The role of cholesterol in membrane fusion
- PMID: 27179407
- PMCID: PMC4972649
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2016.05.003
The role of cholesterol in membrane fusion
Abstract
Cholesterol modulates the bilayer structure of biological membranes in multiple ways. It changes the fluidity, thickness, compressibility, water penetration and intrinsic curvature of lipid bilayers. In multi-component lipid mixtures, cholesterol induces phase separations, partitions selectively between different coexisting lipid phases, and causes integral membrane proteins to respond by changing conformation or redistribution in the membrane. But, which of these often overlapping properties are important for membrane fusion?-Here we review a range of recent experiments that elucidate the multiple roles that cholesterol plays in SNARE-mediated and viral envelope glycoprotein-mediated membrane fusion.
Keywords: Cholesterol; Exocytosis; Fusion peptide; Fusion protein; Membrane fusion; SNARE; Viral envelope protein; Virus entry.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
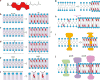
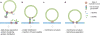
Similar articles
-
Cholesterol: A key player in membrane fusion that modulates the efficacy of fusion inhibitor peptides.Vitam Horm. 2021;117:133-155. doi: 10.1016/bs.vh.2021.06.003. Epub 2021 Jul 12. Vitam Horm. 2021. PMID: 34420578
-
High cholesterol obviates a prolonged hemifusion intermediate in fast SNARE-mediated membrane fusion.Biophys J. 2015 Jul 21;109(2):319-29. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2015.06.022. Biophys J. 2015. PMID: 26200867 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of 25-hydroxycholesterol in viral membrane fusion: Insights on HIV inhibition.Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2018 May;1860(5):1171-1178. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2018.02.001. Epub 2018 Feb 22. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2018. PMID: 29408450
-
How SNARE molecules mediate membrane fusion: recent insights from molecular simulations.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2012 Apr;22(2):187-96. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2012.01.007. Epub 2012 Feb 23. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2012. PMID: 22365575 Review.
-
Mechanisms of membrane fusion: disparate players and common principles.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Jul;9(7):543-56. doi: 10.1038/nrm2417. Epub 2008 May 21. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18496517 Review.
Cited by
-
Increased Alveolar Heparan Sulphate and Reduced Pulmonary Surfactant Amount and Function in the Mucopolysaccharidosis IIIA Mouse.Cells. 2021 Apr 8;10(4):849. doi: 10.3390/cells10040849. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33918094 Free PMC article.
-
Biomembrane Structure and Material Properties Studied With Neutron Scattering.Front Chem. 2021 Apr 27;9:642851. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2021.642851. eCollection 2021. Front Chem. 2021. PMID: 33987167 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cholesterol imbalance and neurotransmission defects in neurodegeneration.Exp Mol Med. 2024 Aug;56(8):1685-1690. doi: 10.1038/s12276-024-01273-4. Epub 2024 Aug 1. Exp Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39085348 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Excipients for Novel Inhaled Dosage Forms: An Overview.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024 Feb 14;25(2):36. doi: 10.1208/s12249-024-02741-w. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024. PMID: 38356031 Review.
-
Averrhoa carambola leaves prevent dyslipidemia and oxidative stress in a rat model of poloxamer-407-induced acute hyperlipidemia.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Feb 6;14:1134812. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1134812. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36814487 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bacia K, Schuette CG, Kahya N, Jahn R, Schwille P. SNAREs prefer liquid-disordered over “raft” (liquid-ordered) domains when reconstituted into giant unilamellar vesicles. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:37951–37955. - PubMed
-
- Baumgart T, Hess ST, Webb WW. Imaging coexisting fluid domains in biomembrane models coupling curvature and line tension. Nature. 2003;425:821–824. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

