p38γ and p38δ Mitogen Activated Protein Kinases (MAPKs), New Stars in the MAPK Galaxy
- PMID: 27148533
- PMCID: PMC4830812
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2016.00031
p38γ and p38δ Mitogen Activated Protein Kinases (MAPKs), New Stars in the MAPK Galaxy
Abstract
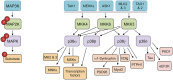
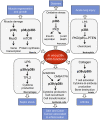
The protein kinases p38γ and p38δ belong to the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) family. p38MAPK signaling controls many cellular processes and is one of the most conserved mechanisms in eukaryotes for the cellular response to environmental stress and inflammation. Although p38γ and p38δ are widely expressed, it is likely that they perform specific functions in different tissues. Their involvement in human pathologies such as inflammation-related diseases or cancer is starting to be uncovered. In this article we give a general overview and highlight recent advances made in defining the functions of p38γ and p38δ, focusing in innate immunity and inflammation. We consider the potential of the pharmacological targeting of MAPK pathways to treat autoimmune and inflammatory diseases and cancer.
Keywords: inflammation; innate response; p38γ; p38δ.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pro-oncogenic role of alternative p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases p38γ and p38δ, linking inflammation and cancer in colitis-associated colon cancer.Cancer Res. 2014 Nov 1;74(21):6150-60. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-0870. Epub 2014 Sep 12. Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 25217523
-
New Insights into the p38γ and p38δ MAPK Pathways.J Signal Transduct. 2012;2012:520289. doi: 10.1155/2012/520289. Epub 2011 Nov 30. J Signal Transduct. 2012. PMID: 22175015 Free PMC article.
-
p38δ genetic ablation protects female mice from anthracycline cardiotoxicity.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2020 Oct 1;319(4):H775-H786. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00415.2020. Epub 2020 Aug 21. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32822209 Free PMC article.
-
p38γ and p38δ: From Spectators to Key Physiological Players.Trends Biochem Sci. 2017 Jun;42(6):431-442. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2017.02.008. Epub 2017 May 1. Trends Biochem Sci. 2017. PMID: 28473179 Review.
-
P38 kinase in gastrointestinal cancers.Cancer Gene Ther. 2023 Sep;30(9):1181-1189. doi: 10.1038/s41417-023-00622-1. Epub 2023 May 29. Cancer Gene Ther. 2023. PMID: 37248432 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Special View of What Was Almost Forgotten: p38δ MAPK.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Apr 25;13(9):2077. doi: 10.3390/cancers13092077. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33923030 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Acupuncture on the p38 Signaling Pathway in Several Nervous System Diseases: A Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 30;21(13):4693. doi: 10.3390/ijms21134693. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32630156 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heat Shock Factor 1 Is a Substrate for p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases.Mol Cell Biol. 2016 Aug 26;36(18):2403-17. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00292-16. Print 2016 Sep 15. Mol Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27354066 Free PMC article.
-
Insights of Crosstalk between p53 Protein and the MKK3/MKK6/p38 MAPK Signaling Pathway in Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2018 May 3;10(5):131. doi: 10.3390/cancers10050131. Cancers (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29751559 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of interleukin-10 receptor alpha (IL10Rα) in Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis infection of a mammary epithelial cell line.BMC Genom Data. 2024 Jun 12;25(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s12863-024-01234-w. BMC Genom Data. 2024. PMID: 38867147 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

