Efficacy and safety of canagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus from India
- PMID: 27186557
- PMCID: PMC4855968
- DOI: 10.4103/2230-8210.179996
Efficacy and safety of canagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus from India
Abstract
Background: This post hoc analysis evaluated the efficacy and safety of canagliflozin, a sodium glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitor, in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) from India.
Methods: Changes from baseline in HbA1c, fasting plasma glucose (FPG), body weight, and blood pressure (BP) with canagliflozin 100 and 300 mg were evaluated in a subgroup of patients from India (n = 124) from 4 randomized, double-blind, placebo- and active-controlled, Phase 3 studies (N = 2313; Population 1). Safety was assessed based on adverse event (AE) reports in these patients and in a broader subgroup of patients from India (n = 1038) from 8 randomized, double-blind, placebo- and active-controlled, Phase 3 studies (N = 9439; Population 2).
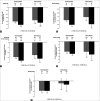
Results: Reductions in HbA1c with canagliflozin 100 and 300 mg were -0.74% and -0.88%, respectively, in patients from India, and -0.81% and -1.00%, respectively, in the 4 pooled Phase 3 studies. In the Indian subgroup, both canagliflozin doses provided reductions in FPG, body weight, and BP that were consistent with findings in the overall population. The incidence of overall AEs in patients from India was generally similar with canagliflozin 100 and 300 mg and noncanagliflozin. The AE profile in patients from India was generally similar to the overall population, with higher rates of genital mycotic infections and osmotic diuresis-related and volume depletion-related AEs with canagliflozin versus noncanagliflozin.
Conclusion: Canagliflozin provided glycemic control, body weight reduction, and was generally well tolerated in patients with T2DM from India.
Keywords: Fasting blood glucose; HbA1c; hyperglycemia; oral medications; type 2 diabetes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety of canagliflozin treatment in older subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized trial.Hosp Pract (1995). 2013 Apr;41(2):72-84. doi: 10.3810/hp.2013.04.1020. Hosp Pract (1995). 2013. PMID: 23680739 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Canagliflozin in Individuals Aged 75 and Older with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Pooled Analysis.J Am Geriatr Soc. 2016 Mar;64(3):543-52. doi: 10.1111/jgs.14028. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2016. PMID: 27000327 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and safety of canagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus from Latin America.Curr Med Res Opin. 2016;32(3):427-39. doi: 10.1185/03007995.2015.1121865. Epub 2016 Jan 14. Curr Med Res Opin. 2016. PMID: 26579834 Clinical Trial.
-
Canagliflozin: a sodium glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitor for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2015 Nov;1358:28-43. doi: 10.1111/nyas.12852. Epub 2015 Aug 25. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2015. PMID: 26305874 Review.
-
A review of clinical efficacy and safety of canagliflozin 300 mg in the management of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2017 Jan-Feb;21(1):196-209. doi: 10.4103/2230-8210.196016. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2017. PMID: 28217522 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genital Infections with Sodium Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors: Occurrence and Management in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2018 Nov-Dec;22(6):837-842. doi: 10.4103/ijem.IJEM_159_17. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2018. PMID: 30766827 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SGLT2 Inhibitors: Paradigm Shift from Diabetes Care to Metabolic Care-An Indian Perspective.Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2024 Jan-Feb;28(1):11-18. doi: 10.4103/ijem.ijem_377_23. Epub 2024 Feb 26. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2024. PMID: 38533279 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sodium-glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors: Moving Beyond the Glycemic Treatment Goal.Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2017 Nov-Dec;21(6):909-918. doi: 10.4103/ijem.IJEM_85_17. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2017. PMID: 29285458 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative Efficacy and Safety Among Sodium-glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors in Type 2 Diabetes - Results from a Retrospective Single-centre Study.Eur Endocrinol. 2019 Aug;15(2):113-118. doi: 10.17925/EE.2019.15.2.113. Epub 2019 Aug 16. Eur Endocrinol. 2019. PMID: 31616503 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of genitourinary infection in diabetic patients treated with SGLT 2 inhibitors.Afr Health Sci. 2023 Mar;23(1):270-275. doi: 10.4314/ahs.v23i1.29. Afr Health Sci. 2023. PMID: 37545909 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Guariguata L, Whiting DR, Hambleton I, Beagley J, Linnenkamp U, Shaw JE. Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2013 and projections for 2035. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2014;103:137–49. - PubMed
-
- Anjana RM, Pradeepa R, Deepa M, Datta M, Sudha V, Unnikrishnan R, et al. Prevalence of diabetes and prediabetes (impaired fasting glucose and/or impaired glucose tolerance) in urban and rural India: Phase I results of the Indian Council of Medical Research-INdia DIABetes (ICMR-INDIAB) study. Diabetologia. 2011;54:3022–7. - PubMed
-
- Ramachandran A, Snehalatha C, Viswanathan V. Burden of type 2 diabetes and its complications – The Indian scenario. Curr Sci. 2002;83:1471–6.
-
- Mohan V, Sandeep S, Deepa R, Shah B, Varghese C. Epidemiology of type 2 diabetes: Indian scenario. Indian J Med Res. 2007;125:217–30. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources