Peptoid Library Agar Diffusion (PLAD) Assay for the High-Throughput Identification of Antimicrobial Peptoids
- PMID: 27186808
- PMCID: PMC5064948
- DOI: 10.1021/acscombsci.6b00039
Peptoid Library Agar Diffusion (PLAD) Assay for the High-Throughput Identification of Antimicrobial Peptoids
Abstract
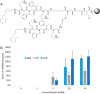
Rapid emergence of antimicrobial resistant organisms necessitates equally rapid methods for the development of new antimicrobial compounds. Of recent interest have been mimics of antimicrobial peptides known as antimicrobial peptoids, which exhibit similar potency to the former but with improved proteolytic stability. Presented herein is a high-throughput method to screen libraries of antimicrobial peptoids immobilized on beads embedded into solid media. Termed the peptoid library agar diffusion (PLAD) assay, this assay allows for individual chemical manipulation of two identical peptoid strands. One strand can be released to diffuse out from a solid support bead and interact with the microorganism during screening. The other strand can be cleaved after screening from beads showing strong antimicrobial activity and analyzed by mass spectrometry to deconvolute the structure of the peptoid. This method was applied to a small library of peptoids to identify an antimicrobial peptoid with modest efficacy against the ESKAPE pathogens.
Keywords: antimicrobial; combinatorial library; high-throughput; peptoids.
Conflict of interest statement
Notes The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

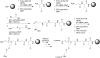

Similar articles
-
Development of an Anti-Biofilm Screening Technique Leads to the Discovery of a Peptoid with Efficacy against Candida albicans.ACS Infect Dis. 2022 Feb 11;8(2):310-320. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.1c00449. Epub 2022 Feb 2. ACS Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 35107257 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the Effect of Peptoid Lipophilicity on Antimicrobial Potency, Cytotoxicity, and Combinatorial Library Design.ACS Comb Sci. 2017 Apr 10;19(4):229-233. doi: 10.1021/acscombsci.7b00007. Epub 2017 Mar 16. ACS Comb Sci. 2017. PMID: 28291947 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis and screening of bead-displayed combinatorial libraries.Methods Enzymol. 2019;622:91-127. doi: 10.1016/bs.mie.2019.02.005. Epub 2019 Mar 8. Methods Enzymol. 2019. PMID: 31155067
-
Evaluation of peptoid mimics of short, lipophilic peptide antimicrobials.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2020 Aug;56(2):106048. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106048. Epub 2020 Jun 12. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2020. PMID: 32540430
-
Peptoids: bio-inspired polymers as potential pharmaceuticals.Curr Pharm Des. 2011;17(25):2732-47. doi: 10.2174/138161211797416066. Curr Pharm Des. 2011. PMID: 21728985 Review.
Cited by
-
Solid-Phase Synthesis of β-Amino Ketones Via DNA-Compatible Organocatalytic Mannich Reactions.ACS Comb Sci. 2018 Feb 12;20(2):55-60. doi: 10.1021/acscombsci.7b00151. Epub 2018 Jan 24. ACS Comb Sci. 2018. PMID: 29316387 Free PMC article.
-
Development of an Anti-Biofilm Screening Technique Leads to the Discovery of a Peptoid with Efficacy against Candida albicans.ACS Infect Dis. 2022 Feb 11;8(2):310-320. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.1c00449. Epub 2022 Feb 2. ACS Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 35107257 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the links between peptoid antibacterial activity and toxicity.Medchemcomm. 2017 Feb 1;8(5):886-896. doi: 10.1039/c6md00648e. eCollection 2017 May 1. Medchemcomm. 2017. PMID: 30108804 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery and Characterization of a Peptoid with Antifungal Activity against Cryptococcus neoformans.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2016 Oct 3;7(12):1139-1144. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.6b00338. eCollection 2016 Dec 8. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2016. PMID: 27994753 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the Effect of Peptoid Lipophilicity on Antimicrobial Potency, Cytotoxicity, and Combinatorial Library Design.ACS Comb Sci. 2017 Apr 10;19(4):229-233. doi: 10.1021/acscombsci.7b00007. Epub 2017 Mar 16. ACS Comb Sci. 2017. PMID: 28291947 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Antimicrobial Resistance: Report on Global Surveillance. World Health Organization; France: 2014.
-
- Antimicrobial Resistance: Tackling a Crisis for the Health and Wealth of Nations. The Review on Antimicrobial Resistance; London: 2014.
-
- Tenover FC. Mechanisms of Antimicrobial Resistance in Bacteria. Am J Med. 2006;119(6):S3–S10. - PubMed
-
- Blair JMA, Webber MA, Baylay AJ, Ogbolu DO, Piddock LJV. Molecular mechanisms of antibiotic resistance. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2015;13:42–51. - PubMed
-
- Brogden. Antimicrobial peptides: pore formers or metabolic inhibitors in bacteria? Nat Rev Microbiol. 2005;3:238–250. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

