Central role for GSK3β in the pathogenesis of arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy
- PMID: 27170944
- PMCID: PMC4861310
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.85923
Central role for GSK3β in the pathogenesis of arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy
Abstract
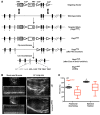
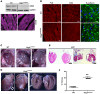
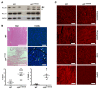
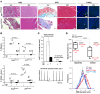
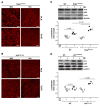
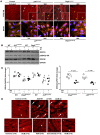
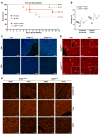
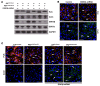
Arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy (ACM) is characterized by redistribution of junctional proteins, arrhythmias, and progressive myocardial injury. We previously reported that SB216763 (SB2), annotated as a GSK3β inhibitor, reverses disease phenotypes in a zebrafish model of ACM. Here, we show that SB2 prevents myocyte injury and cardiac dysfunction in vivo in two murine models of ACM at baseline and in response to exercise. SB2-treated mice with desmosome mutations showed improvements in ventricular ectopy and myocardial fibrosis/inflammation as compared with vehicle-treated (Veh-treated) mice. GSK3β inhibition improved left ventricle function and survival in sedentary and exercised Dsg2mut/mut mice compared with Veh-treated Dsg2mut/mut mice and normalized intercalated disc (ID) protein distribution in both mutant mice. GSK3β showed diffuse cytoplasmic localization in control myocytes but ID redistribution in ACM mice. Identical GSK3β redistribution is present in ACM patient myocardium but not in normal hearts or other cardiomyopathies. SB2 reduced total GSK3β protein levels but not phosphorylated Ser 9-GSK3β in ACM mice. Constitutively active GSK3β worsens ACM in mutant mice, while GSK3β shRNA silencing in ACM cardiomyocytes prevents abnormal ID protein distribution. These results highlight a central role for GSKβ in the complex phenotype of ACM and provide further evidence that pharmacologic GSKβ inhibition improves cardiomyopathies due to desmosome mutations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Therapeutic Modulation of the Immune Response in Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy.Circulation. 2019 Oct 29;140(18):1491-1505. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.040676. Epub 2019 Sep 19. Circulation. 2019. PMID: 31533459 Free PMC article.
-
High-Fat Diet Augments Myocardial Inflammation and Cardiac Dysfunction in Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy.Nutrients. 2024 Jun 29;16(13):2087. doi: 10.3390/nu16132087. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38999835 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise triggers CAPN1-mediated AIF truncation, inducing myocyte cell death in arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy.Sci Transl Med. 2021 Feb 17;13(581):eabf0891. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abf0891. Sci Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 33597260 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular insight into arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy caused by DSG2 mutations.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Nov;167:115448. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115448. Epub 2023 Sep 9. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 37696084 Review.
-
Arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy: a disease of intercalated discs.Cell Tissue Res. 2015 Jun;360(3):491-500. doi: 10.1007/s00441-014-2015-5. Epub 2014 Oct 26. Cell Tissue Res. 2015. PMID: 25344329 Review.
Cited by
-
Glycogen synthase kinase 3-β inhibition induces lymphangiogenesis through β-catenin-dependent and mTOR-independent pathways.PLoS One. 2019 Apr 9;14(4):e0213831. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0213831. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30964887 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Exercise Restriction on Arrhythmic Risk Among Patients With Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy.J Am Heart Assoc. 2018 Jun 16;7(12):e008843. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.118.008843. J Am Heart Assoc. 2018. PMID: 29909402 Free PMC article.
-
NFĸB signaling drives myocardial injury via CCR2+ macrophages in a preclinical model of arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy.J Clin Invest. 2024 Apr 2;134(10):e172014. doi: 10.1172/JCI172014. J Clin Invest. 2024. PMID: 38564300 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Pathways and Animal Models of Arrhythmias.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1441:1057-1090. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-44087-8_67. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 38884769
-
Endurance Training Provokes Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy Phenotype in Heterozygous Desmoglein-2 Mutants: Alleviation by Preload Reduction.Biomedicines. 2024 Apr 30;12(5):985. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12050985. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38790949 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

