Microglia protect against brain injury and their selective elimination dysregulates neuronal network activity after stroke
- PMID: 27139776
- PMCID: PMC4857403
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms11499
Microglia protect against brain injury and their selective elimination dysregulates neuronal network activity after stroke
Abstract
Microglia are the main immune cells of the brain and contribute to common brain diseases. However, it is unclear how microglia influence neuronal activity and survival in the injured brain in vivo. Here we develop a precisely controlled model of brain injury induced by cerebral ischaemia combined with fast in vivo two-photon calcium imaging and selective microglial manipulation. We show that selective elimination of microglia leads to a striking, 60% increase in infarct size, which is reversed by microglial repopulation. Microglia-mediated protection includes reduction of excitotoxic injury, since an absence of microglia leads to dysregulated neuronal calcium responses, calcium overload and increased neuronal death. Furthermore, the incidence of spreading depolarization (SD) is markedly reduced in the absence of microglia. Thus, microglia are involved in changes in neuronal network activity and SD after brain injury in vivo that could have important implications for common brain diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
B.L.W. is an employee of Plexxikon. G.K. and B.R. are founders of Femtonics Kft. B.R. is a member of its scientific advisory board.
Figures
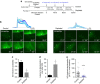
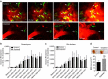
Similar articles
-
Resting microglia directly monitor the functional state of synapses in vivo and determine the fate of ischemic terminals.J Neurosci. 2009 Apr 1;29(13):3974-80. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4363-08.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19339593 Free PMC article.
-
Microglia inflict delayed brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage.Acta Neuropathol. 2015 Aug;130(2):215-31. doi: 10.1007/s00401-015-1440-1. Epub 2015 May 9. Acta Neuropathol. 2015. PMID: 25956409
-
Perivascular microglia promote blood vessel disintegration in the ischemic penumbra.Acta Neuropathol. 2015 Feb;129(2):279-95. doi: 10.1007/s00401-014-1372-1. Epub 2014 Dec 13. Acta Neuropathol. 2015. PMID: 25500713
-
Neuroplasticity in stroke recovery. The role of microglia in engaging and modifying synapses and networks.Eur J Neurosci. 2018 Jun;47(12):1414-1428. doi: 10.1111/ejn.13959. Epub 2018 Jun 8. Eur J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29786167 Review.
-
Mechanisms and potential therapeutic applications of microglial activation after brain injury.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2015 Apr;21(4):309-19. doi: 10.1111/cns.12360. Epub 2014 Dec 4. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2015. PMID: 25475659 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting SRSF3 restores immune mRNA translation in microglia/macrophages following cerebral ischemia.Mol Ther. 2024 Mar 6;32(3):783-799. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2024.01.004. Epub 2024 Jan 8. Mol Ther. 2024. PMID: 38196192
-
Nanotechnology approaches to drug delivery for the treatment of ischemic stroke.Bioact Mater. 2024 Sep 23;43:145-161. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2024.09.016. eCollection 2025 Jan. Bioact Mater. 2024. PMID: 39386225 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microglia in neuroimmunopharmacology and drug addiction.Mol Psychiatry. 2024 Jun;29(6):1912-1924. doi: 10.1038/s41380-024-02443-6. Epub 2024 Feb 2. Mol Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38302560 Review.
-
Microglial activation after ischaemic stroke.Stroke Vasc Neurol. 2019 May 10;4(2):71-74. doi: 10.1136/svn-2018-000196. eCollection 2019 Jul. Stroke Vasc Neurol. 2019. PMID: 31338213 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Influence of Microglial Elimination and Repopulation on Stress Sensitization Induced by Repeated Social Defeat.Biol Psychiatry. 2019 Apr 15;85(8):667-678. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2018.10.009. Epub 2018 Oct 25. Biol Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 30527629 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kettenmann H., Hanisch U. K., Noda M. & Verkhratsky A. Physiology of microglia. Physiol. Rev. 91, 461–553 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Block M. L., Zecca L. & Hong J. S. Microglia-mediated neurotoxicity: uncovering the molecular mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 8, 57–69 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Dheen S. T., Kaur C. & Ling E. A. Microglial activation and its implications in the brain diseases. Curr. Med. Chem. 14, 1189–1197 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Denes A., Thornton P., Rothwell N. J. & Allan S. M. Inflammation and brain injury: acute cerebral ischaemia, peripheral and central inflammation. Brain Behav. Immun. 24, 708–723 (2010). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

