Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Triple Negative Breast Cancer: An Observational Study
- PMID: 27131315
- PMCID: PMC7838690
- DOI: 10.3727/096504016X14562725373879
Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Triple Negative Breast Cancer: An Observational Study
Abstract
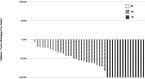
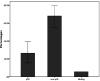
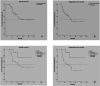
Triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) is a phenotype of breast cancer with aggressive clinical behavior. Because of the absence of optimal treatment, the prognosis of this disease is poor. The main purpose of this study was to detect the response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT) in a TNBC cohort and compare the long-term survival between patients with and without pathological complete response (pCR). A total of 53 patients diagnosed with TNBC from 2005 to 2013 who received NACT at the University Hospital Birmingham were enrolled in this study. Overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) were compared between the pCR group and non-pCR group. Demographic information and clinical or pathologic parameters were also analyzed to explore potential predictive and prognostic factors. Fourteen patients (26.4%) achieved pCR to NACT. In univariate analysis, patients with pCR had longer PFS time (p = 0.013) and OS time (p = 0.054) compared with their counterparts without pCR. In multivariate analysis, the existence of lymphovascular invasion (LVI) significantly reduced OS (HR = 17.404, 95% CI = 2.923-103.644) and PFS (HR = 7.776, 95% CI = 1.645-36.753). The achievement of pCR to NACT can significantly postpone the incidence of disease progression in patients with TNBC. There is not enough evidence showing its influence on ultimate survival. LVI may be a more potent prognostic factor than pCR in the TNBC cohort.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy of Neoadjuvant Versus Adjuvant Chemotherapy in Hispanic/Latino (H/L) Women With Local or Locally Advanced Triple-negative Breast Cancer (TNBC).In Vivo. 2019 Jul-Aug;33(4):1227-1234. doi: 10.21873/invivo.11594. In Vivo. 2019. PMID: 31280213 Free PMC article.
-
Survival outcomes of neoadjuvant versus adjuvant chemotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer: a meta-analysis of 36,480 cases.World J Surg Oncol. 2020 Jun 15;18(1):129. doi: 10.1186/s12957-020-01907-7. World J Surg Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32539858 Free PMC article.
-
Neoadjuvant chemotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer: A multicentric retrospective observational study in real-life setting.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Mar;233(3):2313-2323. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26103. Epub 2017 Sep 27. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 28710865
-
A meta-analysis of the effect and safety of platinum-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy in treatment of resectable triple-negative breast cancer.Anticancer Drugs. 2022 Jan 1;33(1):e52-e60. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000001196. Anticancer Drugs. 2022. PMID: 34371505 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of Pathologic Complete Response with Long-Term Survival Outcomes in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Meta-Analysis.Cancer Res. 2020 Dec 15;80(24):5427-5434. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-1792. Epub 2020 Sep 14. Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32928917 Review.
Cited by
-
C/EBPβ regulates the JAK/STAT signaling pathway in triple-negative breast cancer.FEBS Open Bio. 2021 Apr;11(4):1250-1258. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.13138. Epub 2021 Mar 17. FEBS Open Bio. 2021. PMID: 33660927 Free PMC article.
-
PD-L1 Expression in TNBC: A Predictive Biomarker of Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy?Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:1750925. doi: 10.1155/2017/1750925. Epub 2017 Dec 14. Biomed Res Int. 2017. PMID: 29387716 Free PMC article.
-
Paraoxonase-2 is upregulated in triple negative breast cancer and contributes to tumor progression and chemoresistance.Hum Cell. 2023 May;36(3):1108-1119. doi: 10.1007/s13577-023-00892-9. Epub 2023 Mar 10. Hum Cell. 2023. PMID: 36897549
-
Triple-Negative Apocrine Breast Carcinoma Has Better Prognosis despite Poor Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy.J Clin Med. 2022 Mar 14;11(6):1607. doi: 10.3390/jcm11061607. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35329934 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of CK5/6 and EGFR and Its Effect on Prognosis of Triple Negative Breast Cancer.Front Oncol. 2021 Jan 20;10:575317. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.575317. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33552956 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bosch A.; Eroles P.; Zaragoza R.; Viña J. R.; Lluch A. Triple-negative breast cancer: Molecular features, pathogenesis, treatment and current lines of research. Cancer Treat. Rev. 36(3):206–215; 2010. - PubMed
-
- Bryan B. B.; Schnitt S. J.; Collins L. C. Ductal carcinoma in situ with basal-like phenotype: A possible precursor to invasive basal-like breast cancer. Mod. Pathol. 19(5):617–621; 2010. - PubMed
-
- Thike A. A.; Cheok P. Y.; Jara-Lazaro A. R.; Tan B.; Tan P.; Tan P. H. Triple-negative breast cancer: Clinicopathological characteristics and relationship with basal-like breast cancer. Mod. Pathol. 23(1):123–133; 2010. - PubMed
-
- Morris G. J.; Naidu S.; Topham A. K.; Guiles F.; Xu Y.; McCue P.; Schwartz G. F.; Park P. K.; Rosenberg A. L.; Brill K.; Mitchell E. P. Differences in breast carcinoma characteristics in newly diagnosed African-American and Caucasian patients: A single-institution compilation compared with the national cancer institute’s surveillance, epidemiology, and end results database. Cancer 110(4):876–884; 2007. - PubMed
-
- Silver D. P.; Richardson A. L.; Eklund A. C.; Wang Z. C.; Szallasi Z.; Li Q.; Juul N.; Leong C. O.; Calogrias D.; Buraimoh A.; Fatima A.; Gelman R. S.; Ryan P. D.; Tung N. M.; De Nicolo A.; Ganesan S.; Miron A.; Colin C.; Sgroi D. C.; Ellisen L. W.; Winer E. P.; Garber J. E. Efficacy of neoadjuvant cisplatin in triple-negative breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 28(7):1145–1153; 2010. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
