone formers.Minerva Urol Nefrol. 2016 Dec;68(6):496-515. Epub 2016 Jul 21. Minerva Urol Nefrol. 2016. PMID: 27441596 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic Background but Not Intestinal Microbiota After Co-Housing Determines Hyperoxaluria-Related Nephrocalcinosis in Common Inbred Mouse Strains.Front Immunol. 2021 Apr 21;12:673423. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.673423. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33968083 Free PMC article.
-
Acoustic emission of kidney stones: a medical adaptation of statistical breakdown mechanisms.Urolithiasis. 2024 Feb 20;52(1):36. doi: 10.1007/s00240-024-01531-0. Urolithiasis. 2024. PMID: 38376662 Free PMC article.
-
Massive Ureterolithiasis.Cureus. 2022 Jul 25;14(7):e27234. doi: 10.7759/cureus.27234. eCollection 2022 Jul. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36039196 Free PMC article.
-
Incremental Healthcare Cost Implications of Retreatment Following Ureteroscopy or Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy for Upper Urinary Tract Stones: A Population-Based Study of Commercially-Insured US Adults.Med Devices (Auckl). 2022 Nov 10;15:371-384. doi: 10.2147/MDER.S384823. eCollection 2022. Med Devices (Auckl). 2022. PMID: 36389203 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophage Function in Calcium Oxalate Kidney Stone Formation: A Systematic Review of Literature.Front Immunol. 2021 May 24;12:673690. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.673690. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34108970 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

