Prolactin Signaling Stimulates Invasion via Na(+)/H(+) Exchanger NHE1 in T47D Human Breast Cancer Cells
- PMID: 27176613
- PMCID: PMC5426576
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2015-1299
Prolactin Signaling Stimulates Invasion via Na(+)/H(+) Exchanger NHE1 in T47D Human Breast Cancer Cells
Abstract
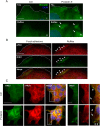
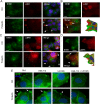
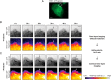
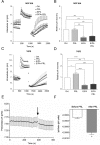
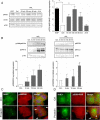
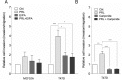
Prolactin (PRL) and its receptor (PRLR) are implicated in breast cancer invasiveness, although their exact roles remain controversial. The Na(+)/H(+) exchanger (NHE1) plays essential roles in cancer cell motility and invasiveness, but the PRLR and NHE1 have not previously been linked. Here we show that in T47D human breast cancer cells, which express high levels of PRLR and NHE1, exposure to PRL led to the activation of Janus kinase-2 (JAK2)/signal transducer and activator of transcription-5 (STAT5), Akt, and ERK1/2 signaling and the rapid formation of peripheral membrane ruffles, known to be associated with cell motility. NHE1 was present in small ruffles prior to PRL treatment and was further recruited to the larger, more dynamic ruffles induced by PRL exposure. In PRL-induced ruffles, NHE1 colocalized with activated Akt, ERK1/2, and the ERK effector p90Ribosomal S kinase (p90RSK), known regulators of NHE1 activity. Stimulation of T47D cells with PRL augmented p90RSK activation, Ser703-phosphorylation of NHE1, NHE1-dependent intracellular pH recovery, pericellular acidification, and NHE1-dependent invasiveness. NHE1 activity and localization to ruffles were attenuated by the inhibition of Akt and/or ERK1/2. In contrast, noncancerous MCF10A breast epithelial cells expressed NHE1 and PRLR at lower levels than T47D cells, and their stimulation with PRL induced neither NHE1 activation nor NHE1-dependent invasiveness. In conclusion, we show for the first time that PRLR activation stimulates breast cancer cell invasiveness via the activation of NHE1. We propose that PRL-induced NHE1 activation and the resulting NHE1-dependent invasiveness may contribute to the metastatic behavior of human breast cancer cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Coactivation of janus tyrosine kinase (Jak)1 positively modulates prolactin-Jak2 signaling in breast cancer: recruitment of ERK and signal transducer and activator of transcription (Stat)3 and enhancement of Akt and Stat5a/b pathways.Mol Endocrinol. 2007 Sep;21(9):2218-32. doi: 10.1210/me.2007-0173. Epub 2007 Jun 5. Mol Endocrinol. 2007. PMID: 17550976
-
Prolactin modulates phosphorylation, signaling and trafficking of epidermal growth factor receptor in human T47D breast cancer cells.Oncogene. 2006 Dec 7;25(58):7565-76. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209740. Epub 2006 Jun 19. Oncogene. 2006. PMID: 16785991
-
The role of prolactin receptor in GH signaling in breast cancer cells.Mol Endocrinol. 2013 Feb;27(2):266-79. doi: 10.1210/me.2012-1297. Epub 2012 Nov 28. Mol Endocrinol. 2013. PMID: 23192981 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and Functional Changes in the Na+/H+ Exchanger Isoform 1, Induced by Erk1/2 Phosphorylation.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 May 14;20(10):2378. doi: 10.3390/ijms20102378. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31091671 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tyrosyl phosphorylated serine-threonine kinase PAK1 is a novel regulator of prolactin-dependent breast cancer cell motility and invasion.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015;846:97-137. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-12114-7_5. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015. PMID: 25472536 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Membrane Ruffles: Composition, Function, Formation and Visualization.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 12;25(20):10971. doi: 10.3390/ijms252010971. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39456754 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acid-base transporters in the context of tumor heterogeneity.Pflugers Arch. 2024 Apr;476(4):689-701. doi: 10.1007/s00424-024-02918-z. Epub 2024 Feb 9. Pflugers Arch. 2024. PMID: 38332178 Review.
-
The human Na(+)/H(+) exchanger 1 is a membrane scaffold protein for extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2.BMC Biol. 2016 Apr 15;14:31. doi: 10.1186/s12915-016-0252-7. BMC Biol. 2016. PMID: 27083547 Free PMC article.
-
The intracellular lipid-binding domain of human Na+/H+ exchanger 1 forms a lipid-protein co-structure essential for activity.Commun Biol. 2020 Dec 3;3(1):731. doi: 10.1038/s42003-020-01455-6. Commun Biol. 2020. PMID: 33273619 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in research on the regulatory mechanism of NHE1 in tumors.Oncol Lett. 2021 Apr;21(4):273. doi: 10.3892/ol.2021.12534. Epub 2021 Feb 10. Oncol Lett. 2021. PMID: 33717270 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

