Glioma progression is mediated by an addiction to aberrant IGFBP2 expression and can be blocked using anti-IGFBP2 strategies
- PMID: 27125842
- PMCID: PMC4915980
- DOI: 10.1002/path.4734
Glioma progression is mediated by an addiction to aberrant IGFBP2 expression and can be blocked using anti-IGFBP2 strategies
Abstract
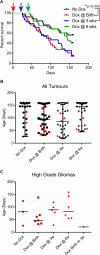
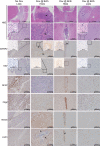
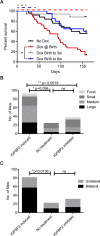
Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 2 (IGFBP2) overexpression is common in high-grade glioma and is both a strong biomarker of aggressive behaviour and a well-documented prognostic factor. IGFBP2 is a member of the secreted IGFBP family that functions by interacting with circulating IGFs to modulate IGF-mediated signalling. This traditional view of IGFBP2 activities has been challenged by the recognition of the diverse functions and cellular locations of members of the IGFBP family. IGFBP2 has been previously established as a driver of glioma progression to a higher grade. In this study, we sought to determine whether IGFBP2-overexpressing tumours are dependent on continued oncogene expression and whether IGFBP2 is a viable therapeutic target in glioma. We took advantage of the well-characterized RCAS/Ntv-a mouse model to create a doxycycline-inducible IGFBP2 model of glioma and demonstrated that the temporal expression of IGFBP2 has dramatic impacts on tumour progression and survival. Further, we demonstrated that IGFBP2-driven tumours are dependent on the continued expression of IGFBP2, as withdrawal of this oncogenic signal led to a significant decrease in tumour progression and prolonged survival. Inhibition of IGFBP2 also impaired tumour cell spread. To assess a therapeutically relevant inhibition strategy, we evaluated a neutralizing antibody against IGFBP2 and demonstrated that it impaired downstream IGFBP2-mediated oncogenic signalling pathways. The studies presented here indicate that IGFBP2 not only is a driver of glioma progression and a prognostic factor but is also required for tumour maintenance and thus represents a viable therapeutic target in the treatment of glioma. Copyright © 2016 Pathological Society of Great Britain and Ireland. Published by John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Keywords: IGFBP2; RCAS mouse model; glioma.
Copyright © 2016 Pathological Society of Great Britain and Ireland. Published by John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Figures
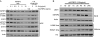
Similar articles
-
IGFBP2 expression predicts IDH-mutant glioma patient survival.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 3;8(1):191-202. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13329. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 27852048 Free PMC article.
-
JNK mediates insulin-like growth factor binding protein 2/integrin alpha5-dependent glioma cell migration.Int J Oncol. 2010 Jul;37(1):143-53. doi: 10.3892/ijo_00000662. Int J Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20514406
-
Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 2 promotes glioma development and progression.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Jul 10;104(28):11736-41. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0703145104. Epub 2007 Jul 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17606927 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 2: gene expression microarrays and the hypothesis-generation paradigm.Brain Pathol. 2002 Jan;12(1):87-94. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2002.tb00425.x. Brain Pathol. 2002. PMID: 11770904 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IGFBP2: integrative hub of developmental and oncogenic signaling network.Oncogene. 2020 Mar;39(11):2243-2257. doi: 10.1038/s41388-020-1154-2. Epub 2020 Jan 10. Oncogene. 2020. PMID: 31925333 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of Hypoxia Prognostic Signature in Glioblastoma Multiforme Based on Bulk and Single-Cell RNA-Seq.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Feb 1;16(3):633. doi: 10.3390/cancers16030633. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38339384 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of simulated microgravity on proliferation and apoptosis in U251 glioma cells.In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2017 Sep;53(8):744-751. doi: 10.1007/s11626-017-0178-6. Epub 2017 Jul 13. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2017. PMID: 28707224
-
Cytokine profile of cerebrospinal fluid in pediatric patients with metastatic medulloblastoma.Heliyon. 2024 Sep 26;10(21):e38504. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e38504. eCollection 2024 Nov 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39524698 Free PMC article.
-
IGFBP2 Is a Potential Master Regulator Driving the Dysregulated Gene Network Responsible for Short Survival in Glioblastoma Multiforme.Front Genet. 2021 Jun 15;12:670240. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.670240. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34211498 Free PMC article.
-
Anoikis resistance in diffuse glioma: The potential therapeutic targets in the future.Front Oncol. 2022 Aug 15;12:976557. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.976557. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36046036 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fuller GN, Rhee CH, Hess KR, et al. Reactivation of insulin-like growth factor binding protein 2 expression in glioblastoma multiforme: a revelation by parallel gene expression profiling. Cancer Res. 1999;59:4228–4232. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

