C-C Motif Chemokine Receptor 9 Exacerbates Pressure Overload-Induced Cardiac Hypertrophy and Dysfunction
- PMID: 27146447
- PMCID: PMC4889199
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.116.003342
C-C Motif Chemokine Receptor 9 Exacerbates Pressure Overload-Induced Cardiac Hypertrophy and Dysfunction
Abstract
Background: Maladaptive cardiac hypertrophy is a major risk factor for heart failure, which is the leading cause of death worldwide. C-C motif chemokine receptor 9 (CCR9), a subfamily of the G protein-coupled receptor supergene family, has been highlighted as an immunologic regulator in the development and homing of immune cells and in immune-related diseases. Recently, CCR9 was found to be involved in the pathogenesis of other diseases such as cardiovascular diseases; however, the effects that CCR9 exerts in cardiac hypertrophy remain elusive.
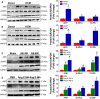
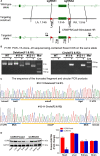
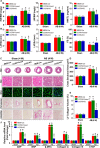
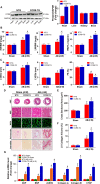
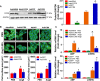
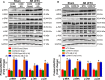
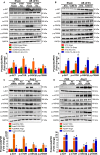
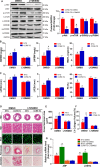
Methods and results: We observed significantly increased CCR9 protein levels in failing human hearts and in a mouse or cardiomyocyte hypertrophy model. In loss- and gain-of-function experiments, we found that pressure overload-induced hypertrophy was greatly attenuated by CCR9 deficiency in cardiac-specific CCR9 knockout mice, whereas CCR9 overexpression in cardiac-specific transgenic mice strikingly enhanced cardiac hypertrophy. The prohypertrophic effects of CCR9 were also tested in vitro, and a similar phenomenon was observed. Consequently, we identified a causal role for CCR9 in pathological cardiac hypertrophy. Mechanistically, we revealed a lack of difference in the expression levels of mitogen-activated protein kinases between groups, whereas the phosphorylation of AKT/protein kinase B and downstream effectors significantly decreased in CCR9 knockout mice and increased in CCR9 transgenic mice after aortic binding surgery.
Conclusions: The prohypertrophic effects of CCR9 were not attributable to the mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway but rather to the AKT-mammalian target of rapamycin-glycogen synthase kinase 3β signaling cascade.
Keywords: AKT; C‐C motif chemokine receptor 9; cardiac dysfunction; cardiac hypertrophy; cardiovascular disease; cardiovascular research; heart failure; hypertrophy.
© 2016 The Authors. Published on behalf of the American Heart Association, Inc., by Wiley Blackwell.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cardiac-specific Traf2 overexpression enhances cardiac hypertrophy through activating AKT/GSK3β signaling.Gene. 2014 Feb 25;536(2):225-31. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2013.12.052. Epub 2013 Dec 27. Gene. 2014. PMID: 24378234
-
Novel Role for Pleckstrin Homology-Like Domain Family A, Member 3 in the Regulation of Pathological Cardiac Hypertrophy.J Am Heart Assoc. 2019 Aug 20;8(16):e011830. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.118.011830. Epub 2019 Aug 20. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019. PMID: 31426686 Free PMC article.
-
Restoration of Circulating MFGE8 (Milk Fat Globule-EGF Factor 8) Attenuates Cardiac Hypertrophy Through Inhibition of Akt Pathway.Hypertension. 2017 Oct;70(4):770-779. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.117.09465. Epub 2017 Aug 21. Hypertension. 2017. PMID: 28827473
-
Regulator of G-Protein Signaling 10 Negatively Regulates Cardiac Remodeling by Blocking Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase-Extracellular Signal-Regulated Protein Kinase 1/2 Signaling.Hypertension. 2016 Jan;67(1):86-98. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.115.05957. Epub 2015 Nov 16. Hypertension. 2016. PMID: 26573707 Review.
-
Role of the CC chemokine receptor 9/TECK interaction in apoptosis.Apoptosis. 2002 Jun;7(3):271-6. doi: 10.1023/a:1015320321511. Apoptosis. 2002. PMID: 11997671 Review.
Cited by
-
Abrogation of CC Chemokine Receptor 9 Ameliorates Ventricular Electrical Remodeling in Mice After Myocardial Infarction.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Oct 12;8:716219. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.716219. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34712704 Free PMC article.
-
MIP-1α Level and Its Correlation with the Risk of Left Atrial Remodeling in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation.Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2022 Jun 24;2022:1756268. doi: 10.1155/2022/1756268. eCollection 2022. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2022. Retraction in: Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2023 Jul 19;2023:9839576. doi: 10.1155/2023/9839576 PMID: 35845739 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Abrogation of CC chemokine receptor 9 ameliorates ventricular remodeling in mice after myocardial infarction.Sci Rep. 2016 Sep 2;6:32660. doi: 10.1038/srep32660. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27585634 Free PMC article.
-
Alterations in Th17 Cells and Non-Classical Monocytes as a Signature of Subclinical Coronary Artery Atherosclerosis during ART-Treated HIV-1 Infection.Cells. 2024 Jan 15;13(2):157. doi: 10.3390/cells13020157. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38247848 Free PMC article.
-
The Roles of CCR9/CCL25 in Inflammation and Inflammation-Associated Diseases.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Aug 19;9:686548. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.686548. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34490243 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

