NF-κB Signaling Regulates Expression of Epstein-Barr Virus BART MicroRNAs and Long Noncoding RNAs in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
- PMID: 27147748
- PMCID: PMC4936125
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00613-16
NF-κB Signaling Regulates Expression of Epstein-Barr Virus BART MicroRNAs and Long Noncoding RNAs in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
Abstract
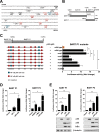
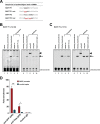
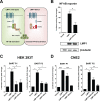
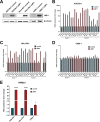
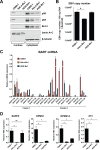
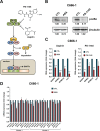
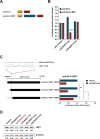
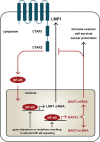
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) expresses few viral proteins in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) but high levels of BamHI-A rightward transcripts (BARTs), which include long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) and BART microRNAs (miRNAs). It is hypothesized that the mechanism for regulation of BARTs may relate to EBV pathogenesis in NPC. We showed that nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) activates the BART promoters and modulates the expression of BARTs in EBV-infected NPC cells but that introduction of mutations into the putative NF-κB binding sites abolished activation of BART promoters by NF-κB. Binding of p50 subunits to NF-κB sites in the BART promoters was confirmed in electrophoretic mobility shift assays (EMSA) and further demonstrated in vivo using chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) analysis. Expression of BART miRNAs and lncRNAs correlated with NF-κB activity in EBV-infected epithelial cells, while treatment of EBV-harboring NPC C666-1 cells with aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid [ASA]) and the IκB kinase inhibitor PS-1145 inhibited NF-κB activity, resulting in downregulation of BART expression. Expression of EBV LMP1 activates BART promoters, whereas an LMP1 mutant which cannot induce NF-κB activation does not activate BART promoters, further supporting the idea that expression of BARTs is regulated by NF-κB signaling. Expression of LMP1 is tightly regulated in NPC cells, and this study confirmed that miR-BART5-5p downregulates LMP1 expression, suggesting a feedback loop between BART miRNA and LMP1-mediated NF-κB activation in the NPC setting. These findings provide new insights into the mechanism underlying the deregulation of BARTs in NPC and identify a regulatory loop through which BARTs support EBV latency in NPC.
Importance: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) cells are ubiquitously infected with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). Notably, EBV expresses very few viral proteins in NPC cells, presumably to avoid triggering an immune response, but high levels of EBV BART miRNAs and lncRNAs which exhibit complex functions associated with EBV pathogenesis. The mechanism for regulation of BARTs is critical for understanding NPC oncogenesis. This study provides multiple lines of evidence to show that expression of BARTs is subject to regulation by NF-κB signaling. EBV LMP1 is a potent activator of NF-κB signaling, and we demonstrate that LMP1 can upregulate expression of BARTs through NF-κB signaling and that BART miRNAs are also able to downregulate LMP1 expression. It appears that aberrant NF-κB signaling and expression of BARTs form an autoregulatory loop for maintaining EBV latency in NPC cells. Further exploration of how targeting NF-κB signaling interrupts EBV latency in NPC cells may reveal new options for NPC treatment.
Copyright © 2016 Verhoeven et al.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Host Gene Expression Is Regulated by Two Types of Noncoding RNAs Transcribed from the Epstein-Barr Virus BamHI A Rightward Transcript Region.J Virol. 2015 Nov;89(22):11256-68. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01492-15. Epub 2015 Aug 26. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26311882 Free PMC article.
-
EBV-encoded miRNAs target ATM-mediated response in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.J Pathol. 2018 Apr;244(4):394-407. doi: 10.1002/path.5018. Epub 2018 Feb 16. J Pathol. 2018. PMID: 29230817 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr Virus MicroRNA miR-BART5-3p Inhibits p53 Expression.J Virol. 2018 Nov 12;92(23):e01022-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01022-18. Print 2018 Dec 1. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 30209170 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenic role of Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein-1 in the development of nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Cancer Lett. 2013 Aug 28;337(1):1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2013.05.018. Epub 2013 May 17. Cancer Lett. 2013. PMID: 23689138 Review.
-
Role of Viral and Host microRNAs in Immune Regulation of Epstein-Barr Virus-Associated Diseases.Front Immunol. 2020 Mar 3;11:367. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00367. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32194570 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
EBV-miR-BART8-3p induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition and promotes metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells through activating NF-κB and Erk1/2 pathways.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Nov 26;37(1):283. doi: 10.1186/s13046-018-0953-6. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30477559 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr Virus BART Long Non-coding RNAs Function as Epigenetic Modulators in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2019 Oct 22;9:1120. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.01120. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31696060 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3) functions as a pivotal target in latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1)-mediated nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell proliferation.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2020 Feb 1;13(2):153-162. eCollection 2020. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32211095 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of Inflammasomes in Epstein-Barr Virus-Associated Nasopharyngeal Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Apr 8;13(8):1786. doi: 10.3390/cancers13081786. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33918087 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long non-coding RNAs in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: biological functions and clinical applications.Mol Cell Biochem. 2021 Sep;476(9):3537-3550. doi: 10.1007/s11010-021-04176-4. Epub 2021 May 17. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021. PMID: 33999333 Review.
References
-
- Henle G, Henle W, Clifford P, Diehl V, Kafuko GW, Kirya BG, Klein G, Morrow RH, Munube GM, Pike P, Tukei PM, Ziegler JL. 1969. Antibodies to Epstein-Barr virus in Burkitt's lymphoma and control groups. J Natl Cancer Inst 43:1147–1157. - PubMed
-
- Henle W, Henle G. 1970. Evidence for a relation of Epstein-Barr virus to Burkitt's lymphoma and nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Bibl Haematol 36:706–713. - PubMed
-
- Young LS, Rowe M. 1992. Epstein-Barr virus, lymphomas and Hodgkin's disease. Semin Cancer Biol 3:273–284. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

