Inhibition of SHP2 ameliorates the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 27183387
- PMCID: PMC4887187
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI87037
Inhibition of SHP2 ameliorates the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
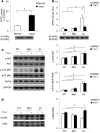
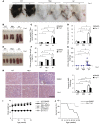
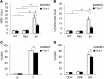
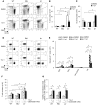
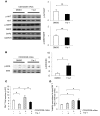
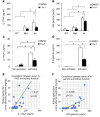
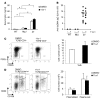
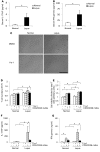
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a devastating multisystemic autoimmune disorder. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying its pathogenesis remain elusive. Some patients with Noonan syndrome, a congenital disorder predominantly caused by gain-of-function mutations in the protein tyrosine phosphatase SH2 domain-containing PTP (SHP2), have been shown to develop SLE, suggesting a functional correlation between phosphatase activity and systemic autoimmunity. To test this directly, we measured SHP2 activity in spleen lysates isolated from lupus-prone MRL/lpr mice and found it was markedly increased compared with that in control mice. Similar increases in SHP2 activity were seen in peripheral blood mononuclear cells isolated from lupus patients relative to healthy patients. To determine whether SHP2 alters autoimmunity and related immunopathology, we treated MRL/lpr mice with an SHP2 inhibitor and found increased life span, suppressed crescentic glomerulonephritis, reduced spleen size, and diminished skin lesions. SHP2 inhibition also reduced numbers of double-negative T cells, normalized ERK/MAPK signaling, and decreased production of IFN-γ and IL-17A/F, 2 cytokines involved in SLE-associated organ damage. Moreover, in cultured human lupus T cells, SHP2 inhibition reduced proliferation and decreased production of IFN-γ and IL-17A/F, further implicating SHP2 in lupus-associated immunopathology. Taken together, these data identify SHP2 as a critical regulator of SLE pathogenesis and suggest targeting of its activity as a potent treatment for lupus patients.
Figures
Comment in
-
Systemic lupus erythematosus: SHP2 inhibition ameliorates disease in lupus-prone mice.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016 Jul;12(7):376. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2016.94. Epub 2016 Jun 3. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 27256710 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Cryptotanshinone ameliorates the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus by blocking T cell proliferation.Int Immunopharmacol. 2019 Sep;74:105677. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.105677. Epub 2019 Jun 7. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31177018
-
Inhibition of glutaminolysis ameliorates lupus by regulating T and B cell subsets and downregulating the mTOR/P70S6K/4EBP1 and NLRP3/caspase-1/IL-1β pathways in MRL/lpr mice.Int Immunopharmacol. 2022 Nov;112:109133. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.109133. Epub 2022 Sep 13. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36113317
-
SHP2: its association and roles in systemic lupus erythematosus.Inflamm Res. 2023 Jul;72(7):1501-1512. doi: 10.1007/s00011-023-01760-w. Epub 2023 Jun 23. Inflamm Res. 2023. PMID: 37351631
-
Effector T-cell subsets in systemic lupus erythematosus: update focusing on Th17 cells.Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2011 Sep;23(5):444-8. doi: 10.1097/BOR.0b013e328349a255. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2011. PMID: 21720245 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The central and multiple roles of B cells in lupus pathogenesis.Immunol Rev. 1999 Jun;169:107-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1999.tb01310.x. Immunol Rev. 1999. PMID: 10450512 Review.
Cited by
-
Intramolecular Interaction with the E6 Region Stabilizes the Closed Conformation of the N-SH2 Domain and Concurs with the Self-Inhibitory Docking in Downregulating the Activity of the SHP2 Tyrosine Phosphatase: A Molecular Dynamics Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 27;23(9):4794. doi: 10.3390/ijms23094794. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563185 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of small peptide compounds, molecular docking, and inhibitory activity evaluation against phosphatases PTP1B and SHP2.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018 Dec 5;12:4139-4147. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S186614. eCollection 2018. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018. PMID: 30584278 Free PMC article.
-
SHP2 promotes sarcoidosis severity by inhibiting SKP2-targeted ubiquitination of TBET in CD8+ T cells.Sci Transl Med. 2023 Sep 13;15(713):eade2581. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.ade2581. Epub 2023 Sep 13. Sci Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37703351 Free PMC article.
-
The Tyrosine Phosphatase SHP2: A New Target for Insulin Resistance?Biomedicines. 2022 Aug 31;10(9):2139. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10092139. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36140242 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transancestral mapping and genetic load in systemic lupus erythematosus.Nat Commun. 2017 Jul 17;8:16021. doi: 10.1038/ncomms16021. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 28714469 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

