ConSurf 2016: an improved methodology to estimate and visualize evolutionary conservation in macromolecules
- PMID: 27166375
- PMCID: PMC4987940
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkw408
ConSurf 2016: an improved methodology to estimate and visualize evolutionary conservation in macromolecules
Abstract
The degree of evolutionary conservation of an amino acid in a protein or a nucleic acid in DNA/RNA reflects a balance between its natural tendency to mutate and the overall need to retain the structural integrity and function of the macromolecule. The ConSurf web server (http://consurf.tau.ac.il), established over 15 years ago, analyses the evolutionary pattern of the amino/nucleic acids of the macromolecule to reveal regions that are important for structure and/or function. Starting from a query sequence or structure, the server automatically collects homologues, infers their multiple sequence alignment and reconstructs a phylogenetic tree that reflects their evolutionary relations. These data are then used, within a probabilistic framework, to estimate the evolutionary rates of each sequence position. Here we introduce several new features into ConSurf, including automatic selection of the best evolutionary model used to infer the rates, the ability to homology-model query proteins, prediction of the secondary structure of query RNA molecules from sequence, the ability to view the biological assembly of a query (in addition to the single chain), mapping of the conservation grades onto 2D RNA models and an advanced view of the phylogenetic tree that enables interactively rerunning ConSurf with the taxa of a sub-tree.
© The Author(s) 2016. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
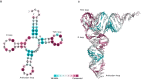
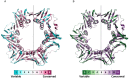
Similar articles
-
The ConSurf-HSSP database: the mapping of evolutionary conservation among homologs onto PDB structures.Proteins. 2005 Feb 15;58(3):610-7. doi: 10.1002/prot.20305. Proteins. 2005. PMID: 15614759
-
ConSurf: identification of functional regions in proteins by surface-mapping of phylogenetic information.Bioinformatics. 2003 Jan;19(1):163-4. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/19.1.163. Bioinformatics. 2003. PMID: 12499312
-
ConSurf 2010: calculating evolutionary conservation in sequence and structure of proteins and nucleic acids.Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Jul;38(Web Server issue):W529-33. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq399. Epub 2010 May 16. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 20478830 Free PMC article.
-
Energy-based RNA consensus secondary structure prediction in multiple sequence alignments.Methods Mol Biol. 2014;1097:125-41. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-709-9_7. Methods Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24639158 Review.
-
Prediction of structural and functional features of protein and nucleic acid sequences by artificial neural networks.Biochemistry. 1992 Aug 18;31(32):7211-8. doi: 10.1021/bi00147a001. Biochemistry. 1992. PMID: 1510913 Review.
Cited by
-
SIRT6 transcriptionally regulates fatty acid transport by suppressing PPARγ.Cell Rep. 2021 Jun 1;35(9):109190. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109190. Cell Rep. 2021. PMID: 34077730 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation in Novel Mitochondrial Creatine Kinase Tyrosine Residues Render Cardioprotection against Hypoxia/Reoxygenation Injury.J Lipid Atheroscler. 2021 May;10(2):223-239. doi: 10.12997/jla.2021.10.2.223. Epub 2021 Jan 19. J Lipid Atheroscler. 2021. PMID: 34095014 Free PMC article.
-
Rational Design of Resveratrol O-methyltransferase for the Production of Pinostilbene.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 21;22(9):4345. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094345. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33919396 Free PMC article.
-
Intranasal Multiepitope PD-L1-siRNA-Based Nanovaccine: The Next-Gen COVID-19 Immunotherapy.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Oct;11(40):e2404159. doi: 10.1002/advs.202404159. Epub 2024 Aug 8. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 39116324 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of structure-specific DNA binding by the FANCM branchpoint translocase.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Oct 14;52(18):11029-11044. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae727. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 39189453 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Glaser F., Pupko T., Paz I., Bell R.E., Bechor-Shental D., Martz E., Ben-Tal N. ConSurf: identification of functional regions in proteins by surface-mapping of phylogenetic information. Bioinformatics. 2003;19:163–164. - PubMed
-
- Celniker G., Nimrod G., Ashkenazy H., Glaser F., Martz E., Mayrose I., Pupko T., Ben-Tal N. ConSurf: using evolutionary data to raise testable hypotheses about protein function. Isr. J. Chem. 2013;53:199–206.
-
- Kessel A., Ben-Tal N. Introduction to proteins: structure, function, and motion. Boca Raton: CRC Press; 2010.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

